Related Research Articles

The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) is a large-scale physics experiment and observatory designed to detect cosmic gravitational waves and to develop gravitational-wave observations as an astronomical tool. Two large observatories were built in the United States with the aim of detecting gravitational waves by laser interferometry. These observatories use mirrors spaced four kilometers apart which are capable of detecting a change of less than one ten-thousandth the charge diameter of a proton.

Kip Stephen Thorne is an American theoretical physicist known for his contributions in gravitational physics and astrophysics. Along with Rainer Weiss and Barry C. Barish, he was awarded the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physics for his contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves.

Rainer "Rai" Weiss is a German-born American physicist, known for his contributions in gravitational physics and astrophysics. He is a professor of physics emeritus at MIT and an adjunct professor at LSU. He is best known for inventing the laser interferometric technique which is the basic operation of LIGO. He was Chair of the COBE Science Working Group.

GEO600 is a gravitational wave detector located near Sarstedt, a town 20 km to the south of Hanover, Germany. It is designed and operated by scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics, Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics and the Leibniz Universität Hannover, along with University of Glasgow, University of Birmingham and Cardiff University in the United Kingdom, and is funded by the Max Planck Society and the Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC). GEO600 is capable of detecting gravitational waves in the frequency range 50 Hz to 1.5 kHz, and is part of a worldwide network of gravitational wave detectors. This instrument, and its sister interferometric detectors, when operational, are some of the most sensitive gravitational wave detectors ever designed. They are designed to detect relative changes in distance of the order of 10−21, about the size of a single atom compared to the distance from the Sun to the Earth. Construction on the project began in 1995.

Ronald William Prest Drever was a Scottish experimental physicist. He was a professor emeritus at the California Institute of Technology, co-founded the LIGO project, and was a co-inventor of the Pound–Drever–Hall technique for laser stabilisation, as well as the Hughes–Drever experiment. This work was instrumental in the first detection of gravitational waves in September 2015.

The Virgo interferometer is a large Michelson interferometer designed to detect the gravitational waves predicted by general relativity. It is located in Santo Stefano a Macerata, near the city of Pisa, Italy. The instrument's two arms are three kilometres long, housing its mirrors and instrumentation inside an ultra-high vacuum.
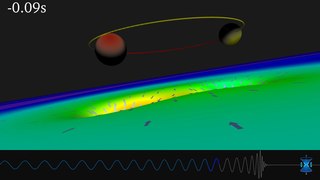
Gravitational waves are waves of the intensity of gravity that are generated by the accelerated masses of binary stars and other motions of gravitating masses, and propagate as waves outward from their source at the speed of light. They were first proposed by Oliver Heaviside in 1893 and then later by Henri Poincaré in 1905 as the gravitational equivalent of electromagnetic waves. Gravitational waves are sometimes called gravity waves, but gravity waves typically refer to displacement waves in fluids. In 1916 Albert Einstein demonstrated that gravitational waves result from his general theory of relativity as ripples in spacetime.

A gravitational-wave detector is any device designed to measure tiny distortions of spacetime called gravitational waves. Since the 1960s, various kinds of gravitational-wave detectors have been built and constantly improved. The present-day generation of laser interferometers has reached the necessary sensitivity to detect gravitational waves from astronomical sources, thus forming the primary tool of gravitational-wave astronomy.
Gravitational-wave astronomy is an emerging field of science, concerning the observations of gravitational waves to collect relatively unique data and make inferences about objects such as neutron stars and black holes, events such as supernovae, and processes including those of the early universe shortly after the Big Bang.
The LIGO Scientific Collaboration (LSC) is a scientific collaboration of international physics institutes and research groups dedicated to the search for gravitational waves.
David Howard Reitze is an American laser physicist who is professor of physics at the University of Florida and served as the scientific spokesman of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) experiment in 2007-2011. In August 2011, he took a leave of absence from the University of Florida to be the Executive Director of LIGO, stationed at the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California. He obtained his BA in 1983 from Northwestern University, his PhD in physics from the University of Texas at Austin in 1990, and had positions at Bell Communications Research and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, before taking his faculty position at the University of Florida. He is a Fellow of the American Physical Society, the Optical Society, and the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
INDIGO or IndIGO is a consortium of Indian gravitational wave physicists. It is an initiative to set up advanced experimental facilities for a multi-institutional observatory project in gravitational-wave astronomy to be located near Aundha Nagnath, Hingoli District, Maharashtra, India. Predicted date of commission is in 2030.

Barry Clark Barish is an American experimental physicist and Nobel Laureate. He is a Linde Professor of Physics, emeritus at California Institute of Technology and a leading expert on gravitational waves.

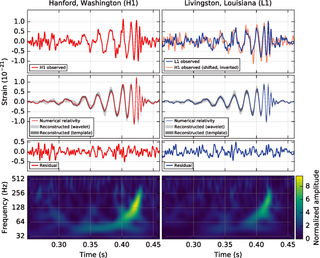
The first direct observation of gravitational waves was made on 14 September 2015 and was announced by the LIGO and Virgo collaborations on 11 February 2016. Previously, gravitational waves had been inferred only indirectly, via their effect on the timing of pulsars in binary star systems. The waveform, detected by both LIGO observatories, matched the predictions of general relativity for a gravitational wave emanating from the inward spiral and merger of a pair of black holes of around 36 and 29 solar masses and the subsequent "ringdown" of the single resulting black hole. The signal was named GW150914. It was also the first observation of a binary black hole merger, demonstrating both the existence of binary stellar-mass black hole systems and the fact that such mergers could occur within the current age of the universe.
David Ernest McClelland is an Australian physicist, with his research focused on the development of the manipulation and control of optical quantum states, and its implementation into gravitational wave observatories. He is a Fellow of the Australian Academy of Science, the American Physical Society and the Optical Society of America. Since 2001, he has been a professor at the Australian National University (ANU) in the Research School of Physics and Engineering, in Canberra (Australia). He is Director of the ANU's Centre for Gravitational Astrophysics and Deputy Director of OzGrav - the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence in Gravitational Wave Discovery.

GW 170817 was a gravitational wave (GW) signal observed by the LIGO and Virgo detectors on 17 August 2017, originating from the shell elliptical galaxy NGC 4993. The signal was produced by the last moments of the inspiral process of a binary pair of neutron stars, ending with their merger. It is the first GW observation that has been confirmed by non-gravitational means. Unlike the five previous GW detections—which were of merging black holes and thus not expected to produce a detectable electromagnetic signal—the aftermath of this merger was seen across the electromagnetic spectrum by 70 observatories on 7 continents and in space, marking a significant breakthrough for multi-messenger astronomy. The discovery and subsequent observations of GW 170817 were given the Breakthrough of the Year award for 2017 by the journal Science.

Karan Jani is an Indian astrophysicist working on black holes, gravitational waves, and testing Albert Einstein's General Theory of Relativity. He is currently an assistant professor of physics and astronomy at Vanderbilt University, and holds the endowed position of Cornelius Vanderbilt Dean’s Faculty Fellow. He has worked at the LIGO Livingston Observatory in the US, the Albert Einstein Institute in Germany, the Georgia Institute of Technology, and the Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics in Canada. He is a member of the Indian Initiative in Gravitational-wave Observations effort to build a gravitational wave detector LIGO in India.
Stanley Ernest Whitcomb is an American physicist and was the chief scientist at the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) project when the first direct detection of gravitational waves was made in September 2015.

Rana X. Adhikari is an American experimental physicist. He is a professor of physics at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and an associate faculty member of the International Centre for Theoretical Sciences of Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (ICTS-TIFR).

C. S. Unnikrishnan is an Indian physicist and professor known for his contributions in multiple areas of experimental and theoretical physics. He has been a professor at the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai and is currently a professor in the School of Quantum Technology at the Defence Institute of Advanced Technology in Pune. He has made significant contributions in foundational issues in gravity and quantum physics and has published over 250 research papers and articles. Unnikrishnan is also a key member of the LIGO-India project and a member of the global LIGO Scientific Collaboration
References
- ↑ "Sanjeev's Home page".
- ↑ "Gravitational waves: They scorned Sanjeev Dhurandhar three decades ago, today he is the toast of modern science". The Indian Express. 12 February 2016.
- ↑ Pallava Bagla (12 February 2016). "37 Indians Played A Role In Discovering Gravitational Waves". NDTV.com.
- ↑ "'It's all about extracting wave signal from noise'". The Times of India. 12 February 2016.
- ↑ Bala Iyer; Tarun Souradeep; C.S. Unnikrishnan; Sanjeev Dhurandhar; Sendhil Raja; Ajai Kumar; Anand Sengupta (10 November 2011). LIGO-INDIA: Proposal for an Interferometric Gravitation-Wave Observatory (PDF) (Report). Indian Initiative in Gravitational wave Observations – via LIGO Document Control Center.
- ↑ "Celebrating 22 Years of H. K. Firodia Awards for Excellence in Science & Technology". H. K. Firodia Memorial Foundation. Retrieved 1 May 2018.