
In geometry, the Schiffler point of a triangle is a triangle center, a point defined from the triangle that is equivariant under Euclidean transformations of the triangle. This point was first defined and investigated by Schiffler et al. (1985).

In geometry, the Schiffler point of a triangle is a triangle center, a point defined from the triangle that is equivariant under Euclidean transformations of the triangle. This point was first defined and investigated by Schiffler et al. (1985).
A triangle △ABC with the incenter I has its Schiffler point at the point of concurrence of the Euler lines of the four triangles △BCI, △CAI, △ABI, △ABC. Schiffler's theorem states that these four lines all meet at a single point. [1]
Trilinear coordinates for the Schiffler point are
or, equivalently,
where a, b, c denote the side lengths of triangle △ABC.

In geometry a quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon, having four edges (sides) and four corners (vertices). The word is derived from the Latin words quadri, a variant of four, and latus, meaning "side". It is also called a tetragon, derived from Greek "tetra" meaning "four" and "gon" meaning "corner" or "angle", in analogy to other polygons. Since "gon" means "angle", it is analogously called a quadrangle, or 4-angle. A quadrilateral with vertices , , and is sometimes denoted as .
In geometry, a tetrahedron, also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertices. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polyhedra.
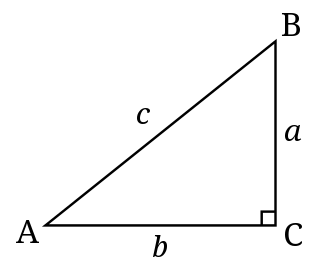
A right triangle or right-angled triangle, sometimes called an orthogonal triangle or rectangular triangle, is a triangle in which two sides are perpendicular, forming a right angle.

The orthocenter of a triangle, usually denoted by H, is the point where the three altitudes intersect. The orthocenter lies inside the triangle if and only if the triangle is acute. For a right triangle, the orthocenter coincides with the vertex at the right angle.

In geometry, the incircle or inscribed circle of a triangle is the largest circle that can be contained in the triangle; it touches the three sides. The center of the incircle is a triangle center called the triangle's incenter.

In Euclidean geometry, a cyclic quadrilateral or inscribed quadrilateral is a quadrilateral whose vertices all lie on a single circle. This circle is called the circumcircle or circumscribed circle, and the vertices are said to be concyclic. The center of the circle and its radius are called the circumcenter and the circumradius respectively. Other names for these quadrilaterals are concyclic quadrilateral and chordal quadrilateral, the latter since the sides of the quadrilateral are chords of the circumcircle. Usually the quadrilateral is assumed to be convex, but there are also crossed cyclic quadrilaterals. The formulas and properties given below are valid in the convex case.

In geometry, the Euler line, named after Leonhard Euler, is a line determined from any triangle that is not equilateral. It is a central line of the triangle, and it passes through several important points determined from the triangle, including the orthocenter, the circumcenter, the centroid, the Exeter point and the center of the nine-point circle of the triangle.

In geometry, the incenter of a triangle is a triangle center, a point defined for any triangle in a way that is independent of the triangle's placement or scale. The incenter may be equivalently defined as the point where the internal angle bisectors of the triangle cross, as the point equidistant from the triangle's sides, as the junction point of the medial axis and innermost point of the grassfire transform of the triangle, and as the center point of the inscribed circle of the triangle.

In geometry, a set of points are said to be concyclic if they lie on a common circle. A polygon whose vertices are concyclic is called a cyclic polygon, and the circle is called its circumscribing circle or circumcircle. All concyclic points are equidistant from the center of the circle.

In the geometry of triangles, the incircle and nine-point circle of a triangle are internally tangent to each other at the Feuerbach point of the triangle. The Feuerbach point is a triangle center, meaning that its definition does not depend on the placement and scale of the triangle. It is listed as X(11) in Clark Kimberling's Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers, and is named after Karl Wilhelm Feuerbach.

In mathematics, a cubic plane curve is a plane algebraic curve C defined by a cubic equation

In Euclidean geometry, the medial triangle or midpoint triangle of a triangle △ABC is the triangle with vertices at the midpoints of the triangle's sides AB, AC, BC. It is the n = 3 case of the midpoint polygon of a polygon with n sides. The medial triangle is not the same thing as the median triangle, which is the triangle whose sides have the same lengths as the medians of △ABC.
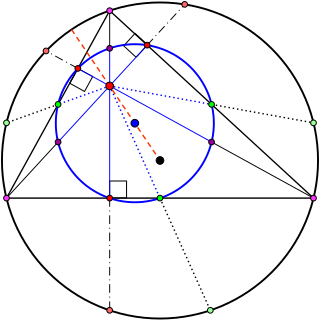
In geometry, the nine-point center is a triangle center, a point defined from a given triangle in a way that does not depend on the placement or scale of the triangle. It is so called because it is the center of the nine-point circle, a circle that passes through nine significant points of the triangle: the midpoints of the three edges, the feet of the three altitudes, and the points halfway between the orthocenter and each of the three vertices. The nine-point center is listed as point X(5) in Clark Kimberling's Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers.

In geometry, the mittenpunkt of a triangle is a triangle center: a point defined from the triangle that is invariant under Euclidean transformations of the triangle. It was identified in 1836 by Christian Heinrich von Nagel as the symmedian point of the excentral triangle of the given triangle.
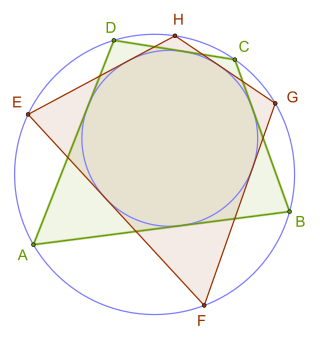
In Euclidean geometry, a bicentric quadrilateral is a convex quadrilateral that has both an incircle and a circumcircle. The radii and centers of these circles are called inradius and circumradius, and incenter and circumcenter respectively. From the definition it follows that bicentric quadrilaterals have all the properties of both tangential quadrilaterals and cyclic quadrilaterals. Other names for these quadrilaterals are chord-tangent quadrilateral and inscribed and circumscribed quadrilateral. It has also rarely been called a double circle quadrilateral and double scribed quadrilateral.
In Euclidean geometry, the Apollonius point is a triangle center designated as X(181) in Clark Kimberling's Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers (ETC). It is defined as the point of concurrence of the three line segments joining each vertex of the triangle to the points of tangency formed by the opposing excircle and a larger circle that is tangent to all three excircles.
In geometry, central lines are certain special straight lines that lie in the plane of a triangle. The special property that distinguishes a straight line as a central line is manifested via the equation of the line in trilinear coordinates. This special property is related to the concept of triangle center also. The concept of a central line was introduced by Clark Kimberling in a paper published in 1994.
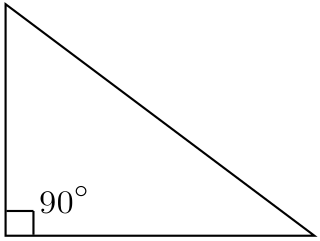
An acute triangle is a triangle with three acute angles. An obtuse triangle is a triangle with one obtuse angle and two acute angles. Since a triangle's angles must sum to 180° in Euclidean geometry, no Euclidean triangle can have more than one obtuse angle.
Kurt Schiffler was a German engineer, entrepreneur, inventor and amateur geometer.