
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference and identifiable chemical change. These reactions involve electrons moving via an electronically-conducting phase between electrodes separated by an ionically conducting and electronically insulating electrolyte.
Extractive metallurgy is a branch of metallurgical engineering wherein process and methods of extraction of metals from their natural mineral deposits are studied. The field is a materials science, covering all aspects of the types of ore, washing, concentration, separation, chemical processes and extraction of pure metal and their alloying to suit various applications, sometimes for direct use as a finished product, but more often in a form that requires further working to achieve the given properties to suit the applications.

Chalcopyrite ( KAL-kə-PY-ryte, -koh-) is a copper iron sulfide mineral and the most abundant copper ore mineral. It has the chemical formula CuFeS2 and crystallizes in the tetragonal system. It has a brassy to golden yellow color and a hardness of 3.5 to 4 on the Mohs scale. Its streak is diagnostic as green-tinged black.
Iron(III) chloride describes the inorganic compounds with the formula FeCl3(H2O)x. Also called ferric chloride, these compounds are some of the most important and commonplace compounds of iron. They are available both in anhydrous and in hydrated forms which are both hygroscopic. They feature iron in its +3 oxidation state. The anhydrous derivative is a Lewis acid, while all forms are mild oxidizing agents. It is used as a water cleaner and as an etchant for metals.

Copper extraction refers to the methods used to obtain copper from its ores. The conversion of copper ores consists of a series of physical, chemical and electrochemical processes. Methods have evolved and vary with country depending on the ore source, local environmental regulations, and other factors.

Lead(II) chloride (PbCl2) is an inorganic compound which is a white solid under ambient conditions. It is poorly soluble in water. Lead(II) chloride is one of the most important lead-based reagents. It also occurs naturally in the form of the mineral cotunnite.
Neodymium(III) chloride or neodymium trichloride is a chemical compound of neodymium and chlorine with the formula NdCl3. This anhydrous compound is a mauve-colored solid that rapidly absorbs water on exposure to air to form a purple-colored hexahydrate, NdCl3·6H2O. Neodymium(III) chloride is produced from minerals monazite and bastnäsite using a complex multistage extraction process. The chloride has several important applications as an intermediate chemical for production of neodymium metal and neodymium-based lasers and optical fibers. Other applications include a catalyst in organic synthesis and in decomposition of waste water contamination, corrosion protection of aluminium and its alloys, and fluorescent labeling of organic molecules (DNA).

Samarium(III) chloride, also known as samarium trichloride, is an inorganic compound of samarium and chloride. It is a pale yellow salt that rapidly absorbs water to form a hexahydrate, SmCl3.6H2O. The compound has few practical applications but is used in laboratories for research on new compounds of samarium.
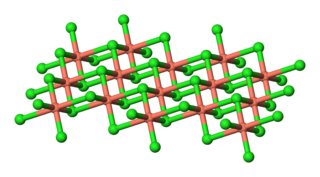
Copper(II) chloride, also known as cupric chloride, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuCl2. The monoclinic yellowish-brown anhydrous form slowly absorbs moisture to form the orthorhombic blue-green dihydrate CuCl2·2H2O, with two water molecules of hydration. It is industrially produced for use as a co-catalyst in the Wacker process.
Hydrometallurgy is a technique within the field of extractive metallurgy, the obtaining of metals from their ores. Hydrometallurgy involve the use of aqueous solutions for the recovery of metals from ores, concentrates, and recycled or residual materials. Processing techniques that complement hydrometallurgy are pyrometallurgy, vapour metallurgy, and molten salt electrometallurgy. Hydrometallurgy is typically divided into three general areas:

The FFC Cambridge process is an electrochemical method for producing Titanium (Ti) from titanium oxide by electrolysis in molten calcium salts.

Tin(II) chloride, also known as stannous chloride, is a white crystalline solid with the formula SnCl2. It forms a stable dihydrate, but aqueous solutions tend to undergo hydrolysis, particularly if hot. SnCl2 is widely used as a reducing agent (in acid solution), and in electrolytic baths for tin-plating. Tin(II) chloride should not be confused with the other chloride of tin; tin(IV) chloride or stannic chloride (SnCl4).

In coordination chemistry, metal ammine complexes are metal complexes containing at least one ammonia ligand. "Ammine" is spelled this way for historical reasons; in contrast, alkyl or aryl bearing ligands are spelt with a single "m". Almost all metal ions bind ammonia as a ligand, but the most prevalent examples of ammine complexes are for Cr(III), Co(III), Ni(II), Cu(II) as well as several platinum group metals.

Electrometallurgy is a method in metallurgy that uses electrical energy to produce metals by electrolysis. It is usually the last stage in metal production and is therefore preceded by pyrometallurgical or hydrometallurgical operations. The electrolysis can be done on a molten metal oxide which is used for example to produce aluminium from aluminium oxide via the Hall-Hérault process. Electrolysis can be used as a final refining stage in pyrometallurgical metal production (electrorefining) and it is also used for reduction of a metal from an aqueous metal salt solution produced by hydrometallurgy (electrowinning).

Molten salt is salt which is solid at standard temperature and pressure but liquified due to elevated temperature. A salt that is liquid even at standard temperature and pressure is usually called a room-temperature ionic liquid, and molten salts are technically a class of ionic liquids.
In chemistry, oxychlorination is a process for generating the equivalent of chlorine gas (Cl2) from hydrogen chloride and oxygen. This process is attractive industrially because hydrogen chloride is less expensive than chlorine.

Non-ferrous extractive metallurgy is one of the two branches of extractive metallurgy which pertains to the processes of reducing valuable, non-iron metals from ores or raw material. Metals like zinc, copper, lead, aluminium as well as rare and noble metals are of particular interest in this field, while the more common metal, iron, is considered a major impurity. Like ferrous extraction, non-ferrous extraction primarily focuses on the economic optimization of extraction processes in separating qualitatively and quantitatively marketable metals from its impurities (gangue).
Mineral processing and extraction of metals are very energy-intensive processes, which are not exempted of producing large volumes of solid residues and wastewater, which also require energy to be further treated and disposed. Moreover, as the demand for metals increases, the metallurgical industry must rely on sources of materials with lower metal contents both from a primary and/or secondary raw materials. Consequently, mining activities and waste recycling must evolve towards the development of more selective, efficient and environmentally friendly mineral and metal processing routes.











