Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 475,807.63 km2 (182,812 mi.2), including adjacent islands such as the Simeulue, Nias, Mentawai, Enggano, Riau Islands, Bangka Belitung and Krakatoa archipelago.

North Sulawesi is a province of Indonesia. It is located on the Minahasa Peninsula of the island of Sulawesi, south of the Philippines and southeast of Sabah, Malaysia. It borders the Philippine province of Davao Occidental and Soccsksargen regions of the Philippines to the north, the Maluku Sea to the east, Gorontalo and Celebes Sea to the west and the Gulf of Tomini to the southwest. With the outlying island of Miangas to its north, it is the northernmost island of Indonesia. The province's area is 14,500.28 square kilometres (5,598.59 sq mi), and its population was 2,270,596 according to the 2010 census; this rose to 2,621,923 at the 2020 Census, while the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 2,659,543. North Sulawesi is known as a heaven for divers around the world.
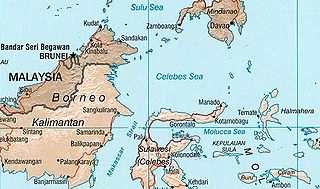
The Celebes Sea or Sulawesi Sea of the western Pacific Ocean is bordered on the north by the Sulu Archipelago and Sulu Sea and Mindanao Island of the Philippines, on the east by the Sangihe Islands chain, on the south by Sulawesi's Minahasa Peninsula, and on the west by northern Kalimantan in Indonesia. It extends 420 miles (675 km) north-south by 520 mi (840 km) east-west and has a total surface area of 110,000 square miles (280,000 km2), to a maximum depth of 20,300 feet (6,200 m). South of the Cape Mangkalihat, the sea opens southwest through the Makassar Strait into the Java Sea.

The Sangihe tarsier, also known as Sangihe Island tarsier, is a small primate found on Sangir Island, which is located about 200 kilometers north-east of the island of Sulawesi in Indonesia. In 2008 a population of the Sangihe tarsier was determined to be a distinct species, the Siau Island tarsier.

The Sangihe Islands – Indonesian: Kepulauan Sangihe – are a group of islands which constitute two regencies within the province of North Sulawesi, in northern Indonesia, the Sangihe Islands Regency and the Sitaro Islands Regency. They are located north-east of Sulawesi between the Celebes Sea and the Molucca Sea, roughly halfway between Sulawesi and Mindanao, in the Philippines; the Sangihes form the eastern limit of the Celebes Sea. The islands combine to total 813 square kilometers (314 sq mi), with many of the islands being actively volcanic with fertile soil and mountains.

Mount Awu is the largest volcano in the Sangihe chain, located on Sangir Island in North Sulawesi, Indonesia. Powerful eruptions occurred in 1711, 1812, 1856, 1822, 1892, and 1966 with devastating pyroclastic flows and lahars that have resulted in 11,048 fatalities. A total of 18 eruptions are recorded from 1640, with two of VEI 4 and 3 with VEI 3, one eruption every ~ 20 years. The hazardous nature of the volcano is determined from the continuous lava source driven by the geodynamic setting and the presence of a crater lake, sustained by the consistent rainfall on the island, on top of a lava dome. This setting creates the conditions for water injection in the lava dome, which can cause a water-magma explosion.
Mount Sahendaruman is an extinct volcano located in southern part of Indonesian island of Sangihe.
Sangirese, also known as Sangihé, Sangi, and Sangih, is an Austronesian language spoken on the islands linking northern Sulawesi, Indonesia, with Mindanao, Philippines by the Sangirese people.
Sangir, Sangihe, Sangi or Sanghir may refer to:

The red-and-blue lory is a small, strikingly-colored parrot endemic to Indonesia. The species inhabits a single island, Karakelong, in the Indonesian archipelago, although it was formerly found on the Sangihe Islands and other parts of the Talaud Islands.

The Sangihe whistler or Sangihe shrikethrush is a species of bird in the family Pachycephalidae. It is endemic to Sangihe Island in Indonesia. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist montane forests. It is threatened by habitat loss. Originally, the Sangihe shrikethrush was described in the genus Pinarolestes. It was re-classified from the genus Colluricincla to Coracornis in 2013. Alternate names include the Sahengbalira shrike-thrush and Sangir whistler.
The Sangiric languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages spoken in North Sulawesi, Indonesia and several small islands to the north which belong to the Philippines. They are classified as a branch of the Philippine subgroup.

The Siau Island tarsier is a species of tarsier from the tiny volcanic island of Siau in Indonesia. The T. tumpara species is one of 14 species and 7 subspecies in the tarsier family called "Tarsiidae". They belong to the Haplorrhini suborder, known as the "dry-nosed" primates. The tarsier's eyes are so big that they do not move in its socket and they are almost as big as its brain. The name tumpara, which means tarsier in the local language of Sulawesi, was an attempt to encourage the community in preserving this biological heritage.

The Sangihe Islands Regency is a regency of North Sulawesi Province, Indonesia. It comprises a group of islands situated to the North of Sulawesi. It covers a land area of 736.98 km2, and had a population of 126,100 at the 2010 census and 139,262 at the 2020 census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 140,165. The principal island is also named Sangihe, on which lies the main town of Tahuna. Minor island groups within the Regency include the Marore group considerably to the north of Sangihe Island, the Tatoareng group to the south, and the Nusa Tabukan group off the northeast coast of Sangihe Island. It borders the Philippines in the north, making it one of Indonesia's border regions.

The Talaud Islands Regency is a regency of North Sulawesi province, Indonesia. The Talaud Islands form an archipelago situated to the north-east of the Minahasa Peninsula, with a land area of 1,251.02 km2. It had a population of 83,434 at the 2010 Census, increasing to 94,521 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 95,545. The largest island is Karakelong, on which lies the regency seat in the town of Melonguane. To its south lie the islands of Salibabu and Kabaruan, while the Nanusa group of 7 small islands lies to the northeast of Karakelong, and Miangas island is situated midway between Karakelong and the Philippines. It is one of the three regencies to the north of North Sulawesi that are located between Sulawesi and the Philippines, along with the Sitaro Islands Regency and Sangihe Islands Regency; originally these formed a single regency, but on 110 April 2002 the Talaud Islands were split off to form their own Regency. The island of Miangas is the most northerly island in the regency and widely regarded as the northernmost point of Indonesia. As the result, it is often referenced to describe the territorial integrity of Indonesia in various patriotic statements and songs together with Sabang, Merauke, and Rote Island.

Miangas or Palmas is North Sulawesi's northernmost island, and one of 92 officially listed outlying islands of Indonesia.

Sangirese or Sangihe people are one of the native people to the Sangir Islands in the northern chain of islands in Sulawesi and the southern part of Mindanao. The Sangirese people are fishermen and nutmeg growers in their home areas and also work as wage labourers in industrial crops enterprises in Bolaang Mongondow Regency and Minahasa Regency.
The Sangihe golden bulbul is a species of passerine bird in the bulbul family Pycnonotidae. It is endemic to the Sangihe Islands which lie northeast of Sulawesi in Indonesia. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests.

Londe or londi is a traditional boat from North Sulawesi, Indonesia. They are thought to have existed since 1500s, developed from ancient Sangir islands boat called bininta which is now enshrined in the symbol of the region of Sangir Islands District.