
Darlington is a market and industrial town in County Durham, England. It is the main administrative centre of the unitary authority Borough of Darlington. The borough is a constituent member of the devolved Tees Valley area.

Yarm, also referred to as Yarm-on-Tees, is a market town and civil parish in the Borough of Stockton-on-Tees, North Yorkshire, England. It is in Teesdale with a town centre on a small meander of the River Tees. To the south-east, it extends to the River Leven, to the south it extends into the Kirklevington.
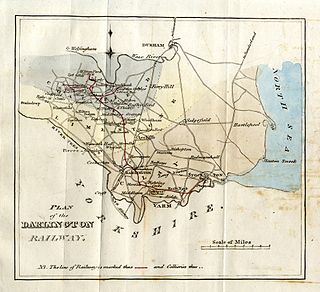
The Stockton and Darlington Railway (S&DR) was a railway company that operated in north-east England from 1825 to 1863. The world's first public railway to use steam locomotives, its first line connected collieries near Shildon with Darlington and Stockton in County Durham, and was officially opened on 27 September 1825. The movement of coal to ships rapidly became a lucrative business, and the line was soon extended to a new port at Middlesbrough. While coal waggons were hauled by steam locomotives from the start, passengers were carried in coaches drawn by horses until carriages hauled by steam locomotives were introduced in 1833.

The A66 is a major road in Northern England, which in part follows the course of the Roman road from Scotch Corner to Penrith. It runs from east of Middlesbrough in North Yorkshire to Workington in Cumbria. The road has been progressively improved with dual carriageway sections, but with stretches of single carriageway road. The road is set to be completely dualled between Scotch Corner and Penrith, with a £1.3 billion scheme being announced in March 2024.

Tees Valley is a combined authority area in North East England, around the lower River Tees. The area is not a geographical valley; the local term for the valley is Teesdale. The combined authority covers five council areas: Darlington, Hartlepool, Middlesbrough, Redcar and Cleveland and Stockton-on-Tees.

Merrybent is a linear village in the civil parish of Low Coniscliffe and Merrybent in County Durham, in England. It is situated on the A67 road to the west of Darlington, a short distance to the north of the River Tees and the Teesdale Way. At the beginning of the 20th century there were hardly any buildings here, and its main feature at that time was Merrybent Nurseries with its many glasshouses. The nursery was cut through by the A1 road in the 1960s; at this point it runs on the trackbed of the old Merrybent railway. The village is now a settlement of modern housing.

Stagecoach North East operates both local and regional bus services in County Durham, Cumbria, Northumberland, North Yorkshire and Tyne and Wear, England. It is a subsidiary of the Stagecoach Group, which operates bus, coach, rail and tram services across the United Kingdom.

Newton Aycliffe is a railway station on the Tees Valley Line, which runs between Bishop Auckland and Saltburn via Darlington. The station, situated 7 miles 4 chains (11.3 km) north-west of Darlington, serves the town of Newton Aycliffe in County Durham, England. It is owned by Network Rail and managed by Northern Trains.

Eaglescliffe is a railway station on the Tees Valley Line, which runs between Bishop Auckland and Saltburn via Darlington. The station, situated 8 miles 63 chains east of Darlington, serves the village of Eaglescliffe, Borough of Stockton-on-Tees in County Durham, England. It is owned by Network Rail and managed by Northern Trains.

The Borough of Darlington is a unitary authority area with borough status in County Durham, England. Since 1997 Darlington Borough Council has been a unitary authority; it is independent from Durham County Council. It is named after its largest settlement, the town of Darlington, where the council is based. The borough also includes a rural area surrounding the town which contains several villages. The population of the borough at the 2021 census was 107,800, of which over 86% (93,015) lived in the built-up area of Darlington itself.

Hopetown Darlington, previously known as Head of Steam and formerly known as the Darlington Railway Centre and Museum, is a railway museum located on the 1825 route of the Stockton and Darlington Railway, which was the world's first steam-powered passenger railway. It is based inside the station building at the North Road railway station. Its exhibits are devoted to the area formerly served by the North Eastern Railway with a particular focus on the Stockton & Darlington Railway and the railway industry of Darlington. In 2022, plans were submitted to expand the museum as part of the Railway Heritage Quarter. In December 2023, the museum temporarily closed its doors to undergo a £35 million redevelopment.

The Tees Valley Railway was an 8+3⁄4-mile (14.1 km) branch railway line that ran between Barnard Castle on the South Durham & Lancashire Union Railway line between Bishop Auckland and Kirkby Stephen East, and Middleton-in-Teesdale via three intermediate stations Cotherstone, Romaldkirk and Mickleton.

The Teesside Steelworks was a large steelworks that formed a continuous stretch along the south bank of the River Tees from the towns of Middlesbrough to Redcar in North Yorkshire, England. At its height there were 91 blast furnaces within a 10-mile radius of the area. By the end of the 1970s there was only one left on Teesside. Opened in 1979 and located near the mouth of the River Tees, the Redcar blast furnace was the second largest in Europe.

John Marley was an English mining engineer from Darlington who together with ironmaster John Vaughan made the "commercial discovery" of the Cleveland Ironstone Formation, the basis of the wealth of their company Bolckow Vaughan and the industrial growth of Middlesbrough. He was an effective leader of engineering operations at Bolckow Vaughan's mines and collieries. He ended his career as a wealthy independent mine-owner and president of the North of England Institute of Mining and Mechanical Engineers (NEIMME).

Ferryhill railway station was located in Ferryhill, County Durham, Northeast England. It was located on what became the East Coast Main Line between Darlington and Durham, close to the junctions with several former branches, including the extant freight-only Stillington Line to Norton-on-Tees and Stockton.

The Darlington and Barnard Castle Railway, was an east–west railway line that connected Darlington and Barnard Castle in County Durham, England. Besides the main running line, it had two branches that headed south into Yorkshire that were only used for freight. The whole system opened up by July 1856 and was closed completely by 1966. The former Merrybent freight branch is now used as part of the A1(M) road that bypasses to the west of Darlington.

Yarm Viaduct is a railway viaduct carrying the railways above the town of Yarm in North Yorkshire, England. It crosses the River Tees which forms the boundary between North Yorkshire and County Durham. The railway runs between Northallerton and Eaglescliffe, and was opened in 1852 as part of the extension of the Leeds Northern Railway to Stockton-on-Tees. The line and viaduct are currently owned and maintained by Network Rail and carries passenger traffic for TransPennine Express and Grand Central train operating companies. It also sees a variety of freight traffic.

Blackwell Bridge is a masonry road bridge spanning the River Tees between County Durham and North Yorkshire, in Northern England. The bridge was built in 1832, and widened in 1961. It carries the A66 road, which stems from the A66(M) spur off the A1(M) motorway. It used to be the main route north on the A1 until a bypass was opened in 1965.


















