Related Research Articles

The Baja California peninsula is a peninsula in northwestern Mexico. It separates the Gulf of California from the Pacific Ocean. The peninsula extends from Mexicali, Baja California, in the north to Cabo San Lucas, Baja California Sur, in the south.
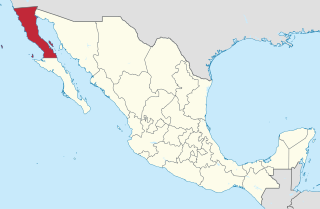
Baja California, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California, is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1952, the area was known as the North Territory of Baja California. It has an area of 70,113 km2 (27,071 sq mi) and comprises the northern half of the Baja California Peninsula, north of the 28th parallel, plus oceanic Guadalupe Island. The mainland portion of the state is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean; on the east by Sonora, the U.S. state of Arizona, and the Gulf of California; on the north by the U.S. state of California; and on the south by Baja California Sur.

Baja California Sur, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California Sur, is the least populated state and the 31st admitted state of the 32 federal entities which comprise the 31 States of Mexico. It is also the ninth-largest Mexican state in terms of area.

Sierra de San Pedro Mártir is a mountain range located within southern Ensenada Municipality and southern Baja California state, of northwestern Mexico.

The Peninsular Ranges are a group of mountain ranges that stretch 1,500 km (930 mi) from Southern California to the southern tip of the Baja California peninsula; they are part of the North American Coast Ranges, which run along the Pacific Coast from Alaska to Mexico. Elevations range from 150 to 3,300 m.

Cupressus arizonica, the Arizona cypress, is a North American species of tree in the cypress family Cupressaceae, native to the southwestern United States and Mexico. Populations may be scattered rather than in large, dense stands.

The Baja California Desert is a desert ecoregion of Mexico's Baja California Peninsula. This ecoregion occupies the western portion of the Baja California peninsula, and occupies most of the Mexican states of Baja California Sur and Baja California. It covers 77,700 square kilometers. The climate is dry, but its proximity of the Pacific Ocean provides humidity and moderates the temperature. The flora mostly consists of xeric shrubs and over 500 species of recorded vascular plants.
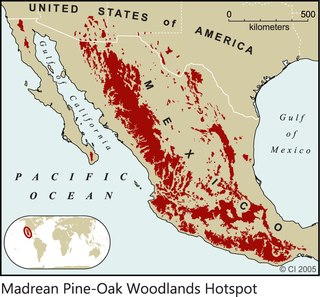
The Madrean pine–oak woodlands are subtropical woodlands found in the mountains of Mexico and the southwestern United States. They are a biogeographic region of the tropical and subtropical coniferous forests and temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biomes, located in North America.

Mission Santa Catarina was a Spanish mission in present-day Valle del Álamo in Baja California, Mexico. It was founded on 12 November 1797 by the Dominican missionary José Loriente. Virtually nothing remains of the original structures. Archaeological investigations of the mission's traces are in progress.

Federal Highway 1 is a free (libre) part of the federal highway corridors of Mexico, and the highway follows the length of the Baja California Peninsula from Tijuana, Baja California, in the north to Cabo San Lucas, Baja California Sur, in the south. The road connects with Via Rapida, which merges into the American Interstate 5 (I-5) at the San Ysidro Port of Entry, which crosses the international border south of San Ysidro, California.

The Sierra de Juárez, also known as the Sierra Juarez, is a mountain range located in Tecate Municipality and northern Ensenada Municipality, within the northern Baja California state of northwestern Mexico.

The Sierra Juárez and San Pedro Mártir pine–oak forests is a Nearctic temperate coniferous forests ecoregion that covers the higher elevations of the Sierra Juárez and Sierra San Pedro Mártir ranges of the Peninsular Ranges, of the northern Baja California Peninsula of Mexico. The pine–oak forests extend throughout the central portion of the Mexican state of Baja California and terminate near the border with the U.S. state of California.

Sierra de San Pedro Mártir National Park is a national park in the Mexican state of Baja California. The Park is part of the municipality of Ensenada, Baja California. The area was first explored by Europeans in 1701 by Eusebio Francisco Kino by Dominican orders.

Eriogonum wrightii is a species of wild buckwheat known by the common names bastardsage and Wright's buckwheat. It is native to the Southwestern United States, California, and northwest Mexico, where it grows in many plant communities, such as chaparral, in rocky habitats from mountains to deserts.

Constitution 1857 National Park is located in the pine forests of the Sierra de Juárez mountain range in the northern part of Baja California, Mexico. The park is an important preserve for many native wild animals like bighorn sheep and mule deer. The park is characterized by the large variety of coniferous plant species.
The Baja California rainbow trout or San Pedro Martir trout or Nelson's trout is a localized subspecies of the rainbow trout, a freshwater fish in the family Salmonidae.

Valle Chico Hot Springs is a subaerial thermal spring located at in the Sierra San Pedro Martir mountains of Baja California, Mexico.

Dudleya pauciflora is a species of succulent plant in the stonecrop family known by the common name few-flower liveforever. It is characterized by its small crowded rosettes of narrow leaves and its colorful inflorescence with red-yellow flowers. Found growing on rocky outcrops and cliffs in the high elevation mountains of the Sierra de San Pedro Martir and the Sierra de San Borja, it is endemic to the state of Baja California, Mexico.

The Mexican mole is a species of mammal in the family Talpidae. It is endemic to Baja California in Mexico, where it is restricted to the highlands of the Sierra de San Pedro Mártir mountain range. Its specific epithet references naturalist Alfred Webster Anthony.

San Felipe is the newest municipality in the Mexican state of Baja California. Inaugurated on 1 January 2022, it is located approximately 190 kilometres (120 mi) south of Mexicali, the state capital.
References
- ↑ Edward William Nelson, Lower California and Its Natural Resources, Volume 1, U.S. Government Printing Office, 1921, p.76.
- ↑ Nelson, Lower California and Its Natural Resources, p.17
Coordinates: 31°18′47″N115°29′18″W / 31.31306°N 115.48833°W