
A roof is the top covering of a building, including all materials and constructions necessary to support it on the walls of the building or on uprights, providing protection against rain, snow, sunlight, extremes of temperature, and wind. A roof is part of the building envelope.

BoPET is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity, gas and aroma barrier properties, and electrical insulation.

Drywall is a panel made of calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum), with or without additives, typically extruded between thick sheets of facer and backer paper, used in the construction of interior walls and ceilings. The plaster is mixed with fiber, plasticizer, foaming agent, and various additives that can reduce mildew, flammability, and water absorption.

A radiant barrier is a type of building material that reflects thermal radiation and reduces heat transfer. Because thermal energy is also transferred by conduction and convection, in addition radiation, radiant barriers are often supplemented with thermal insulation that slows down heat transfer by conduction or convection.
This page is a list of construction topics.

A flat roof is a roof which is almost level in contrast to the many types of sloped roofs. The slope of a roof is properly known as its pitch and flat roofs have up to approximately 10°. Flat roofs are an ancient form mostly used in arid climates and allow the roof space to be used as a living space or a living roof. Flat roofs, or "low-slope" roofs, are also commonly found on commercial buildings throughout the world. The National Roofing Contractors Association defines a low-slope roof as having a slope of 3 in 12 (1:4) or less.
Underlay may refer to flooring or roofing materials, bed padding, or a musical notation.

Roof shingles are a roof covering consisting of individual overlapping elements. These elements are typically flat, rectangular shapes laid in courses from the bottom edge of the roof up, with each successive course overlapping the joints below. Shingles are held by the roof rafters and are made of various materials such as wood, slate, flagstone, metal, plastic, and composite materials such as fibre cement and asphalt shingles. Ceramic roof tiles, which still dominate in Europe and some parts of Asia, are still usually called tiles. Roof shingles may deteriorate faster and need to repel more water than wall shingles. They are a very common roofing material in the United States.

A batten is most commonly a strip of solid material, historically wood but can also be of plastic, metal, or fiberglass. Battens are variously used in construction, sailing, and other fields.

A scrim is a woven material, either finely woven lightweight fabric widely used in theatre, or a heavy, coarse woven material used for reinforcement in both building and canvasmaking.

A purlin is a longitudinal, horizontal, structural member in a roof. In traditional timber framing there are three basic types of purlin: purlin plate, principal purlin, and common purlin.
A metal roof is a roofing system made from metal pieces or tiles characterized by its high resistance, impermeability and longevity. It is a component of the building envelope. Zinc, copper and steel alloys are commonly used.
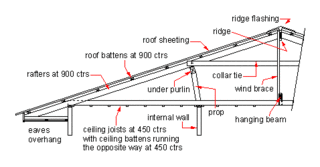
Domestic roof construction is the framing and roof covering which is found on most detached houses in cold and temperate climates. Such roofs are built with mostly timber, take a number of different shapes, and are covered with a variety of materials.

An asphalt shingle is a type of wall or roof shingle that uses asphalt for waterproofing. It is one of the most widely used roofing covers in North America because it has a relatively inexpensive up-front cost and is fairly simple to install.

Building insulation is any object in a building used as insulation for thermal management. While the majority of insulation in buildings is for thermal purposes, the term also applies to acoustic insulation, fire insulation, and impact insulation. Often an insulation material will be chosen for its ability to perform several of these functions at once.

A sod roof, or turf roof, is a traditional Scandinavian type of green roof covered with sod on top of several layers of birch bark on gently sloping wooden roof boards. Until the late 19th century, it was the most common roof on rural log houses in Norway and large parts of the rest of Scandinavia. Its distribution roughly corresponds to the distribution of the log building technique in the vernacular architecture of Finland and the Scandinavian peninsula. The load of approximately 250 kg per m2 of a sod roof is an advantage because it helps to compress the logs and make the walls more draught-proof. In winter the total load may well increase to 400 or 500 kg per m2 because of snow. Sod is also a reasonably efficient insulator in a cold climate. The birch bark underneath ensures that the roof will be waterproof.

Bituminous waterproofing systems are designed to protect residential and commercial buildings. Bitumen is a mixed substance made up of organic liquids that are highly sticky, viscous, and waterproof. These systems are sometimes used to construct roofs, in the form of roofing felt or roll roofing products.

Asphalt roll roofing or membrane is a roofing material commonly used for buildings that feature a low sloped roof pitch in North America. The material is based on the same materials used in asphalt shingles; an organic felt or fiberglass mat, saturated with asphalt, and faced with granular stone aggregate. The installation process, known as Torch On Roofing, is often used on commercial properties in North America.

A board roof or boarded roof is a roofing method of using boards as the weather barrier on a roof. Board roofs can be applied in several ways, the basic types have the boards installed vertically and installed horizontally. Double board roofs were sometimes used on railroad cars.
















