
Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about 1,100 nautical miles north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about 110 are permanently inhabited—and more than 500 islets, amounting to a total land area of about 18,300 square kilometres (7,100 sq mi). The most outlying island group is Ono-i-Lau. About 87% of the total population live on the two major islands, Viti Levu and Vanua Levu. About three-quarters of Fijians live on Viti Levu's coasts, either in the capital city of Suva, or in smaller urban centres such as Nadi or Lautoka. The interior of Viti Levu is sparsely inhabited because of its terrain.

The Gilbert Islands are a chain of sixteen atolls and coral islands in the Pacific Ocean, about halfway between Papua New Guinea and Hawaii. They constitute the main part of the country of Kiribati.

Rotuma is a self-governing heptarchy, generally designated a dependency of Fiji. Rotuma commonly refers to the Rotuma Island, the only permanently inhabited and by far the largest of all the islands in the Rotuma Group. Officially, the Rotuma Act declares that Rotuma consists of Rotuma Island as well as its neighbouring islands, rocks, and reefs across the entire Rotuma Group. The dependency is situated around 500 km west of the French islands of Wallis and Futuna and a similar distance north of the Fijian mainland. Its capital is Ahau, a hamlet consisting of a number of colonial-era buildings. Rotuma exists as a dependency of Fiji but itself contains its own socioreligious pene-enclave known traditionally as Faguta where the chiefs and their villages adhere to the practices of worship, festival dates, and French-based writing system of the Marists, based at Sumi.

RatuSeru Epenisa Cakobau was a Fijian chief, monarch, and warlord (Vunivalu) who united part of Fiji's warring tribes under his leadership, establishing a united Fijian kingdom. He was born on Natauloa, Nairai Island in Lomaiviti but spent his youth on Vanuaso, Gau, Lomaiviti, later returning to Bau to re-establish his Father's Ratu Tanoa Visawaqa reign. Ratu Epenisa Seru Visawaqa was given the name "Cakobau" meaning destroyer of Bau, in reference to his grandfathers' (Nailatikau) effort to first claim the tile from the people of Butoni and Lovoni, returned with most of his warriors from Vanuaso, Gau, Lomaiviti to coup the leadership in Bau then and later takeover his father's title; known after his father as the 6th "Vunivalu" or Warlord of Bau.

Firewalking is the act of walking barefoot over a bed of hot embers or stones. It has been practiced by many people and cultures in many parts of the world, with the earliest known reference dating from Iron Age India c. 1200 BCE. It is often used as a rite of passage, as a test of strength and courage, and in religion as a test of faith.
The House of Chiefs in Fiji consists of the Fijian nobility, composed of about seventy chiefs of various ranks, majority of which are related. It is not a formal political body and is not the same as the Great Council of Chiefs, a political body which had a prescribed role under the 1997 Constitution of Fiji, although the membership of the two bodies did overlap to a great extent.
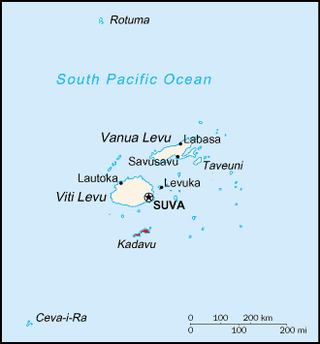
Kadavu, with an area of 411 square kilometres (159 sq mi), is the fourth largest island in Fiji, and the largest island in the Kadavu Group, a volcanic archipelago consisting of Kadavu, Ono, Galoa and a number of smaller islands in the Great Astrolabe Reef. Its main administrative centre is Vunisea, which has an airport, a high school, a hospital, and a government station, on the Namalata Isthmus where the island is almost cut in two. Suva, Fiji's capital, lies 88 kilometres to the north of Kadavu. The population of the island province was 10,167 at the most recent census in 2007.
The culture of Fiji is a tapestry of native Fijian, Indian, European, Chinese and other nationalities. Culture polity traditions, language, food costume, belief system, architecture, arts, craft, music, dance, and sports will be discussed in this article to give you an indication of Fiji's indigenous community but also the various communities which make up Fiji as a modern culture and living. The indigenous culture is an active and living part of everyday life for the majority of the population.

Beqa is an island in Fiji, an outlier to the main island of Viti Levu, 10 kilometres to the south. The island has a land area of 36.3 square kilometres and reaches a maximum elevation of 440 metres. Beqa has 9 villages divided between 2 tikinas (districts): Sawau and Raviravi. To the west is the island of Yanuca.
Yanuca is an inhabited coral island in Fiji. It is administratively part of Serua province. The island has a land area of 1.5 square kilometres and reaches a maximum elevation of 100 metres. It is characterized by white sandy beaches and lush vegetation, and is now a camping site. To the east is the island of Beqa.
Bulou is a title used by Fijian women of chiefly rank, in the Provinces of Nadroga-Navosa and Kadavu, and parts of Serua Province, in Fiji.

According to the most recent census in 2007, most people have a Christian background, with a sizable Hindu (27.9%) and Muslim (6.3%) minority. Religion tends to split along ethnic lines with most Indigenous Fijians being Christian and most Indo-Fijians being mostly Hindu or in some cases, Muslim.
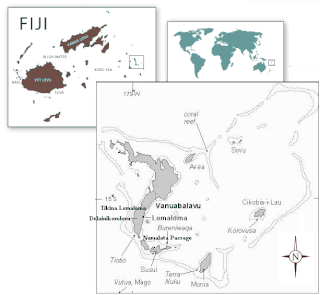
Turaga na Rasau is a traditional Fijian chiefly title of the Lau Islands. Prior to Fiji's colonial days, Fiji had many different Vanua with their own Paramount Chieftain which exercised no authority over the other; a saying from the island of Kadavu aptly summarises it "Nomu Turaga o sega na noqu Turaga" or "Your Chief is not my Chief" also the people of Beqa Island were of a similar opinion saying "Qali Cuva Ki Lagi" or "Subject only to heaven" and would bow to no outside Chieftain, but at the turn of the 20th century aspects of the traditional social structure remained, but for administrative purposes three main Matanitu were solidified and formed as they were the dominant consolidated powers at the time being that of Kubuna, Burebasaga and Tovata. With regard to the Rasau while its traditional origins were in Kubuna on Bau the titles traditional authority in modern Fiji is now in Tovata, Lau in particular Lomaloma Tikina on the Island of Vanua Balavu.
The People of Paradise is a six-part documentary film series produced and presented by David Attenborough. The series exhibits the people and geography of Oceania; particularly, of Fiji and Tonga. BBC Television Service transmitted The People of Paradise in 1960.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Gene was the deadliest storm as well as the most damaging tropical cyclone of the 2007–08 South Pacific cyclone season east of 160ºE. RSMC Nadi monitored Gene as the 12th tropical disturbance, as well as the fourth tropical cyclone and the third severe tropical cyclone to form west of 160ºE during the 2007–08 South Pacific cyclone season. Gene was also recognised by RSMC Nadi as the fifth tropical cyclone and fourth severe tropical cyclone to form within the South Pacific Ocean during the 2007-08 season.
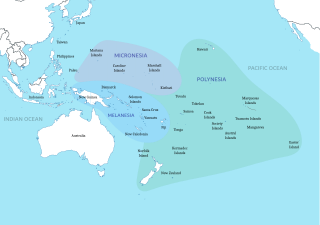
Polynesia is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in common, including linguistic relations, cultural practices, and traditional beliefs. In centuries past, they had a strong shared tradition of sailing and using stars to navigate at night.

Thomas Baker was a Methodist missionary in Fiji, known as being the only missionary in the archipelago to be killed and eaten, along with seven of his Fijian followers. The incident occurred in the Navosa Highlands of western Viti Levu in July 1867, and the rock used to kill Baker is still displayed in the village of Nabutatau. The soles of his leather sandals, which were also cooked by the cannibal tribe, are preserved at the Fiji Museum in Suva. Records show that Baker was killed and eaten as a result of him touching a chief's head, which is considered disrespectful in Fijian culture.
Kadavu Province is one of fourteen provinces of Fiji, and forms part of the Eastern Division, which also includes the provinces of Lau, Lomaiviti and Rotuma. Kadavu also belongs to the Burebasaga Confederacy, a hierarchy of chiefs from southern and western Fiji with Roko Tui Dreketi of Rewa as the paramount chief.
The 1953 Suva earthquake occurred on 14 September at 00:26 UTC near Suva, Fiji, just off the southeast shore of Viti Levu. This earthquake had an estimated magnitude of 6.8 and 6.4. The earthquake triggered a coral reef platform collapse and a submarine landslide that caused a tsunami. Eight people were reported killed.
In Fiji, Turaga na Roko Tui Bau is a vassal chief of the Vunivalu of Bau. From his seat at the residence of Naicobocobo, the Roko Tui Bau rules the Vusaratu chiefs and has relationships with the Roko Tui Dreketi, Ratu Mai Verata, Roko Tui Namata, Roko Tui Veikau, Tui Vuya and other members of Fiji's House of Chiefs.













