
"Junk food" is a term used to describe food that is high in calories from macronutrients such as sugar and/or fat, and possibly sodium, making it hyperpalatable, but with insufficient dietary fiber, protein, or micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals. It is also known as HFSS food. The term junk food is a pejorative dating back to the 1950s. Many variations of junk food can be easily found in most supermarkets and fast-food restaurants. Due to easy accessibility, commercially-oriented packaging, and often-low prices, people are most likely to consume it.

A food pyramid is a representation of the optimal number of servings to be eaten each day from each of the basic food groups. The first pyramid was published in Sweden in 1974. The 1992 pyramid introduced by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) was called the "Food Guide Pyramid" or "Eating Right Pyramid". It was updated in 2005 to "MyPyramid", and then it was replaced by "MyPlate" in 2011.

Convenience food is food that is commercially prepared for ease of consumption, and is usually ready to eat without further preparation. It may also be easily portable, have a long shelf life, or offer a combination of such convenient traits. Convenience foods include ready-to-eat dry products, frozen food such as TV dinners, shelf-stable food, prepared mixes such as cake mix, and snack food. Food scientists now consider most of these products to be ultra-processed foods and link them to poor health outcomes.

Food processing is the transformation of agricultural products into food, or of one form of food into other forms. Food processing takes many forms, from grinding grain into raw flour, home cooking, and complex industrial methods used in the making of convenience foods. Some food processing methods play important roles in reducing food waste and improving food preservation, thus reducing the total environmental impact of agriculture and improving food security.
Lunchables is an American brand of food and snacks manufactured by Kraft Heinz in Chicago, Illinois, and marketed under the Oscar Mayer brand. They were initially introduced in Seattle in 1988 before being released nationally in 1989. Many Lunchables products are produced in a Garland, Texas, facility, and are then distributed across the United States.

A healthy diet is a diet that maintains or improves overall health. A healthy diet provides the body with essential nutrition: fluid, macronutrients such as protein, micronutrients such as vitamins, and adequate fibre and food energy.
The Center for Science in the Public Interest (CSPI) is a Washington, D.C.-based non-profit watchdog and consumer advocacy group that advocates for safer and healthier foods.

Michael F. Jacobson is an American scientist and nutrition advocate. He holds a Ph.D. in microbiology from Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Stephen W. Sanger is a former chairman and chief executive officer of General Mills, former chairman of Wells Fargo, as well as a director of Target Corporation, and Pfizer.

Gary Taubes is an American journalist, writer, and low-carbohydrate / high-fat (LCHF) diet advocate. His central claim is that carbohydrates, especially sugar and high-fructose corn syrup, overstimulate the secretion of insulin, causing the body to store fat in fat cells and the liver, and that it is primarily a high level of dietary carbohydrate consumption that accounts for obesity and other metabolic syndrome conditions. He is the author of Nobel Dreams (1987); Bad Science: The Short Life and Weird Times of Cold Fusion (1993); Good Calories, Bad Calories (2007), titled The Diet Delusion (2008) in the UK and Australia; Why We Get Fat: And What to Do About It (2010); The Case Against Sugar (2016); and The Case for Keto: Rethinking Weight Control and the Science and Practice of Low-Carb/High-Fat Eating (2020). Taubes's work often goes against accepted scientific, governmental, and popular tenets such as that obesity is caused by eating too much and exercising too little and that excessive consumption of fat, especially saturated fat in animal products, leads to cardiovascular disease.
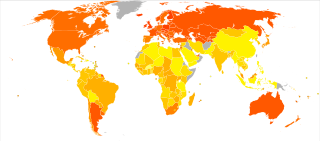
Diet plays an important role in the genesis of obesity. Personal choices, food advertising, social customs and cultural influences, as well as food availability and pricing all play a role in determining what and how much an individual eats.
Howard Moskowitz is an American market researcher and psychophysicist. He is known for the detailed study he made of the types of spaghetti sauce and horizontal segmentation. By providing a large number of options for consumers, Moskowitz pioneered the idea of intermarket variability as applied to the food industry.

Criticism of fast food includes claims of negative health effects, animal cruelty, cases of worker exploitation, children-targeted marketing and claims of cultural degradation via shifts in people's eating patterns away from traditional foods. Fast food chains have come under fire from consumer groups, such as the Center for Science in the Public Interest, a longtime fast food critic over issues such as caloric content, trans fats and portion sizes. Social scientists have highlighted how the prominence of fast food narratives in popular urban legends suggests that modern consumers have an ambivalent relationship with fast food, particularly in relation to children.
Michael Moss is an American journalist, author, and public speaker. He was awarded the Pulitzer Prize for Explanatory Reporting in 2010, and was a finalist for the prize in 2006 and 1999. He is also the recipient of the Gerald Loeb Award for Large Newspapers, an Overseas Press Club citation, and a James Beard Foundation Award for Literary Writing. Before joining The New York Times, he was a reporter for The Wall Street Journal, New York Newsday, The Atlanta Journal-Constitution, The Grand Junction Daily Sentinel and High Country News. His authorships include Salt Sugar Fat: How the Food Giants Hooked Us that was #1 on The New York Times Best Seller list and has been translated into 22 languages. His television appearances include on CBS, CNN, NPR, The Daily Show, and Fox, and he has spoken at more than 60 companies, organizations, and schools including Cornell University, Yale University, Columbia University, Duke University, Nestlé, Bloomberg, the World Health Organization, and the Smithsonian Institution. He has been a fellow of Columbia University's Gannett Center for Media Studies, a fellow of the German Marshall Fund, and an adjunct professor at the Columbia Graduate School of Journalism. He currently lives in Brooklyn with his wife and two sons.
Barry Michael Popkin is an American nutrition and obesity researcher at the Carolina Population Center and the W.R. Kenan Jr. Distinguished Professor of Nutrition at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Public Health, where he is the director of the Global Food Research Program. He developed the concept of "nutrition transition". He is the author of over 650 journal articles and a book, The World is Fat, translated into a dozen languages.

Fed Up is a 2014 American documentary film directed, written and produced by Stephanie Soechtig. The film focuses on the causes of obesity in the US, presenting evidence showing large quantities of sugar in processed foods are an overlooked root of the problem, and points to the monied lobbying power of "Big Sugar" in blocking attempts to enact policies to address the issue.
The bliss point is the amount of an ingredient such as salt, sugar or fat which optimizes deliciousness.

The sugar industry subsumes the production, processing and marketing of sugars. Globally, most sugar is extracted from sugar cane and sugar beet.

The Sugar Association is a trade association for the sugar industry of the United States. Its members include nearly 142,000 growers, processors and refiners of sugar beet and sugarcane plants.

Pure, White and Deadly is a 1972 book by John Yudkin, a British nutritionist and former Chair of Nutrition at Queen Elizabeth College, London. Published in New York, it was the first publication by a scientist to anticipate the adverse health effects, especially in relation to obesity and heart disease, of the public's increased sugar consumption. At the time of publication, Yudkin sat on the advisory panel of the British Department of Health's Committee on the Medical Aspects of Food and Nutrition Policy (COMA). He stated his intention in writing the book in the last paragraph of the first chapter: "I hope that when you have read this book I shall have convinced you that sugar is really dangerous."













