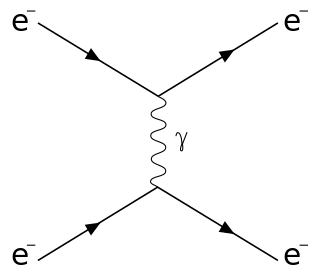
Scatter may refer to:
- Scattering, in physics, the study of collisions
- Statistical dispersion or scatter
- Scatter (modeling), a substance used in the building of dioramas and model railways
- Scatter, in computer programming, a parameter in network broadcasting
- Scatter (band), a Scottish improvisational music collective