
A calendar is a system of organizing days for social, religious, commercial or administrative purposes. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A date is the designation of a single, specific day within such a system. A calendar is also a physical record of such a system. A calendar can also mean a list of planned events, such as a court calendar or a partly or fully chronological list of documents, such as a calendar of wills.

The Hebrew calendar, also called Jewish calendar, is a lunisolar calendar used today predominantly for Jewish religious observances. It determines the dates for Jewish holidays and the appropriate public reading of Torah portions, yahrzeits, and daily Psalm readings, among many ceremonial uses. In Israel, it is used for religious purposes, provides a time frame for agriculture and is an official calendar for civil purposes, although the latter usage has been steadily declining in favor of the Gregorian calendar.

The Islamic calendar, also known as the Hijri, Lunar Hijri, Muslim or Arabic calendar, is a lunar calendar consisting of 12 lunar months in a year of 354 or 355 days. It is used to determine the proper days of Islamic holidays and rituals, such as the annual period of fasting and the proper time for the Hajj. The civil calendar of almost all countries where the religion is predominantly Muslim is the Gregorian calendar, with Syriac month-names used in the Levant and Mesopotamia. Notable exceptions to this rule are Iran and Afghanistan, which use the Solar Hijri calendar. Rents, wages and similar regular commitments are generally paid by the civil calendar.
Intercalation or embolism in timekeeping is the insertion of a leap day, week, or month into some calendar years to make the calendar follow the seasons or moon phases. Lunisolar calendars may require intercalations of both days and months.
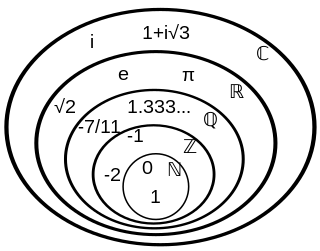
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Individual numbers can be represented by symbols, called numerals; for example, "5" is a numeral that represents the number five. As only a small number of symbols can be memorized, basic numerals are commonly organized in a numeral system, which is an organized way to represent any number. The most common numeral system is the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, which allows representing any number by a combination of ten basic numerals called digits. In addition to their use in counting and measuring, numerals are often used for labels, for ordering, and for codes. In common usage, a numeral is not clearly distinguished from the number that it represents.
The Revised Julian calendar, also known as the Milanković calendar, or, less formally, new calendar, is a calendar proposed by the Serbian scientist Milutin Milanković in 1923, which effectively discontinued the 340 years of divergence between the naming of dates sanctioned by those Eastern Orthodox churches adopting it and the Gregorian calendar that has come to predominate worldwide. This calendar was intended to replace the ecclesiastical calendar based on the Julian calendar hitherto in use by all of the Eastern Orthodox Church. From 1 March 1600 through 28 February 2800, the Revised Julian calendar aligns its dates with the Gregorian calendar, which was proclaimed in 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII for adoption by the Christian world. The calendar has been adopted by the Orthodox churches of Constantinople, Albania, Alexandria, Antioch, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Greece, and Romania.
Julian day is the continuous count of days since the beginning of the Julian Period and is used primarily by astronomers, and in software for easily calculating elapsed days between two events.
In metaphysics, extension signifies both 'stretching out' as well as later 'taking up space', and most recently, spreading one's internal mental cognition into the external world.

Savant syndrome is a rare condition in which someone with significant mental disabilities demonstrates certain abilities far in excess of average. The skills that savants excel at are generally related to memory. This may include rapid calculation, artistic ability, map making, or musical ability. Usually, only one exceptional skill is present.
The determination of the day of the week for any date may be performed with a variety of algorithms. In addition, perpetual calendars require no calculation by the user, and are essentially lookup tables. A typical application is to calculate the day of the week on which someone was born or a specific event occurred.
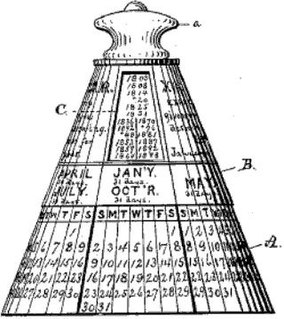
A perpetual calendar is a calendar valid for many years, usually designed to look up the day of the week for a given date in the future.

The Doomsday rule is an algorithm of determination of the day of the week for a given date. It provides a perpetual calendar because the Gregorian calendar moves in cycles of 400 years. The algorithm for mental calculation was devised by John Conway in 1973, drawing inspiration from Lewis Carroll's perpetual calendar algorithm. It takes advantage of each year having a certain day of the week upon which certain easy-to-remember dates, called the doomsdays, fall; for example, the last day of February, 4/4, 6/6, 8/8, 10/10, and 12/12 all occur on the same day of the week in any year. Applying the Doomsday algorithm involves three steps: Determination of the anchor day for the century, calculation of the anchor day for the year from the one for the century, and selection of the closest date out of those that always fall on the doomsday, e.g., 4/4 and 6/6, and count of the number of days between that date and the date in question to arrive at the day of the week. The technique applies to both the Gregorian calendar and the Julian calendar, although their doomsdays are usually different days of the week.
In astronomy, a Julian year is a unit of measurement of time defined as exactly 365.25 days of 86400 SI seconds each. The length of the Julian year is the average length of the year in the Julian calendar that was used in Western societies until the adoption of the Gregorian Calendar, and from which the unit is named. Nevertheless, because astronomical Julian years are measuring duration rather than designating dates, this Julian year does not correspond to years in the Julian calendar or any other calendar. Nor does it correspond to the many other ways of defining a year.
The Buddhist calendar is a set of lunisolar calendars primarily used in mainland Southeast Asian countries of Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar and Thailand as well as in Sri Lanka and Chinese populations of Malaysia and Singapore for religious or official occasions. While the calendars share a common lineage, they also have minor but important variations such as intercalation schedules, month names and numbering, use of cycles, etc. In Thailand, the name Buddhist Era is a year numbering system shared by the traditional Thai lunisolar calendar and by the Thai solar calendar.

Dominic O'Brien is a British mnemonist and an author of memory-related books. He is the eight time World Memory Champion and works as a trainer for Peak Performance Training.
The Mental Calculation World Cup is an international competition for mental calculators, held every two years in Germany.

Ben Pridmore is a former world memory champion, memory sport competitor and accountant.
Rata Die (R.D.) is a system for assigning numbers to calendar days, independent of any calendar, for the purposes of calendrical calculations. It was named by Howard Jacobson. The same system was used earlier, e.g., the REXX programming language since about 1980:
The base date of 1 January 0001 is determined by extending the current Gregorian calendar backward.
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most of the world. It is named after Pope Gregory XIII, who introduced it in October 1582.

Scott Flansburg is an American dubbed "The Human Calculator" and listed in the Guinness Book of World Records for speed of mental calculation. He is the annual host and ambassador for The National Counting Bee, a math educator, and media personality. He has published the books Math Magic and Math Magic for Your Kids..










