This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page . (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
This is the discography of rapper and producer Sam the Kid.
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page . (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
This is the discography of rapper and producer Sam the Kid.
| Year | Title |
|---|---|
| 1999 | Entre(tanto)
|
| 2002 | Sobre(tudo)
|
Beats Vol 1: Amor
| |
| 2004 | Sobre(tudo) (Special Edition)
|
| 2006 | Pratica(mente)
|
| 2008 | Pratica(mente) (Special Edition)
|
| Year | Song | Album |
|---|---|---|
| 1999 | "Lágrimas" | Entre(tanto) |
| 2002 | "Não Percebes" | Sobre(tudo) |
| 2002 | "Alma Gémea" | Beats Vol 1: Amor |
| 2004 | "Motivação" | Comp. Poesia Urbana vol.1 |
| 2006 | "Poetas de Karaoke" | Pratica(mente) |
| 2007 | "Abstenção" | Pratica(mente) |
| 2007 | "À procura da perfeita repetição" | Pratica(mente) |
| Year | Artist | Album | Song title(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | TPC | TPC - Sessões de Hip Hop Vol. 1 (Compilation album) | "100" featuring GQ |
| 2000 | DJ Cruzfader | Ressureição | "Paiador do Hip-Hop" |
| 2001 | Xeg | Ritmo & Poesia | "Questionário" |
| 2002 | DJ Bomberjack | Bomba Relógio | "A Diferença" featuring Adamastor & Bónus "Trabalha" |
| 2002 | Dupla Consciência | Conexão Verbal Vol. 1 | "Vamos em Frente" featuring Telma & Paranóia |
| June 2002 | Regula | 1ª Jornada | "Pimbas" |
| 2002 | Da Blazz | Dados | "Movimenta-se" |
| September 2002 | Valete | Educação Visual | "Beleza Artificial" |
| September 2002 | Guardiões do Movimento Sagrado | Guerrilheiros do Hip Hop | "00 Hip-Hop" featuring Chullage |
| July 2003 | Bad Spirit | Odiado E Mal Amado | "No Estúdio" |
| November 2003 | Kacetado | Ontem, Hoje & Amanhã | "Versos" |
| April 2004 | DJ Kronic | Projecto Inoxidável II | "6 Ta Feira" |
| November 2004 | DJ Assassino | Time Code | "O Ideal" |
| December 2004 | Tekilla | Tekillogia | "À Vontade do Freguês" |
| March 2005 | Boss AC | Ritmo Amor Palavras | "Dicas", "Brasas" |
| July 2005 | MadVision | MadVision | (entire album) |
| June 2006 | O Crime Do Padre Amaro - Banda Sonora | "Auto de Fé" "Esquemas" "O Crime Do Padre Amaro" | |
| June 2006 | SP & Wilson | Barulho | "Sente Mo Style" |
| October 2006 | Valete | Serviço Público | "Pela Música pt.2" |

The Apache HTTP Server is a free and open-source cross-platform web server, released under the terms of Apache License 2.0. It is developed and maintained by a community of developers under the auspices of the Apache Software Foundation.

In computing, Common Gateway Interface (CGI) is an interface specification that enables web servers to execute an external program to process HTTP or HTTPS user requests.

HTTP is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, where hypertext documents include hyperlinks to other resources that the user can easily access, for example by a mouse click or by tapping the screen in a web browser.

Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It uses encryption for secure communication over a computer network, and is widely used on the Internet. In HTTPS, the communication protocol is encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS) or, formerly, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). The protocol is therefore also referred to as HTTP over TLS, or HTTP over SSL.

The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable.
A Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), formerly Universal Resource Identifier, is a unique sequence of characters that identifies an abstract or physical resource, such as resources on a webpage, mail address, phone number, books, real-world objects such as people and places, concepts. URIs are used to identify anything described using the Resource Description Framework (RDF), for example, concepts that are part of an ontology defined using the Web Ontology Language (OWL), and people who are described using the Friend of a Friend vocabulary would each have an individual URI.

The World Wide Web is an information system that enables content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond IT specialists and hobbyists. It allows documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet according to specific rules of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
A web browser is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. By 2020, an estimated 4.9 billion people had used a browser. The most-used browser is Google Chrome, with a 67% global market share on all devices, followed by Safari with 18%.

A web server is computer software and underlying hardware that accepts requests via HTTP or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiates communication by making a request for a web page or other resource using HTTP, and the server responds with the content of that resource or an error message. A web server can also accept and store resources sent from the user agent if configured to do so.

In computer network communications, the HTTP 404, 404 not found, 404, 404 error, page not found, or file not found error message is a hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) standard response code, to indicate that the browser was able to communicate with a given server, but the server could not find what was requested. The error may also be used when a server does not wish to disclose whether it has the requested information.

In computer networking, a proxy server is a server application that acts as an intermediary between a client requesting a resource and the server providing that resource. It improves privacy, security, and possibly performance in the process.
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a cryptographic protocol designed to provide communications security over a computer network, such as the Internet. The protocol is widely used in applications such as email, instant messaging, and voice over IP, but its use in securing HTTPS remains the most publicly visible.
URL redirection, also called URL forwarding, is a World Wide Web technique for making a web page available under more than one URL address. When a web browser attempts to open a URL that has been redirected, a page with a different URL is opened. Similarly, domain redirection or domain forwarding is when all pages in a URL domain are redirected to a different domain, as when wikipedia.com and wikipedia.net are automatically redirected to wikipedia.org.
REST is a software architectural style that was created to guide the design and development of the architecture for the World Wide Web. REST defines a set of constraints for how the architecture of a distributed, Internet-scale hypermedia system, such as the Web, should behave. The REST architectural style emphasises uniform interfaces, independent deployment of components, the scalability of interactions between them, and creating a layered architecture to promote caching to reduce user-perceived latency, enforce security, and encapsulate legacy systems.

HTTP cookies are small blocks of data created by a web server while a user is browsing a website and placed on the user's computer or other device by the user's web browser. Cookies are placed on the device used to access a website, and more than one cookie may be placed on a user's device during a session.

The X-Forwarded-For (XFF) HTTP header field is a common method for identifying the originating IP address of a client connecting to a web server through an HTTP proxy or load balancer.
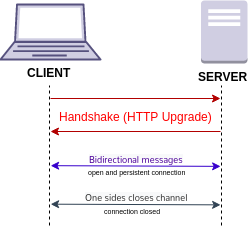
WebSocket is a computer communications protocol, providing a simultaneous two-way communication channel over a single Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) connection. The WebSocket protocol was standardized by the IETF as RFC 6455 in 2011. The current specification allowing web applications to use this protocol is known as WebSockets. It is a living standard maintained by the WHATWG and a successor to The WebSocket API from the W3C.
HTTP/2 is a major revision of the HTTP network protocol used by the World Wide Web. It was derived from the earlier experimental SPDY protocol, originally developed by Google. HTTP/2 was developed by the HTTP Working Group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). HTTP/2 is the first new version of HTTP since HTTP/1.1, which was standardized in RFC 2068 in 1997. The Working Group presented HTTP/2 to the Internet Engineering Steering Group (IESG) for consideration as a Proposed Standard in December 2014, and IESG approved it to publish as Proposed Standard on February 17, 2015. The initial HTTP/2 specification was published as on May 14, 2015.
A uniform resource locator (URL), colloquially known as an address on the Web, is a reference to a resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A URL is a specific type of Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), although many people use the two terms interchangeably. URLs occur most commonly to reference web pages (HTTP/HTTPS) but are also used for file transfer (FTP), email (mailto), database access (JDBC), and many other applications.