
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of pain sensation. In the context of surgery, a local anesthetic creates an absence of pain in a specific location of the body without a loss of consciousness, as opposed to a general anesthetic. When it is used on specific nerve pathways, paralysis also can be achieved.

A ventilator is a machine that provides mechanical ventilation by moving breathable air into and out of the lungs, to deliver breaths to a patient who is physically unable to breathe, or breathing insufficiently. Ventilators are computerized microprocessor-controlled machines, but patients can also be ventilated with a simple, hand-operated bag valve mask. Ventilators are chiefly used in intensive-care medicine, home care, and emergency medicine and in anesthesiology.
Medical fetishism refers to a number of sexual fetishes in which participants derive sexual pleasure from medical scenarios including objects, practices, environments, and situations of a medical or clinical nature. In sexual roleplay, a hospital or medical scene involves the sex partners assuming the roles of doctors, nurses, surgeons and patients to act out specific or general medical fetishes. Medical fantasy is a genre in pornography, though the fantasy may not necessarily involve pornography or sexual activity.

Nasogastric intubation is a medical process involving the insertion of a plastic tube through the nose, past the throat, and down into the stomach. Orogastric intubation is a similar process involving the insertion of a plastic tube through the mouth. Abraham Louis Levin invented the NG tube. Nasogastric tube is also known as Ryle's tube in Commonwealth countries, after John Alfred Ryle.
The year 1890 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
Rubber band ligation (RBL) is an outpatient treatment for internal hemorrhoids of any grade. There are several different devices a physician may use to perform the procedure, including the traditional metal devices, endoscopic banding, and the CRH O'Regan System.

An anesthetic or anaesthetic is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into two broad classes: general anesthetics, which result in a reversible loss of consciousness, and local anesthetics, which cause a reversible loss of sensation for a limited region of the body without necessarily affecting consciousness.

A laryngeal mask airway (LMA), also known as laryngeal mask, is a medical device that keeps a patient's airway open during anaesthesia or while they are unconscious. It is a type of supraglottic airway device. They are most commonly used by anaesthetists to channel oxygen or inhalational anaesthetic to the lungs during surgery and in the pre-hospital setting for unconscious patients.
A breathing mask is a mask that covers the mouth, and usually other parts of the face or head, designed to direct the wearer's breath to and/or from a particular apparatus. It may mean, or be part of, one of these:
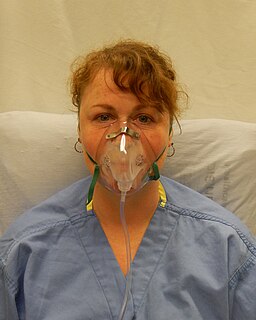
An oxygen mask provides a method to transfer breathing oxygen gas from a storage tank to the lungs. Oxygen masks may cover only the nose and mouth or the entire face. They may be made of plastic, silicone, or rubber. In certain circumstances, oxygen may be delivered via a nasal cannula instead of a mask.

An inhalational anesthetic is a chemical compound possessing general anesthetic properties that can be delivered via inhalation. They are administered through a face mask, laryngeal mask airway or tracheal tube connected to an anesthetic vaporiser and an anesthetic delivery system. Agents of significant contemporary clinical interest include volatile anesthetic agents such as isoflurane, sevoflurane and desflurane, as well as certain anesthetic gases such as nitrous oxide and xenon.

A bag valve mask (BVM), sometimes known by the proprietary name Ambu bag or generically as a manual resuscitator or "self-inflating bag", is a hand-held device commonly used to provide positive pressure ventilation to patients who are not breathing or not breathing adequately. The device is a required part of resuscitation kits for trained professionals in out-of-hospital settings (such as ambulance crews) and is also frequently used in hospitals as part of standard equipment found on a crash cart, in emergency rooms or other critical care settings. Underscoring the frequency and prominence of BVM use in the United States, the American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiac Care recommend that "all healthcare providers should be familiar with the use of the bag-mask device." Manual resuscitators are also used within the hospital for temporary ventilation of patients dependent on mechanical ventilators when the mechanical ventilator needs to be examined for possible malfunction or when ventilator-dependent patients are transported within the hospital. Two principal types of manual resuscitators exist; one version is self-filling with air, although additional oxygen (O2) can be added but is not necessary for the device to function. The other principal type of manual resuscitator (flow-inflation) is heavily used in non-emergency applications in the operating room to ventilate patients during anesthesia induction and recovery.

Methoxyflurane, sold under the brand name Penthrox among others, is an inhaled medication primarily used to reduce pain following trauma. It may also be used for short episodes of pain as a result of medical procedures. Onset of pain relief is rapid and of a short duration. Use is only recommended with direct medical supervision.

An anesthetic technician is an allied healthcare worker who performs a patient care role predominantly assisting with the administration and monitoring of anesthesia and has an extensive knowledge of anesthesia techniques, instruments, supplies and technology.

Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is a form of positive airway pressure (PAP) ventilation in which a constant level of pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is continuously applied to the upper respiratory tract of a person. The application of positive pressure may be intended to prevent upper airway collapse, as occurs in obstructive sleep apnea, or to reduce the work of breathing in conditions such as acute decompensated heart failure. CPAP therapy is highly effective for managing obstructive sleep apnea. Compliance and acceptance of use of CPAP therapy can be a limiting factor, with 8% of people stopping use after the first night and 50% within the first year.
Curt Theodor Schimmelbusch was a German physician and pathologist who invented the Schimmelbusch mask, for the safe delivery of anaesthetics to surgical patients. He was also a key figure in the development of mechanical methods of sterilisation and disinfection for surgical procedures, on which his Anleitung zur aseptischen Wundbehandlung was considered a seminal work.
Following is a list of instruments used in the practice of anesthesia
A breathing tube is a device or tool that can serve as a conduit for breathing. Various types of breathing tubes are available for different specific applications.

An anesthetic vaporizer or anaesthetic vaporiser is a device generally attached to an anesthetic machine which delivers a given concentration of a volatile anesthetic agent. It works by controlling the vaporization of anesthetic agents from liquid, and then accurately controlling the concentration in which these are added to the fresh gas flow. The design of these devices takes account of varying: ambient temperature, fresh gas flow, and agent vapor pressure.

The nipple tattoo, or tittoo as it is occasionally known, is a body trend which gained widespread recognition in 2013. It is a type of tattoo which appears on the areola and is semi-permanent.













