
The province of Benevento is a province in the Campania region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Benevento.

The province of Ragusa was a province in the autonomous region of Sicily, in southern Italy, located in the south-east of the island. Following the abolition of the Sicilian provinces, it was replaced in 2015 by the Free municipal consortium of Ragusa. Its capital is the city of Ragusa, Sicily, which is the most southerly provincial capital in Italy.

Ragusa is a city and comune in southern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Ragusa, on the island of Sicily, with 73,288 inhabitants in 2016. It is built on a wide limestone hill between two deep valleys, Cava San Leonardo and Cava Santa Domenica. Together with seven other cities in the Val di Noto, it is part of a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
San Giorgio, is the Italian form of Saint George. When used as the name of a person it is frequently contracted to Sangiorgio.

Sicilian Baroque is the distinctive form of Baroque architecture which evolved on the island of Sicily, off the southern coast of Italy, in the 17th and 18th centuries, when it was part of the Spanish Empire. The style is recognisable not only by its typical Baroque curves and flourishes, but also by distinctive grinning masks and putti and a particular flamboyance that has given Sicily a unique architectural identity.

Rosario Gagliardi (1698–1762) was an Italian architect born in Syracuse. He was one of the leading architects working in the Sicilian Baroque. In spite of never leaving Sicily his work showed great understanding of the style, but was a progression from the style of baroque as deployed by Bernini. He worked mostly in the Sicilian Baroque beginning with the cathedral at Modica in 1702.

Val di Noto is a historical and geographical area encompassing the south-eastern third of Sicily; it is dominated by the limestone Hyblaean plateau. Historically, it was one of the three valli of Sicily.

Modica is a city and comune of 54,456 inhabitants in the Province of Ragusa, Sicily, southern Italy. The city is situated in the Hyblaean Mountains.

Scicli is a town and municipality in the Province of Ragusa in the south east of Sicily, southern Italy. It is 25 kilometres (16 mi) from Ragusa, and 188 kilometres (117 mi) from Palermo, and has a population (2017) of 27,051. Alongside seven other cities in the Val di Noto, it has been listed as one of UNESCO's World Heritage Sites.
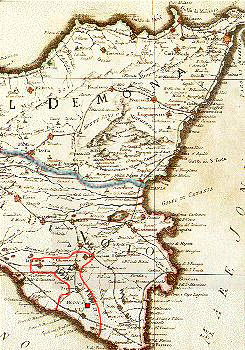
The County of Modica was a feudal territory within the Kingdom of Sicily from 1296 to 1812. Its capital was Modica, on the southern tip of the island, although the cities of Ragusa and Scicli housed some government offices for a period. Today it is perpetuated only as a title held by the head of the House of Alba, Carlos Fitz-James Stuart, 19th Duke of Alba.

Padua Cathedral, or Basilica Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Assumption, is a Catholic church and minor basilica located on the east end of Piazza Duomo, adjacent to the bishop's palace in Padua, Veneto, Italy.

San Giorgio Maggiore is a basilica church located on the corner of Via vicaria Vecchia and Via Duomo, in central Naples, Italy. The apse of the church lies diagonally across the street from San Severo al Pendino.

San Severo al Pendino is a former Roman Catholic church, located on Via Duomo, just south of San Giorgio Maggiore and adjacent to the Museo Civico Gaetano Filangieri, in central Naples, Italy.

Ragusa Cathedral is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Ragusa, Sicily, dedicated to Saint John the Baptist. The present church dates from the early 18th century. It has been the seat of the Bishops of Ragusa since the establishment of the diocese in 1950.

Comacchio Cathedral, also the Basilica of San Cassiano, is a Baroque Roman Catholic cathedral and minor basilica dedicated to Saint Cassian of Imola in the city of Comacchio, in the province of Ferrara, Emilia-Romagna, Italy. Formerly the seat of the bishops of Comacchio, it has been since 1986 a co-cathedral in the Archdiocese of Ferrara-Comacchio.

The Duomo of San Giorgio is a Baroque church located in Ragusa Ibla, Sicily, Italy.
Duomo of San Giorgio or Duomo di San Giorgio may refer to:

Santa Maria dell' Itria is a Baroque-style, Roman Catholic church located in the city of Ragusa, in southern Sicily, Italy.

The Chiesa del Purgatorio, also called the Chiesa delle Santissime Anime del Purgatorio) is a Roman Catholic church located on Piazza della Repubblica in the city of Ragusa, in southern Sicily, Italy. The church is dedicated to those praying for the souls in purgatory.

Caccamo Cathedral is the main church in the Italian city of Caccamo in Sicily. The largest church in the city, it belongs to the Archdiocese of Palermo and the 'arcipretura' of Caccamo. The present building on Piazza Duomo dates to 1616. Its dedication to the warrior saint George the Martyr originated with the Normans and was in memory of their victory over the Saracens near Cerami in 1090.



















