
The Viceroyalty of Peru, officially known as the Kingdom of Peru, was a Spanish imperial provincial administrative district, created in 1542, that originally contained modern-day Peru and most of the Spanish Empire in South America, governed from the capital of Lima. Along with the Viceroyalty of New Spain, Peru was one of two Spanish viceroyalties in the Americas from the sixteenth to the eighteenth centuries.

Andrés de Santa Cruz y Calahumana was a Bolivian general and politician who served as interim president of Peru in 1827, the interim president of Peru from 1836 to 1838 and the sixth president of Bolivia from 1829 to 1839. He also served as Supreme Protector of the short-lived Peru-Bolivian Confederation from 1836 to 1839, a political entity created mainly by his personal endeavors.

The National University of Saint Anthony the Abbot in Cuzco (UNSAAC), also known as Saint Anthony University of Cusco or University of Cusco, is a public university in Cusco, Peru and one of the oldest in the country. Its foundation was first proposed on March 1, 1692, at the urging and support of Pope Innocent XII. The document in which Pope Innocent XII sponsored the founding of the university was signed in Madrid, Spain by King Charles II on June 1, 1692, thus becoming Cusco's principal and oldest university. The university was authorized to confer the bachelors, licentiate, masters, and doctorate degrees.

The Belmond Hotel Monasterio is a five-star hotel in Cusco, Peru. It is a refurbished Baroque seminary built in the 17th century on Inca foundations. The hotel is located two blocks from the Plaza de Armas, in the former premises of Saint Anthony the Abbot Seminary.

Víctor Ricardo Mayorga Miranda is a Peruvian lawyer and politician. He was a former Congressman representing the Cusco Region for the 2006–2011 period and was elected under the joint Nationalist-Union for Peru ticket, and belongs to the Peruvian Nationalist Party. Mayorga was a Supplementary Representative to the Andean Parliament between 2011 and 2016, elected under the ticket of the dominated Nationalists-Peru Wins alliance.

The Seminary of Saint Turibius, also known as the Seminary of Lima or, is a priestly seminary in charge of training seminarians to be future priests of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Lima. It is based in Lima, Peru, and is the second oldest seminary in the Americas after that of Bogotá, having been founded on December 7, 1591, by then Archbishop Turibius of Mongrovejo.

Juan de Espinosa Medrano, known in history as Lunarejo, was an Indigenous cleric, sacred preacher, writer, playwright, theologian, archdeacon and polymath from the Viceroyalty of Peru. He is the most prominent figure of the Literary Baroque of Peru and one of the most important intellectuals from Colonial Spanish America.

Oswaldo Mendoza Baca was a Peruvian chemist and professor. He was particularly interested in genetics.
Roque Ceruti was an Italian composer in Peru. He was recruited as conductor of the Viceroy of Peru's private orchestra, and was a dominant italianizing influence during the period, though this was resented by some of the more traditional Spanish musicians.
The Cuzco Rebellion of 1814 was an episode of the Peruvian War of Independence led by the Angulo brothers and Mateo Pumacahua that took place in much of the province of Cuzco, including Huamanga, Arequipa and Puno, as well as part of the province of Charcas. The uprising involved the proclamation of the autonomy and self-government of Cuzco from the Viceroyalty of Peru, governed by Viceroy José Fernando de Abascal y Sousa. The junta was modelled and intended to follow the steps of the Junta of Buenos Aires.

The Iglesia de la Compañía de Jesús is a historic Jesuit church in Cusco, the ancient capital of the Inca Empire, in Cusco Region, Peru. It is situated in the Plaza de Armas de Cusco, the city center. It is built on an Inca palace. It is one of the best examples of Spanish Baroque architecture in Peru. The architecture of this building exerted a great influence on the development of many Baroque architecture in the South Andes. Its construction began in 1576, but it was badly damaged in an earthquake in 1650. The rebuilt church was completed in 1673.

The history of Cusco (Peru), the historical capital of the Incas.
CiroQuispe López is the Bishop-Prelate of Territorial Prelature of Juli (Peru).

Luis Eduardo Valcárcel Vizcarra was a Peruvian historian, anthropologist, writer and activist. He was a researcher of pre-Hispanic Peru and one of the protagonists of the Indigenismo movement. He is considered the father of Peruvian anthropology, and his work focused on two fundamental axes: the revaluation of the Inca Empire and the vindication of the Andean culture. He brought awareness to the continuity that links the peasant of the Andes with the man of the Tahuantinsuyu.

José Gregorio Castro Miranda, O.F.M., was a Roman Catholic prelate who was Bishop of Cuzco from 1910 to 1917. He mainly worked to integrate the local indigenous population to the church's teachings by translating prayers and church music to Quechua.

David Segundo Chaparro Pareja was a Peruvian teacher, politician and jurist. He held a parliamentary position in the Peruvian congress for Cuzco Province.
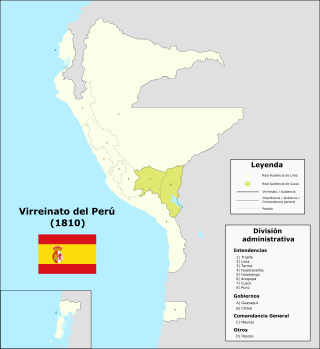
The Intendancy of Arequipa, also known informally as Arequipa Province, was one of the territorial divisions of the Viceroyalty of Peru, ruled from the city of Arequipa and under the jurisdiction of the Bishopric of Arequipa. It existed from 1784 to 1824, receiving the news of the result of the Battle of Ayacucho in late December of the same year.

Pedro Pascual Francisco Farfán de los Godos was a Peruvian Roman Catholic prelate who served as the 28th Archbishop of Lima from 1933 to his death in 1945. Additionally, he also served as Bishop of Cuzco from 1918 to 1933.

Albert Anthony Giesecke was an American teacher who came to Peru contracted by the government of that country. He was entrusted with the rectorship of the National University of San Antonio Abad in Cuzco, where he carried out a significant reform (1910–1923). He also served as the mayor of Cusco.

José Gabriel Cosío Medina was a Peruvian scholar and professor. As a representative of the Peruvian government, he supervised the Yale Peruvian Expedition in 1912 led by Hiram Bingham.

















