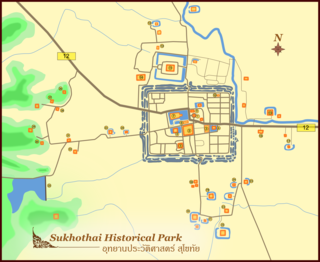
Sukhothai Historical Park covers the ruins of Sukhothai, literally 'dawn of happiness', capital of the Sukhothai Kingdom in the 13th and 14th centuries, in north central Thailand. It is near the city of Sukhothai, capital of Sukhothai Province.

Bamyan or Bamyan Valley ; also spelled Bamiyan or Bamian is the capital of Bamyan Province in central Afghanistan. Its population of approximately 70,000 people makes it the largest city in Hazarajat. Bamyan is at an altitude of about 8,366 feet (2,550 m) above sea level. The Bamyan Airport is located in the middle of the city. The driving distance between Bamyan and Kabul in the southeast is approximately 180 kilometres (110 mi). The Band-e-Amir National Park is to the west, about a half-hour drive from the city of Bamyan.

The Kizil Caves are a set of Buddhist rock-cut caves located near Kizil Township in Baicheng County, Aksu Prefecture, Xinjiang, China. The site is located on the northern bank of the Muzat River 65 kilometres west of Kucha. This area was a commercial hub of the Silk Road. The caves have an important role in Central Asian art and in the Silk Road transmission of Buddhism, and are said to be the earliest major Buddhist cave complex in China, with development occurring between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE. The caves of Kizil are the earlier of their type in China, and their model was later adopted in the construction of Buddhist caves further east. Another name for the site has been Ming-oi, although this term is now mainly used for the site of Shorchuk to the east.

Lingyin Temple is a Buddhist temple of the Chan sect located north-west of Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province, China. The temple's name is commonly literally translated as Temple of the Soul's Retreat. It is one of the largest and wealthiest Buddhist temples in China, and contains numerous pagodas and Buddhist grottoes.

Hpa-an is the capital and largest city of Kayin State, Myanmar (Burma). The population of Hpa-an as of the 2014 census was 421,575. Most of the people in Hpa-an are of the Karen ethnic group.

The Mahamuni Buddha Temple is a Buddhist temple and major pilgrimage site, located southwest of Mandalay, Myanmar (Burma). The Mahamuni Image is enshrined in this temple, and originally came from Arakan. It is highly venerated in Burma and central to many people's lives, as it is seen as an expression of representing the Buddha's life.

The Ananda Temple, located in Bagan, Myanmar is a Buddhist temple built in 1105 AD during the reign (1084–1112/13) of King Kyansittha of the Pagan Dynasty. The temple layout is in a cruciform with several terraces leading to a small pagoda at the top covered by an umbrella known as hti, which is the name of the umbrella or top ornament found in almost all pagodas in Myanmar. The Buddhist temple houses four standing Buddha statues, each one facing the cardinal direction of East, North, West and South. The temple is said to be an architectural wonder in a fusion of Mon and adopted Indian style of architecture. The impressive temple has also been titled the "Westminster Abbey of Burma". The temple has close similarity to the Pathothamya temple of the 10th–11th century, and is also known as “veritable museum of stones”.

The Shwezigon Pagoda or Shwezigon Paya is a Buddhist stupa located in Nyaung-U, Myanmar. A prototype of Burmese stupas, it consists of a circular gold leaf-gilded stupa surrounded by smaller temples and shrines. Construction of the Shwezigon Pagoda began during the reign of King Anawrahta, the founder of the Pagan Empire, in 1059–1060 and was completed in 1102, during the reign of his son King Kyansittha. Over the centuries the pagoda had been damaged by many earthquakes and other natural calamities, and has been refurbished several times. In recent renovations it has been covered by more than 30,000 copper plates. However, the lowest level terraces have remained as they were.

The Badami cave temples are a complex of Hindu and Jain cave temples located in Badami, a town in the Bagalkot district in northern part of Karnataka, India. The caves are important examples of Indian rock-cut architecture, especially Badami Chalukya architecture, and the earliest date from the 6th century. Badami is a modern name and was previously known as Vataapinagara, the capital of the early Chalukya dynasty, which ruled much of Karnataka from the 6th to the 8th century. Badami is situated on the west bank of a man-made lake ringed by an earthen wall with stone steps; it is surrounded on the north and south by forts built in later times. These caves were discovered by Stella Kramrisch in 1924.

The Pindaya Caves, located next to the town of Pindaya, Shan State, Burma (Myanmar) are a Buddhist pilgrimage site and a tourist attraction located on a limestone ridge in the Myelat region. The area is part of the ancestral homeland of the Danu people. There are three caves on the ridge which runs north-south, but only the southern cave can be entered and explored. It is not known whether the other two penetrate for any extended distance into the hillside. Scholars have been pushing for the site's inclusion in the UNESCO World Heritage List.

Phaung Daw U Pagoda, also spelt Phaung Daw Oo or Hpaung Daw Oo, is a notable Buddhist pagoda in Myanmar, located in the village of Ywama on Inle Lake in Shan State. The pagoda is the site of a major annual pagoda festival during which the temple's principal Buddha images are circulated on a royal barge across Inle Lake.

Kaba Aye Pagoda, formally Thiri Mingala Gaba Aye Zedidaw, သီရိမင်္ဂလာကမ္ဘာအေးစေတီတော်), is a Buddhist pagoda located on Kaba Aye Road, Mayangon Township, Yangon, Myanmar. The pagoda was built in 1952 by U Nu in preparation for the Sixth Buddhist Council that he held from 1954 to 1956. The pagoda measures 111 feet (34 m) high and is also 111 feet (34 m) around the base. The pagoda is located approximately 11 km north of Yangon, a little past the Inya Lake Hotel. The Maha Pasana Guha was built simultaneously with the Kaba Aye Pagoda and is located in the same complex. The cave is a replica of the Satta Panni cave, located in India, where the First Buddhist Synod was convened. The six entrances of The Maha Pasana Cave symbolize the Sixth Great Synod. The cave is 455 feet (139 m) long and 370 feet (110 m) wide. Inside, the assembly hall is 220 feet (67 m) long and 140 feet (43 m) wide.

Thầy Temple is a Buddhist temple in Quốc Oai District, Vietnam. The temple is also known as Thiên Phúc Tự. The temple was established in the 11th century during the reign of Emperor Lý Nhân Tông of the Lý dynasty. It is dedicated to Vietnamese Thiền master Từ Đạo Hạnh (1072-1116). It is one of the oldest Buddhist temples in Vietnam, It is well maintained by the monks.

Phowintaung is a Buddhist cave complex located approximately 25 kilometres (16 mi) west of Monywa and 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) southeast of Yinmabin, in Yinmabin Township, Monywa District, Sagaing Region, Northern Burma (Myanmar). It is located on the western bank of the Chindwin River. The name of the complex means Mountain of Isolated Solitary Meditation.

Tantkyitaung Pagoda, located across the Ayeyarwady River in Pakokku District, Magway Division, Myanmar (Burma) is a prominent Burmese Buddhist pagoda near the historic city of Bagan, believed to enshrine four tooth relics of Gautama Buddha.
Jambai is a 1 km2 (0.39 sq mi) village in Tirukkoyilur taluk in Kallakurichi district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. The major occupation of the people living at this place is agriculture and handloom. In 2011, it had a population of 2,000 people.

Ridi Viharaya or Silver Temple is a 2nd-century BCE Theravada Buddhist temple in the village of Ridigama, Sri Lanka. Built during the reign of Dutthagamani of Anuradhapura, the temple is considered as the place where the silver ore, which provided silver to complete Ruwanwelisaya; one of the largest stupa in Sri Lanka, was discovered. According to the chronicles Mahavamsa and Thupavamsa, the Ridi Viharaya complex was built in gratitude for helping him cherish his dream of completing Ruwanwelisaya.

According to the Mahāparinibbāṇa Sutta, after attaining parinirvana, the body of Buddha was cremated and the ashes divided among his lay followers.

Shwethalyaung Hill, also known as Kyaukse Hill, is a 275 metres (902 ft) hill that is located to the east of Kyaukse in Myanmar. Shwethalyaung Hill is known for its abundance of pagodas and monasteries, and has been a sacred pilgrimage site for Burmese Buddhists. At the top of the hill is the Shwethalyaung Pagoda.

The Kawgun Cave is a Buddhist cave temple, located in Kawgun Village, Hpa-An, Kayin State, Myanmar. The cave is lined with thousands of small Buddha statues covering its walls. The cave is an important historical and cultural heritage site in Myanmar. The rear of the cave leads to a row of floating restaurants in the Ruby Lake.


![chng[?]mng[?]:kiupc[?]snny'[?]ape[?]k[?].jpg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/77/%E1%80%86%E1%80%84%E1%80%BA%E1%80%99%E1%80%84%E1%80%BA%E1%80%B8%E1%80%80%E1%80%AD%E1%80%AF%E1%80%95%E1%80%85%E1%80%BA%E1%80%9E%E1%80%8A%E1%80%B7%E1%80%BA%E1%80%A1%E1%80%95%E1%80%B1%E1%80%AB%E1%80%80%E1%80%BA.jpg/120px-%E1%80%86%E1%80%84%E1%80%BA%E1%80%99%E1%80%84%E1%80%BA%E1%80%B8%E1%80%80%E1%80%AD%E1%80%AF%E1%80%95%E1%80%85%E1%80%BA%E1%80%9E%E1%80%8A%E1%80%B7%E1%80%BA%E1%80%A1%E1%80%95%E1%80%B1%E1%80%AB%E1%80%80%E1%80%BA.jpg)





















