
A sandal-bearer is a person who bears the sandals of his superior. The role existed in various cultures and epochs, being first documented in Egypt's Early Dynastic Period (c. 31st century BC).

A sandal-bearer is a person who bears the sandals of his superior. The role existed in various cultures and epochs, being first documented in Egypt's Early Dynastic Period (c. 31st century BC).
In Ancient Egypt the role of sandal-bearer was documented for the first time in history. A sandal-bearer is depicted on the Narmer Macehead, as well as on both sides of the Narmer Palette, in which he is identified by a rosette and a club as the servant of the king. [1] Based on interpretations of these depictions, the sandal-bearer was possibly a high-ranking official, accompanying the pharaoh on important occasions. [2] [3] In addition to carrying the sandals, the sandal-bearer would also perform the ancient practice of washing the king's feet. [4]
Sandal-bearers also existed in Feudal Japan, being a position of relatively high status. Probably the most famous person to take on this role in Japan was Toyotomi Hideyoshi, during the Sengoku period. Being of humble origins, around 1557 he joined the Oda clan, then headed by Oda Nobunaga, as a lowly servant. [5] He became one of Nobunaga's sandal-bearers and was present at the Battle of Okehazama in 1560 when Nobunaga defeated Imagawa Yoshimoto to become one of the most powerful warlords in the Sengoku period. After the death of Nobunaga, he secured a succession of high imperial court titles including, in 1585, the prestigious position of kanpaku (regent). [6]

Oda Nobunaga was a Japanese daimyō and one of the leading figures of the Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods. He was the Tenka-bito and regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. He is sometimes referred as the "Demon Daimyō" and "Demon King of the Sixth Heaven".

Pharaoh is the vernacular term often used for the monarchs of ancient Egypt, who ruled from the First Dynasty until the annexation of Egypt by the Roman Republic in 30 BCE. However, regardless of gender, "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom. The earliest confirmed instances of "pharaoh" used contemporaneously for a ruler were a letter to Akhenaten or an inscription possibly referring to Thutmose III.

Toyotomi Hideyoshi, otherwise known as Kinoshita Tōkichirō and Hashiba Hideyoshi, was a Japanese samurai and daimyō of the late Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods and regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan. Although he came from a peasant background, his immense power earned him the rank and title of Kampaku and Daijō-daijin, the highest official position and title in the nobility class. He was the first person in history to become a Kampaku who was not born a noble. He then passed the position and title of Kampaku to his nephew, Toyotomi Hidetsugu. He remained in power as Taikō (太閤), the title of retired Kampaku, until his death. It is believed, but not certain, that the reason he refused or could not obtain the title of shogun (征夷大将軍), the leader of the warrior class, was because he was of peasant origin.

The Sengoku period, also known as Sengoku Jidai, is the period in Japanese history in which civil wars and social upheavals took place almost continuously in the 15th and 16th centuries. The Kyōtoku incident (1454), Ōnin War (1467), or Meiō incident (1493) is generally chosen as the period's start date, but there are many competing historiographies for its end date, ranging from 1568, the date of Oda Nobunaga's march on Kyoto, to the suppression of the Shimabara Rebellion in 1638, deep into what is traditionally considered the Edo period. Regardless of the dates chosen, the Sengoku period overlaps substantially with the Muromachi period (1336–1573).

The Azuchi–Momoyama period was the final phase of the Sengoku period in Japanese history from 1568 to 1600.

Maeda Toshiie was one of the leading generals of Oda Nobunaga following the Sengoku period of the 16th century extending to the Azuchi–Momoyama period. His preferred weapon was a yari and he was known as "Yari no Mataza" (槍の又左), Matazaemon (又左衛門) being his common name. He was a member of the so-called Echizen Sanninshu along with Sassa Narimasa and Fuwa Mitsuharu. The highest rank from the court that he received is the Great Counselor Dainagon.

Azai Nagamasa was a Japanese daimyō of the Sengoku period known as the brother-in-law and enemy of Oda Nobunaga. Nagamasa was head of the Azai clan seated at Odani Castle in northern Ōmi Province and married Nobunaga's sister Oichi in 1564, fathering her three daughters – Yodo-dono, Ohatsu, and Oeyo – who became prominent figures in their own right.
The Battle of Shizugatake took place during the Sengoku period of Japan between Toyotomi Hideyoshi and Shibata Katsuie in Shizugatake, Ōmi Province over a period of two days beginning on the 20th day of the fourth month of Tenshō 11. Katsuie supported Oda Nobutaka's claim as successor of Oda Nobunaga in a succession dispute within the Oda clan that benefitted Hideyoshi.

The Narmer Palette, also known as the Great Hierakonpolis Palette or the Palette of Narmer, is a significant Egyptian archaeological find, dating from about the 31st century BC, belonging, at least nominally, to the category of cosmetic palettes. It contains some of the earliest hieroglyphic inscriptions ever found. The tablet is thought by some to depict the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the king Narmer. Along with the Scorpion Macehead and the Narmer Maceheads, also found together in the main deposit at Nekhen, the Narmer Palette provides one of the earliest known depictions of an Egyptian king. On one side, the king is depicted with the bulbed White Crown of Upper (southern) Egypt, and the other side depicts the king wearing the level Red Crown of Lower (northern) Egypt, which also makes it the earliest known example of a king wearing both types of headdress. The Palette shows many of the classic conventions of Ancient Egyptian art, which must already have been formalized by the time of the Palette's creation. Egyptologists Bob Brier and A. Hoyt Hobbs have referred to the Narmer Palette as "The oldest Egyption historical record".
Kitsuno was a Japanese woman from the Sengoku period to the Azuchi–Momoyama period. She was a concubine of Oda Nobunaga, a Sengoku Daimyō of the Owari Province.

Yodo-dono (淀殿) or Yodogimi (淀君), also known as Lady Chacha (茶々), was a Japanese historical figure in the late Sengoku period. She was the concubine and the second wife of Japanese ruler Toyotomi Hideyoshi. As the mother of his son and successor Hideyori, she acted as Hideyori's guardian in the restoration of the Toyotomi clan after the fall of the Council of Five Elders, and alongside her son, led the last anti-Tokugawa shogunate resistance in the siege of Osaka.

Kōsa, also known as Hongan-ji Kennyo, was the 11th head of the Hongan-ji in Kyoto, and Chief Abbot of Ishiyama Hongan-ji, cathedral fortress of the Ikkō-ikki, during its siege at the end of the Sengoku period. He engineered many alliances, and organized the defenses of the cathedral to the point that most at the time considered Ishiyama Hongan-ji to be unbreachable.

Scorpion II, also known as King Scorpion, was a ruler during the Protodynastic Period of Upper Egypt.

Yamauchi Kazutoyo, also spelled Yamanouchi, was a retainer of Oda Nobunaga and later Toyotomi Hideyoshi. His father Yamauchi Moritoyo was a descendant of Fujiwara no Hidesato, a senior retainer of the Iwakura Oda clan and lord of Kuroda castle in Owari Province at the end of the Sengoku period of Japan. He was famous as the husband of Yamauchi Chiyo.
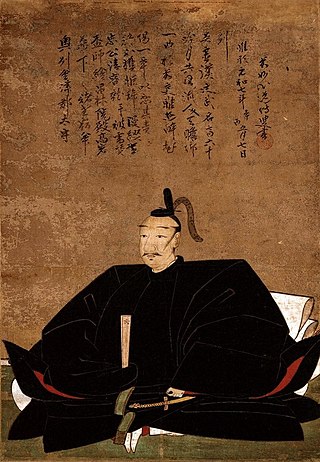
Gamō Ujisato was a Japanese daimyō of the Sengoku and Azuchi–Momoyama periods. He was heir and son of Gamō Katahide, lord of Hino Castle in Ōmi Province, and next managed Ise Province as lord of Matsusaka Castle and finally 920,000 koku in Aizu as lord of Tsurugajo Castle.

Gō: Himetachi no Sengoku is a 2011 Japanese historical drama television series and the 50th NHK taiga drama. It was written for television by Kumiko Tabuchi, based on her own novel of the same name. The drama stars Juri Ueno in the title role, with Rie Miyazawa and Asami Mizukawa as Cha-cha and Hatsu respectively, the sisters of Gō.

The Narmer macehead is an ancient Egyptian decorative stone mace head. It was found in the "main deposit" in the temple area of the ancient Egyptian city of Nekhen (Hierakonpolis) by James Quibell in 1898. It is dated to the Early Dynastic Period reign of king Narmer whose serekh is engraved on it. The macehead is now kept at the Ashmolean Museum, Oxford.
Many significant Japanese historical people of the Sengoku period appear in works of popular culture such as anime, manga, and video games. This article presents information on references to several historical people in such works.

Sengoku Basara: Samurai Kings is a Japanese anime television series based on the Capcom video game series of the same name made by Production I.G, planned and written by Yasuyuki Muto, and chiefly directed by Itsuro Kawasaki. The series started broadcast on Japan's Chubu-Nippon Broadcasting (CBC) station in April 2009; other networks broadcast the episodes within a few days, including TBS, MBS, and Animax. Its first season made its North American television debut on the Funimation Channel on November 16, 2010.
Ikeda Sen, or Anyōin (安養院), was a late-Sengoku period onna-musha. She was the daughter of Ikeda Tsuneoki and the older sister of Ikeda Terumasa. Mori Nagayoshi was her first husband. She was a woman trained in martial arts and was commander of a unit that consisted of 200 female musketeers