Related Research Articles

Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjacent islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. To the south-east, Scotland has its only land border, which is 96 miles (154 km) long and shared with England; the country is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the north-east and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. The population in 2022 was 5,439,842. Edinburgh is the capital and Glasgow is the most populous of the cities of Scotland.
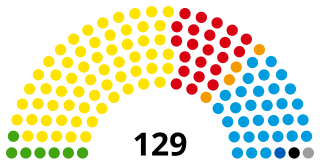
The Scottish Parliament is the unicameral legislature of Scotland. Located in the Holyrood area of the capital city, Edinburgh, it is frequently referred to by the metonym Holyrood. The Parliament is a democratically elected body comprising 129 members known as Members of the Scottish Parliament (MSPs), elected for five-year terms under the regionalised form of Additional-member system (MMP): 73 MSPs represent individual geographical constituencies elected by the plurality (first-past-the-post) system, while a further 56 are returned as list members from eight additional member regions. Each region elects seven party-list MSPs. Each region elects 15 to 17 MSPs in total. The most recent general election to the Parliament was held on 6 May 2021, with the Scottish National Party winning a plurality.

Scottish independence is the idea of Scotland regaining its independence and once again becoming a sovereign state, independent from the United Kingdom. The term Scottish independence refers to the political movement that is campaigning to bring it about.

The politics of Scotland operate within the constitution of the United Kingdom, of which Scotland is a country. Scotland is a democracy, being represented in both the Scottish Parliament and the Parliament of the United Kingdom since the Scotland Act 1998. Most executive power is exercised by the Scottish Government, led by the first minister of Scotland, the head of government in a multi-party system. The judiciary of Scotland, dealing with Scots law, is independent of the legislature and the Scottish Government, and is headed by the Lord Advocate who is the principal legal adviser to the Scottish Government. Scots law is primarily determined by the Scottish Parliament. The Scottish Government shares limited executive powers, notably over reserved matters, with the Scotland Office, a British government department led by the Secretary of State for Scotland.

The Scottish Government is the executive arm of the devolved government of Scotland. It was formed in 1999 as the Scottish Executive following the 1997 referendum on Scottish devolution. It has been described as one of the most powerful devolved governments globally, with full legislative control over the economy, education, healthcare, justice and the legal system, rural affairs, housing, the crown estate, the environment, the fire service, equal opportunities, the transportation network, and tax, amongst others.

Wendy Alexander is a retired Scottish politician and the former Member of the Scottish Parliament (MSP) for Paisley North. She held various Scottish Government cabinet posts and was the Leader of the Scottish Labour Party from 2007 to 2008. In June 2008, the Scottish Parliament's standards committee ruled that Wendy Alexander broke parliament rules by failing to register donations on her MSPs' register of interests. Wendy Alexander quit as Scottish Labour leader. In 2010–2011 she convened the Scotland Bill Committee on financial powers of the Scottish Parliament.

Unionism in Scotland is a political movement which favours the continuation of the political union between Scotland and the other countries of the United Kingdom, and hence is opposed to Scottish independence. Scotland is one of four countries of the United Kingdom which has its own devolved government and Scottish Parliament, as well as representation in the UK Parliament. There are many strands of political Unionism in Scotland, some of which have ties to Unionism and Loyalism in Northern Ireland. The two main political parties in the UK — the Conservatives and Labour — both support Scotland remaining part of the UK.

A devolved English parliament is a proposed institution that would give separate decision-making powers to representatives for voters in England, similar to the representation given by the Senedd, the Scottish Parliament and the Northern Ireland Assembly. A devolved English parliament is an issue in the politics of the United Kingdom.

British national identity is a term referring to the sense of national identity, as embodied in the shared and characteristic culture, languages and traditions, of the British people. It comprises the claimed qualities that bind and distinguish the British people and form the basis of their unity and identity, and the expressions of British culture—such as habits, behaviours, or symbols—that have a common, familiar or iconic quality readily identifiable with the United Kingdom. Dialogue about the legitimacy and authenticity of Britishness is intrinsically tied with power relations and politics; in terms of nationhood and belonging, expressing or recognising one's Britishness provokes a range of responses and attitudes, such as advocacy, indifference, or rejection.

The economy of Scotland is an open mixed economy, mainly services based, which is the second largest economy amongst the countries of the United Kingdom. It had an estimated nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of £218.0 billion in 2023, including oil and gas extraction in the country's continental shelf region. Since the Acts of Union 1707, Scotland's economy has been closely aligned with the economy of the rest of the United Kingdom (UK), and England has historically been its main trading partner. Scotland conducts the majority of its trade within the UK: in 2017, Scotland's exports totalled £81.4 billion, of which £48.9 billion (60%) was within the UK, £14.9 billion with the European Union (EU), and £17.6 billion with other parts of the world. Scotland's imports meanwhile totalled £94.4 billion including intra-UK trade leaving Scotland with a trade deficit of £10.4 billion in 2017.

NHS Scotland, sometimes styled NHSScotland, is the publicly–funded healthcare system in Scotland and one of the four systems that make up the National Health Service in the United Kingdom. It operates 14 territorial NHS boards across Scotland, supported by seven special non-geographic health boards, and Public Health Scotland.
Full fiscal autonomy (FFA) – also known as devolution max, devo-max, or fiscal federalism – is a particular form of far-reaching devolution proposed for Scotland and for Wales. The term has come to describe a constitutional arrangement in which instead of receiving a block grant from His Majesty's Treasury as at present, the Scottish Parliament or the Senedd would receive all taxation levied in Scotland or Wales; it would be responsible for most spending in Scotland or Wales but make payments to the UK government to cover Scotland or Wales's share of the cost of providing certain UK-wide services, largely defence and foreign relations. Scottish/Welsh fiscal autonomy – stopping short of full political independence – is usually promoted by advocates of a federal United Kingdom.

Since 1922, the United Kingdom has been made up of four countries: England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The UK Prime Minister's website has used the phrase "countries within a country" to describe the United Kingdom.

Scottish devolution is the process of the UK Parliament granting powers to the devolved Scottish Parliament. Prior to the advent of devolution, some had argued for a Scottish Parliament within the United Kingdom – while others have since advocated for complete independence. The people of Scotland first got the opportunity to vote in a referendum on proposals for devolution in 1979 and, although a majority of those voting voted 'Yes', the referendum legislation also required 40% of the electorate to vote 'Yes' for the plans to be enacted and this was not achieved. A second referendum opportunity in 1997, this time on a strong proposal, resulted in an overwhelming 'Yes' victory, leading to the Scotland Act 1998 being passed and the Scottish Parliament being established in 1999.

Scottish Parliament committees are small groups of Members of the Scottish Parliament (MSPs) who meet on a regular basis to scrutinise the work of the Scottish Government, conduct inquiries into subjects within their remit and examine legislation. Much of the everyday work of the Scottish Parliament is done by these committees.

A referendum on Scottish independence from the United Kingdom was held in Scotland on 18 September 2014. The referendum question was "Should Scotland be an independent country?", which voters answered with "Yes" or "No". The "No" side won with 2,001,926 (55.3%) voting against independence and 1,617,989 (44.7%) voting in favour. The turnout of 84.6% was the highest recorded for an election or referendum in the United Kingdom since the January 1910 general election, which was held before the introduction of universal suffrage.

In the United Kingdom, devolution is the Parliament of the United Kingdom's statutory granting of a greater level of self-government to the Scottish Parliament, the Senedd, the Northern Ireland Assembly and the London Assembly and to their associated executive bodies: the Scottish Government, the Welsh Government, the Northern Ireland Executive and in England, the Greater London Authority and combined authorities.
Marco Biagi is a Scottish National Party (SNP) politician. He served as the Minister for Local Government and Community Empowerment from 2014 to 2016, and as the Member of the Scottish Parliament (MSP) for Edinburgh Central from 2011 to 2016.
This page lists the public opinion polls that were conducted in relation to the 2014 Scottish independence referendum, that was held on 18 September 2014. Overall, polls showed that support for a "No" vote was dominant until the end of August 2014, when support for a "Yes" vote gained momentum and the gap closed significantly, with at least one poll placing the "Yes" vote ahead. In the final week of the campaign, polls showed the "No" vote to be consistently but somewhat narrowly ahead. There were no exit polls although a YouGov post-election poll was published shortly after the polls closed. For the history of the campaign itself see 2014 Scottish independence referendum, Yes Scotland, and Better Together (campaign).

The Gender Recognition Reform (Scotland) Bill is a bill passed by the Scottish Parliament. The bill seeks to amend the Gender Recognition Act 2004 of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, making it simpler for people to change their legal gender. On 17 January 2023, the United Kingdom government used section 35 of the Scotland Act 1998 to block the bill from receiving royal assent, the first time section 35 has been used.
References
- ↑ "Scottish Social Attitudes Survey". Economic and Social Data Service. Archived from the original on 10 March 2010. Retrieved 26 January 2010.
- ↑ "Nationalists take extra care choosing day to fit the bill". Edinburgh Evening News. 22 January 2010. Retrieved 26 January 2010.
- ↑ Carrell, Severin (14 January 2010). "Scots want greater tax-raising powers for Holyrood, survey finds". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 26 January 2010.