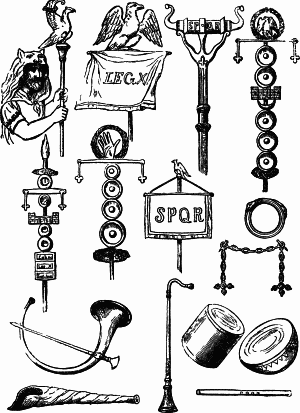A gladiator was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gladiators were volunteers who risked their lives and their legal and social standing by appearing in the arena. Most were despised as slaves, schooled under harsh conditions, socially marginalized, and segregated even in death.

Gladius is a Latin word properly referring to the type of sword that was used by ancient Roman foot soldiers starting from the 3rd century BC and until the 3rd century AD. Linguistically, within Latin, the word also came to mean "sword", regardless of the type used.

The murmillo was a type of gladiator during the Roman Imperial age. The murmillo-class gladiator was adopted in the early Imperial period to replace the early Gallus, named after the warriors of Gaul. As the Gauls inhabiting Italy had become well integrated with the Romans by the time of the reign of Augustus, it became undesirable to portray them as enemy outsiders; the Gallus-class gladiator thus had to be retired.

The falx was a weapon with a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge used by the Thracians and Dacians. The name was later applied to a siege hook used by the Romans.

A secutor was a class of gladiator in ancient Rome. Thought to have originated around 50 AD, the secutor was armed similarly to the Murmillo gladiator and like the Murmillo, was protected by a heavy shield. A secutor usually carried a short sword, a gladius, or a dagger. The secutor was specially trained to fight a retiarius, a type of lightly armoured gladiator armed with a trident and net.

A retiarius was a Roman gladiator who fought with equipment styled on that of a fisherman: a weighted net, a three-pointed trident, and a dagger (pugio). The retiarius was lightly armoured, wearing an arm guard (manica) and a shoulder guard (galerus). Typically, his clothing consisted only of a loincloth (subligaculum) held in place by a wide belt, or of a short tunic with light padding. He wore no head protection or footwear.

A khanjali, also known as a kindjal, is a double-edged dagger used since antiquity in the Caucasus. The shape of the weapon is similar to that of the ancient Roman gladius, the Scottish dirk and the ancient Greek xiphos. Inhabitants of Caucasus have used the Kindjal as a secondary weapon since the 18th century.

Gladiator is a 2000 historical epic film directed by Ridley Scott and written by David Franzoni, John Logan, and William Nicholson. It stars Russell Crowe, Joaquin Phoenix, Connie Nielsen, Oliver Reed, Derek Jacobi, Djimon Hounsou and Richard Harris.
Roman military personal equipment was produced in large numbers to established patterns, and used in an established manner. These standard patterns and uses were called the res militaris or disciplina. Its regular practice during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire led to military excellence and victory. The equipment gave the Romans a very distinct advantage over their barbarian enemies, especially so in the case of armour. This does not mean that every Roman soldier had better equipment than the richer men among his opponents. Roman equipment was not of a better quality than that used by the majority of Rome's adversaries. Other historians and writers have stated that the Roman army's need for large quantities of "mass produced" equipment after the so-called "Marian Reforms" and subsequent civil wars led to a decline in the quality of Roman equipment compared to the earlier Republican era:
The production of these kinds of helmets of Italic tradition decreased in quality because of the demands of equipping huge armies, especially during civil wars...The bad quality of these helmets is recorded by the sources describing how sometimes they were covered by wicker protections, like those of Pompeius' soldiers during the siege of Dyrrachium in 48 BC, which were seriously damaged by the missiles of Caesar's slingers and archers.
It would appear that armour quality suffered at times when mass production methods were being used to meet the increased demand which was very high the reduced size cuirasses would also have been quicker and cheaper to produce, which may have been a deciding factor at times of financial crisis, or where large bodies of men were required to be mobilized at short notice, possibly reflected in the poor-quality, mass produced iron helmets of Imperial Italic type C, as found, for example, in the River Po at Cremona, associated with the Civil Wars of AD 69 AD; Russell Robinson, 1975, 67
Up until then, the quality of helmets had been fairly consistent and the bowls well decorated and finished. However, after the Marian Reforms, with their resultant influx of the poorest citizens into the army, there must inevitably have been a massive demand for cheaper equipment, a situation which can only have been exacerbated by the Civil Wars...
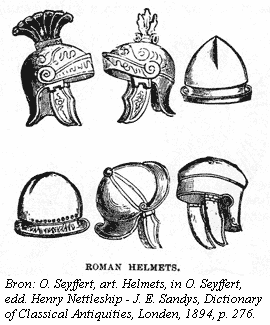
A galea was a Roman soldier's helmet. Some gladiators, specifically myrmillones, also wore bronze galeae with face masks and decorations, often a fish on its crest. The exact form or design of the helmet varied significantly over time, between differing unit types, and also between individual examples – pre-industrial production was by hand – so it is not certain to what degree there was any standardization even under the Roman Empire.

A hoplomachus was a type of gladiator in ancient Rome, armed to resemble a Greek hoplite. The hoplomachus would wear a bronze helmet, a manica on his right arm, loincloth (subligaculum), heavy padding on his legs, and a pair of high greaves reaching to mid-thigh. His weapons were the spear and a short sword. He was often pitted against the murmillo, perhaps as a re-enactment of Rome's wars in Greece and the Hellenistic East. The name hoplomachus means 'armored fighter'. The small, round shield was as much a weapon as a sword or spear, not unlike the original hoplites, who used it primarily for defensive purposes, but also employed it in their charges, using it to ram their opponents at the onset of a fight. They wore no shoes so the sand would chafe their feet, presenting them a greater challenge.

The sica is a short sword or large dagger of ancient Illyrians, Thracians, and Dacians; it was also used in Ancient Rome. It is a shorter form of the falx, and the root of the word is the same as the modern sickle.
The laquearius, laquerarius, or laqueator was a class of Roman gladiator that fought with a lasso or noose (laqueus) in one hand and a poniard or sword in the other. The laquearius appeared late in the history of the Roman games. They may have made up a full-fledged gladiator class that fought actual bouts in the arena. If this was the case, the snarer likely followed the same tactics as the retiarius, a gladiator who wielded a throwing net and trident. Such combat-oriented laquearii fought by attempting to snare their adversaries with the lasso to allow for a follow-up strike from the blade. The snarer's armour was probably similar to that of the retiarius; it consisted mainly of a retiarius armguard worn over the left shoulder. Another possibility is that the laquearius was a kind of paegniarius, or clown. These men fought mock battles in the arena as comic relief between real matches.

A Samnite was a Roman gladiator who fought with equipment styled on that of a warrior from Samnium: a short sword (gladius), a rectangular shield (scutum), a greave (ocrea), and a helmet. Warriors armed in such a way were the earliest gladiators in the Roman games. They appeared in Rome shortly after the defeat of Samnium in the 4th century BC, apparently adopted from the victory celebrations of Rome's allies in Campania. By arming low-status gladiators in the manner of a defeated foe, Romans mocked the Samnites and appropriated martial elements of their culture.

Major innovations in the history of weapons have included the adoption of different materials – from stone and wood to different metals, and modern synthetic materials such as plastics – and the developments of different weapon styles either to fit the terrain or to support or counteract different battlefield tactics and defensive equipment.

Illyrian weaponry played an important role in the makeup of Illyrian armies and in conflicts involving the Illyrians. Of all the ancients sources the most important and abundant writings are those of Ennius, a Roman poet of Messapian origin. Weapons of all sorts were also placed intact in the graves of Illyrian warriors and provide a detailed picture for archaeologists on the distribution and development of Illyrian weaponry.
The dimachaeri were a type of Roman gladiator that fought with two swords. The name is a borrowing into Latin of Ancient Greek διμάχαιρος dimákhairos 'bearing two knives'.
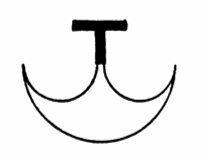
The arbelas was a type of ancient Roman gladiator. The word is a hapax legomenon, occurring only in the Oneirocritica of Artemidorus, a Greek work on dream interpretation that discusses the symbolism of various gladiator types. It may be related to the Greek word arbelos (ἄρβηλος), a cobbler's semicircular blade used to cut leather similar to an ulu.

A crupellarius was a type of heavy armored gladiator during the Roman Imperial age, whose origin was Gaul.