
Scott G. Borg is an American geologist and civil servant. Since 1 September 2017 he has been the Deputy Assistant Director of the Directorate for Geosciences at the United States' National Science Foundation (NSF). [1] [2]

Scott G. Borg is an American geologist and civil servant. Since 1 September 2017 he has been the Deputy Assistant Director of the Directorate for Geosciences at the United States' National Science Foundation (NSF). [1] [2]
Borg graduated from Pomona College with a B.A. in geology, and earned M.S. and Ph.D. degrees from Arizona State University, where his doctoral dissertation was titled Granitoids of Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica (Tectonics, Neodymium-isotopes, Geochemistry, Petrology, Strontium-isotopes). [3] [4]
He began his career as a researcher at the University of California at Berkeley. [3] He later worked for the United States Department of Energy, and subsequently joined the staff of the National Science Foundation. [3] [5] Between 2003 and 2016 he was director of the Division of Antarctic Sciences at the National Science Foundation, [5] and in 2016-17 he served as the acting Section Head for Antarctic Infrastructure and Logistics (AIL) within the National Science Foundation Division of Polar Programs. [3] [6] In 2017, he began serving as associate director for geosciences at the National Science Foundation. [3] [7] [8]
Borg has participated in a total of six research expeditions to Antarctica, four of which he has led. [3] During a 1978–1979 expedition in which he participated, the Sagehen Nunataks were first visited, receiving their name from the Pomona Sagehens, athletic moniker of Borg's alma mater Pomona College. [9] During the same expedition, Borg named Tongue Peak, choosing the name from a tongue-shaped moraine on the peak. [10]
In 1994, Borg Bastion, the summit on Johns Hopkins Ridge, was named in his honor. [11] Borg has received the Samuel J. Heyman Medal from the Partnership for Public Service and been decorated with the Presidential Rank Award of Distinguished Executive. [6] [12] In 2014, United States Representative Gerald Connolly read a statement of recognition into the Congressional Record in which he credited Borg with overseeing "the development of clean drilling technology that retrieved the first-ever pure water samples from an Antarctic lake a half mile below the surface of ice sheet ... [which] may enable researchers to understand what types of life can survive on other worlds". [12]

The U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States federal government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National Institutes of Health. With an annual budget of about $9.9 billion, the NSF funds approximately 25% of all federally supported basic research conducted by the United States' colleges and universities. In some fields, such as mathematics, computer science, economics, and the social sciences, the NSF is the major source of federal backing.

Ross Island is an island in Antarctica lying on the east side of McMurdo Sound and extending 43 nautical miles from Cape Bird in the north to Cape Armitage in the south, and a similar distance from Cape Royds in the west to Cape Crozier in the east. The island is entirely volcanic. Mount Erebus, 3,795 metres (12,451 ft), near the center, is an active volcano. Mount Terror, 3,230 metres (10,600 ft) about 20 nautical miles eastward, is an extinct volcano. Mount Bird rises to 1,765 metres (5,791 ft) just south of Cape Bird. Ross Island lies within the boundary of Ross Dependency, an area of Antarctica claimed by New Zealand.

Mawson Station, commonly called Mawson, is one of three permanent bases and research outposts in Antarctica managed by the Australian Antarctic Division (AAD). Mawson lies in Holme Bay in Mac. Robertson Land, East Antarctica in the Australian Antarctic Territory, a territory claimed by Australia. Established in 1954, Mawson is Australia's oldest Antarctic station and the oldest continuously inhabited Antarctic station south of the Antarctic Circle. It houses approximately 20 personnel over winter and up to 53 in summer.

Mount Terror is an extinct volcano about 3,230 metres (10,600 ft) high on Ross Island, Antarctica, about 20 nautical miles eastward of Mount Erebus. Mount Terror was named in 1841 by polar explorer Sir James Clark Ross for his second ship, HMS Terror. The captain of Terror was Francis Crozier, a close friend of Ross for whom the nearby Cape Crozier is named.

The McMurdo Sound is a sound in Antarctica, known as the southernmost passable body of water in the world, located approximately 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) from the South Pole.

The Leverett Glacier is about 50 nautical miles (90 km) long and 3 to 4 nautical miles wide, flowing from the Antarctic Plateau to the south end of the Ross Ice Shelf through the Queen Maud Mountains. It is an important part of the South Pole Traverse from McMurdo Station to the Admundson–Scott South Pole Station, providing a route for tractors to climb from the ice shelf through the Transantarctic Mountains to the polar plateau.

The United States Antarctic Program is an organization of the United States government which has a presence in the Antarctica continent. Founded in 1959, the USAP manages all U.S. scientific research and related logistics in Antarctica as well as aboard ships in the Southern Ocean.

The Taylor Glacier is a glacier in Antarctica about 35 nautical miles long, flowing from the plateau of Victoria Land into the western end of Taylor Valley, north of the Kukri Hills. It flows to the south of the Asgard Range. The middle part of the glacier is bounded on the north by the Inland Forts and on the south by Beacon Valley.
Operation Deep Freeze is codename for a series of United States missions to Antarctica, beginning with "Operation Deep Freeze I" in 1955–56, followed by "Operation Deep Freeze II", "Operation Deep Freeze III", and so on.. Given the continuing and constant US presence in Antarctica since that date, "Operation Deep Freeze" has come to be used as a general term for US operations in that continent, and in particular for the regular missions to resupply US Antarctic bases, coordinated by the United States military. Task Force 199 was involved.

Lambert Glacier is a major glacier in East Antarctica. At about 80 km (50 mi) wide, over 400 km (250 mi) long, and about 2,500 m (8,200 ft) deep, it is the world's largest glacier. It drains 8% of the Antarctic ice sheet to the east and south of the Prince Charles Mountains and flows northward to the Amery Ice Shelf. It flows in part of Lambert Graben and exits the continent at Prydz Bay.
The Napier Mountains are a group of close set peaks, the highest being Mount Elkins, at about 2,300 meters above sea level. This mountain range is located in Enderby Land, in the claimed Australian Antarctic Territory, East Antarctica.
The Scott Mountains are a large number of isolated peaks lying south of Amundsen Bay in Enderby Land of East Antarctica, Antarctica. Discovered on 13 January 1930 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Sir Douglas Mawson. He named the feature Scott Range after Captain Robert Falcon Scott, Royal Navy. The term mountains is considered more appropriate because of the isolation of its individual features.

Snow Hill Island is an almost completely snowcapped island, 33 km (21 mi) long and 12 km (7.5 mi) wide, lying off the east coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. It is separated from James Ross Island to the north-east by Admiralty Sound and from Seymour Island to the north by Picnic Passage. It is one of several islands around the peninsula known as Graham Land, which is closer to Chile, Argentina and South America than any other part of the Antarctic continent.
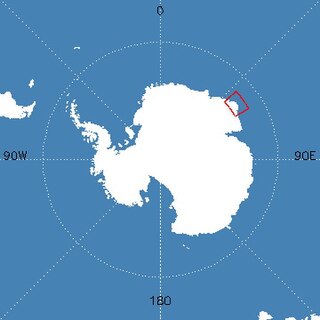
Mount Elkins, also known as Jökelen is a dark, steep-sided mountain with three major peaks, the highest 2,300 meters (7,500 ft) above sea level, in the Napier Mountains of Enderby Land. Enderby Land is part of East Antarctica and is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory. The mountain was named after Terence James Elkins, an ionospheric physicist with the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions at Mawson Station in 1960.

Mount Friesland is a mountain rising to 1,700.2 metres (5,578 ft) in the homonymous Friesland Ridge, one of the two summits of Tangra Mountains and Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica along with neighbouring St. Boris Peak. Its north rib is connected to Pliska Ridge by Nesebar Gap on the west, and to Bowles Ridge by Wörner Gap on the north. On the east, Mount Friesland is connected to Presian Ridge and further on to Catalunyan Saddle and Lyaskovets Peak. On the south-southwest, it is connected by a short saddle to ‘The Synagogue’ a sharp-peaked rock-cored ice formation abutting St. Boris Peak. The peak is heavily glaciated and crevassed, surmounting Huntress Glacier to the west, Perunika Glacier to the north-northwest, Huron Glacier to the northeast and Macy Glacier to the southeast. The local weather is notoriously unpleasant and challenging; according to the seasoned Antarctic mountaineer Damien Gildea who climbed in the area, 'just about the worst weather in the world'.
The Colwell Massif is a rugged rock massif, about 4 nautical miles long, rising to 2,635 metres (8,645 ft) between Palais Glacier, Ferrar Glacier, and Rotunda Glacier, in the Royal Society Range, Victoria Land, Antarctica.
The Mawson Glacier is a large glacier on the east coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica, descending eastward from the Antarctic Plateau to the north of Trinity Nunatak and the Kirkwood Range, to enter the Ross Sea, where it forms the Nordenskjöld Ice Tongue. The glacier was first mapped by the British Antarctic Expedition (1907–09) and named for Douglas Mawson, the expedition physicist, who later led two other Antarctic expeditions, 1911–14, and 1929–31.
Ravens Mountains is a symmetrical group of mountains on the west side of Hughes Basin in Britannia Range, Antarctica. The mountains are 12 nautical miles long and rise to 2,130 metres (6,990 ft) in Doll Peak.
While crime in Antarctica is relatively rare, isolation and boredom affect certain people there negatively and may lead to crime. Alcoholism is a known problem on the continent and has led to fights and indecent exposure. Other types of crime that have occurred in Antarctica include illicit drug use, torturing and killing wildlife, racing motorbikes through environmentally sensitive areas, assault with a deadly weapon, attempted murder and arson. Sexual harassment also has been reported.