
Bahram II was the fifth Sasanian King of Kings (shahanshah) of Iran, from 274 to 293. He was the son and successor of Bahram I. Bahram II, while still in his teens, ascended the throne with the aid of the powerful Zoroastrian priest Kartir, just like his father had done.

Shapur I was the second Sasanian King of Kings of Iran. The precise dating of his reign is disputed, but it is generally agreed that he ruled from 240 to 270, with his father Ardashir I as co-regent until the death of the latter in 242. During his co-regency, he helped his father with the conquest and destruction of the city of Hatra, whose fall was facilitated, according to Islamic tradition, by the actions of his future wife al-Nadirah. Shapur also consolidated and expanded the empire of Ardashir I, waged war against the Roman Empire, and seized its cities of Nisibis and Carrhae while he was advancing as far as Roman Syria. Although he was defeated at the Battle of Resaena in 243 by Roman emperor Gordian III, he was the following year able to win the Battle of Misiche and force the new Roman emperor Philip the Arab to sign a favorable peace treaty that was regarded by the Romans as "a most shameful treaty".
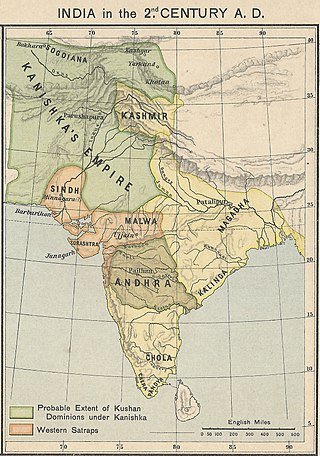
The Kushan Empire was a syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Eastern Iran and Northern India, at least as far as Saketa and Sarnath, near Varanasi, where inscriptions have been found dating to the era of the Kushan emperor Kanishka the Great.
The Indo-Parthian Kingdom was a Parthian kingdom founded by Gondophares, and active from 19 CE to c. 226 CE. At their zenith, they ruled an area covering parts of eastern Iran, various parts of Afghanistan and the northwest regions of the Indian subcontinent. The rulers may have been members of the House of Suren, and the kingdom has even been called the "Suren Kingdom" by some authors.

Gondophares I was the founder of the Indo-Parthian Kingdom and its most prominent king, ruling from 19 to 46. He probably belonged to a line of local princes who had governed the Parthian province of Drangiana since its disruption by the Indo-Scythians in c. 129 BC, and may have been a member of the House of Suren. During his reign, his kingdom became independent from Parthian authority and was transformed into an empire, which encompassed Drangiana, Arachosia, and Gandhara. He is generally known from the Acts of Thomas, the Takht-i-Bahi inscription, and silver and copper coins bearing his visage.

The Indo-Scythians were a group of nomadic people of Iranic Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into the northwestern Indian subcontinent: the present-day South Asian regions of Afghanistan, Pakistan, Eastern Iran and northern India. The migrations persisted from the middle of the second century BCE to the fourth century CE.

Margiana is a historical region centred on the oasis of Merv and was a minor satrapy within the Achaemenid satrapy of Bactria, and a province within its successors, the Seleucid, Parthian and Sasanian empires.
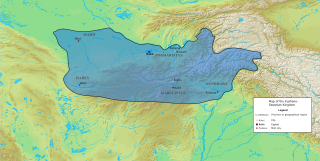
The Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom was a polity established by the Sasanian Empire in Bactria during the 3rd and 4th centuries. The Sasanian Empire captured the provinces of Sogdia, Bactria and Gandhara from the declining Kushan Empire following a series of wars in 225 CE. The local Sasanian governors then went on to take the title of Kushanshah or "King of the Kushans", and to mint coins. They are sometimes considered as forming a "sub-kingdom" inside the Sasanian Empire.

Pacores or Pakores was a king who ruled the remnants of the Indo-Parthian Kingdom in Arachosia from 100–130 AD following Ubouzanes. He was an Indo-Parthian king. He is well-known from coins minted in Seistan and Kandahar, mostly silver drachms and tetradrachms. The time of his reign can be determined as many of his coins over strike those of Vima Takto.

Sistān, also known as Sakastān and Sijistan, is a historical region in present-day south-eastern Iran, south-western Afghanistan and extending across the borders of south-western Pakistan. Mostly corresponding to the then Achaemenid region of Drangiana and extending southwards of the Helmand River not far off from the city of Alexandria in Arachosia. Largely desert, the region is bisected by the Helmand River, the largest river in Afghanistan, which empties into the Hamun Lake that forms part of the border between Iran and Afghanistan.

The Pāratarājas or Pāradarājas was a dynasty of Parthian kings in the territory of modern-day western Pakistan from circa 125 CE to circa 300 CE. It appears to have been a tribal polity of Western Iranic heritage.

Turan was a province of the Sasanian Empire located in present-day Pakistan. The province was mainly populated by Indians, and bordered Paradan in the west, Hind in the east, Sakastan in the north, and Makuran in the south. The main city and bastion of the province was Bauterna (Khuzdar/Quzdar).

Sanabares was an Indo-Parthian king. He was the last Indo-Parthian king to rule in both Sakastan and south Arachosia, as the Kushans under Wima Kadphises made inroads into Indo-Parthian territory. From 160 CE, the remains of the Indo-Parthian kingdom were partitioned between Turan, under Pahares I, and Sakastan under Sanabares II. following the partition of the remains of the Indo-Parthian kingdom into the realms of and Turan. The kingdom of Turan covers the period from 160 to 230 CE.

The Sasanian coinage of Sindh refers to a series of Sasanian-style issues, minted from 325 to 480 CE in Sindh, in the southern part of modern Pakistan, with the coin type of successive Sasanian Empire rulers, from Shapur II to Peroz I. Together with the coinage of the Kushano-Sasanians, these coins are often described as "Indo-Sasanian". They form an important part of Sasanian coinage.

Farn-Sasan was the last king of the Indo-Parthian Kingdom, ruling the region of Sakastan approximately from 210 to 226. Literary sources makes no mention of him, and he is only known through the coins he issued. He was defeated in 226 by the Sasanian ruler Ardashir I, which marked the end of Indo-Parthian rule.
Hind was the name of a southeastern Sasanian province lying near the Indus River. The boundaries of the province are obscure. The Austrian historian and numismatist Nikolaus Schindel has suggested that the province may have corresponded to the Sindh region, where the Sasanians notably minted unique gold coins of themselves. According to the modern historian C. J. Brunner, the province possibly included—whenever jurisdiction was established—the areas of the Indus River, including the southern part of Punjab.

Pahares I was an Indo-Parthian ruler of Turan. Pahares ruled the newly established Kingdom of Turan, following the partition of the remains of the Indo-Parthian kingdom into the realms of Sakastan and Turan. The kingdom of Turan covers the period from 160 to 230 CE. The kingdom of Sakastan was ruled by a second king with the name Sanabares.
The Sasanian–Kushan Wars were a series of wars between the newly established Persian Sasanian empire, under Ardashir I and later his successor Shapur I, against the declining Kushan empire. These wars resulted in the eastward expansion of the Sasanians who conquered much of the Kushan territory including Bactria, Gandhara and Sogdia. The Sassanids, shortly after victory over the declining Parthian empire, extended their dominion to most of former Parthian lands, including Bactria, during the reign of Ardashir I around 230 CE, then they further expanded to the eastern parts of their empire in what is now western Pakistan, at the expense of warring against the declining Kushan empire, during the reign of his son Shapur I (240–270). Thus the Kushans lost their western territory to the rule of Sassanid nobles, who eventually established their own states and were collectively referred to as Kushanshahs or "Kings of the Kushans". At their greatest extent, these Kushano-Sasanians also seem to have expanded eastwards all the way to Gandhara, however do not seem to have crossed the Indus river, since almost none of their coinage has been found in the city of Taxila, just beyond the Indus.















