Related Research Articles
The pound or pound-mass is a unit of mass used in British imperial and United States customary systems of measurement. Various definitions have been used; the most common today is the international avoirdupois pound, which is legally defined as exactly 0.45359237 kilograms, and which is divided into 16 avoirdupois ounces. The international standard symbol for the avoirdupois pound is lb; an alternative symbol is lbm, #, and ℔ or ″̶.

The ton is a unit of measure. It has a long history and has acquired a number of meanings and uses over the years. It is used principally as a unit of weight. Its original use as a measurement of volume has continued in the capacity of cargo ships and in terms such as the freight ton. Recent specialized uses include the ton as a measure of energy and for truck classification. It is also a colloquial term, "ton" is the heaviest unit of weight typically used in colloquial speech. It is also used informally to mean a large amount of something, material or not.

The shilling is a historical coin, and the name of a unit of modern currencies formerly used in the United Kingdom, Ireland, Australia, New Zealand and other British Commonwealth countries.

The schilling was the currency of Austria from 1925 to 1938 and from 1945 to 1999, and the circulating currency until 2002. The euro was introduced at a fixed parity of €1 = 13.7603 schilling to replace it. The schilling was divided into 100 groschen.
Long ton, also known as the imperial ton or displacement ton, is the name for the unit called the "ton" in the avoirdupois system of weights or Imperial system of measurements. It was standardised in the 13th century. It is used in the United Kingdom and several other Commonwealth of Nations countries alongside the mass-based metric tonne defined in 1799, as well as in the United States for bulk commodities.
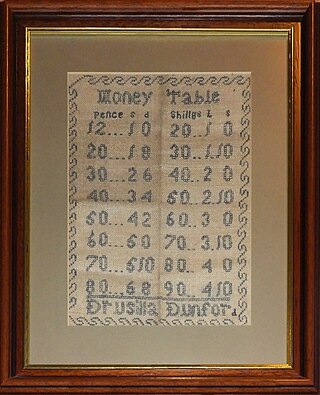
£sd is the popular name for the pre-decimal currencies once common throughout Europe, especially in the British Isles and hence in several countries of the British Empire and subsequently the Commonwealth. The abbreviation originates from the Latin currency denominations librae, solidi, and denarii. In the United Kingdom, these were referred to as pounds, shillings, and pence.
The pfennig or penny is a former German coin or note, which was the official currency from the 9th century until the introduction of the euro in 2002. While a valuable coin during the Middle Ages, it lost its value through the years and was the minor coin of the Mark currencies in the German Reich, West and East Germany, and the reunified Germany until the introduction of the euro. Pfennig was also the name of the subunit of the Danzig mark (1922–1923) and the Danzig gulden (1923–1939) in the Free City of Danzig.

Groschen a name for various coins, especially a silver coin used in various states of the Holy Roman Empire and other parts of Europe. The word is borrowed from the late Latin description of a tornose, a grossus denarius Turnosus, in English the "thick denarius of Tours". Groschen was frequently abbreviated in old documents to gl, whereby the second letter was not an l, but an abbreviation symbol; later it was written as Gr or g.
The apothecaries' system, or apothecaries' weights and measures, is a historical system of mass and volume units that were used by physicians and apothecaries for medical recipes and also sometimes by scientists. The English version of the system is closely related to the English troy system of weights, the pound and grain being exactly the same in both. It divides a pound into 12 ounces, an ounce into 8 drachms, and a drachm into 3 scruples of 20 grains each. This exact form of the system was used in the United Kingdom; in some of its former colonies, it survived well into the 20th century. The apothecaries' system of measures is a similar system of volume units based on the fluid ounce. For a long time, medical recipes were written in Latin, often using special symbols to denote weights and measures.

The Heller, abbreviation hlr, was a coin, originally valued at half a pfennig, that was issued in Switzerland and states of the Holy Roman Empire, surviving in some European countries until the 20th century.

The Lot was a unit of measurement of mass, which was mainly used in German-speaking states of the Holy Roman Empire and in Scandinavia.

The Vereinsthaler was a standard silver coin used in most German states and the Austrian Empire in the years before German unification.

The Conventionstaler or Konventionstaler, was a standard silver coin in Austrian Empire and the southern Germany states of the Holy Roman Empire from the mid-18th to early 19th-centuries. Its most famous example is the Maria Theresa thaler which is still minted today. The Conventionsgulden was equivalent to a 1⁄2Conventionsthaler.
The Austro-German Postal Union was a union of the postal systems of the Austrian Empire and the pre-Empire German states. The union was established on July 1, 1850. The administrative prerequisites were already provided by the German Zollverein established in 1834. On October 18, 1847, the representatives convened to the German Postal Conference in Dresden on a suggestion of Prussia and Austria. Not until 6 April 1850, Prussia and Austria, slowed by political circumstances, closed a contract establishing a German–Austrian Postal Association in Berlin.

The history of Saxon coinage or Meissen-Saxon coinage comprises three major periods: the high medieval regional Pfennig period, the late medieval Pfennig period and the Thaler period, which ended with the introduction of the Mark in 1871/72. Rich silver deposits, which were discovered near Freiberg after the middle of the 12th century, helped Saxony to a leading position in German coinage.

The Sachsenpfennig, sometimes called the Wendenpfennig or the Hochrandpfennig was a well-known coin of the pfennig type minted in the eastern part of the Stem Duchy of Saxony during the 10th and 11th centuries. It had an upturned perimeter and, next to the Otto Adelheid Pfennig was the most common pfennig type of its time. Sachsenpfennigs are the oldest coins minted in Saxony. Its different names represent a lack of clarity within mediaeval numismatics about the coin.
A Münzfuß is an historical term, used especially in the Holy Roman Empire, for an official minting or coinage standard that determines how many coins of a given type were to be struck from a specified unit of weight of precious metal. The Münzfuß, or Fuß ("foot") for short in numismatics), determined how much of a precious metal (fineness) a coin would have. Mintmaster Julian Eberhard Volckmar Claus defined the standard in his 1753 work, Kurzgefaßte Anleitung zum Probieren und Münzen, as follows: "The appropriate proportion of metals and the weight of the coin, measured according to their internal and external worth, or determined according to their quality, additives and fineness, number and weight, is called the Münzfuß."

The Stüber or Stüver was a small groschen coin that was minted in north-west Germany, especially in the territories of today's North Rhine-Westphalia and in the County of East Frisia roughly from the end of the 15th century to the early 19th century.
The schilling was the name of a coin in various historical European states and which gave its name to the English shilling. The schilling was a former currency in many of the German-speaking states of the Holy Roman Empire, including the Hanseatic city states of Hamburg and Lübeck, the March of Brandenburg, and the Duchies of Bavaria, Mecklenburg, and Württemberg. It was also used in Switzerland and in Austria, where silver schillings were introduced as recently as 1923.
The Carolingian pound was a unit of weight that emerged during the reign of Charlemagne. It served both as a trading weight and a coinage weight. It had a mass of about 408 g and was introduced in as part of Charlemagne's monetary reform around AD 793/94. This stipulated that 240 denarii were to be minted from one pound weight of silver.