Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved venom apparatus, such as fangs or a stinger, in a process called envenomation. Venom is often distinguished from poison, which is a toxin that is passively delivered by being ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin, and toxungen, which is actively transferred to the external surface of another animal via a physical delivery mechanism.

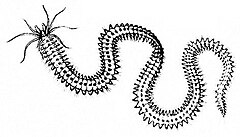
Centipedes are predatory arthropods belonging to the class Chilopoda of the subphylum Myriapoda, an arthropod group which includes millipedes and other multi-legged animals. Centipedes are elongated segmented (metameric) creatures with one pair of legs per body segment. All centipedes are venomous and can inflict painful stings, injecting their venom through pincer-like appendages known as forcipules or toxicognaths, which are actually modified legs instead of fangs. Despite the name, no centipede has exactly 100 legs; the number of pairs of legs is an odd number that ranges from 15 pairs to 191 pairs.
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean and can be further divided into regions by depth. The word pelagic is derived from Ancient Greek πέλαγος (pélagos) 'open sea'. The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the surface of the sea and the bottom. Conditions in the water column change with depth: pressure increases; temperature and light decrease; salinity, oxygen, micronutrients all change. In a manner analogous to stratification in the Earth's atmosphere, the water column can be divided vertically into up to five different layers, with the number of layers depending on the depth of the water.

Myriapods are the members of subphylum Myriapoda, containing arthropods such as millipedes and centipedes. The group contains about 13,000 species, all of them terrestrial.

Scolopendra gigantea, also known as the Peruvian giant yellow-leg centipede or Amazonian giant centipede, is a centipede in the genus Scolopendra. It is the largest centipede species in the world, with a length exceeding 30 centimetres (12 in). Specimens may have 21 or 23 segments. It is found in various places throughout South America and the extreme south Caribbean, where it preys on a wide variety of animals, including other sizable arthropods, amphibians, mammals and reptiles.

The Chinese red-headed centipede, also known as the Chinese red head, is a centipede from East Asia. It averages 20 cm (8 in) in length and lives in damp environments.
Joel Walker Hedgpeth was a marine biologist, environmentalist and author. He was an expert on the marine arthropods known as sea spiders (Pycnogonida), and on the seashore plant and animal life of southern and northern California; he co-authored Between Pacific Tides, the definitive guide to California intertidal organisms. He was a spokesperson for care for the floral and faunal diversity of the California coastline.

Acorn barnacle and acorn shell are vernacular names for certain types of stalkless barnacles, generally excluding stalked or gooseneck barnacles. As adults they are typically cone-shaped, symmetrical, and attached to rocks or other fixed objects in the ocean. Members of the barnacle order Balanomorpha are often called acorn barnacles.

Marine invertebrates are the invertebrates that live in marine habitats. Invertebrate is a blanket term that includes all animals apart from the vertebrate members of the chordate phylum. Invertebrates lack a vertebral column, and some have evolved a shell or a hard exoskeleton. As on land and in the air, marine invertebrates have a large variety of body plans, and have been categorised into over 30 phyla. They make up most of the macroscopic life in the oceans.

Dolabrifera dolabrifera is a species of sea hare, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Aplysiidae, the sea hares. Dolabrifera dolabrifera, otherwise known as a Warty Seacat. The animal goes by many names, including the common sea hare. The Hawaiian name for Dolabrifera dolabrifera, is Kualakai.

Worms are many different distantly related bilateral animals that typically have a long cylindrical tube-like body, no limbs, and usually no eyes.

Neverita lewisii, common name Lewis's moon snail, is a species of large operculated sea snail. It is a predatory marine gastropod in the family Naticidae, the moon snails. Traditionally, this species was assigned to either the genus Lunatia, the genus Polinices or the genus Euspira. Recently, it was assigned to the genus Neverita based on molecular data.

Discurria insessa, common name the seaweed limpet, is a species of sea snail, a true limpet, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Lottiidae.

Grasshopper mice are rodents of the genus Onychomys, occurring in North America. They feed on insects and other arthropods.

Geophilus flavus is a terrestrial, soil-dwelling, species of centipede in the Geophilidae family. G. flavus occurs in a range of habitats across central Europe, North America, Australia and other tropical regions. Geophilomorph centipedes, like centipedes generally, are primary predators, hunting predominantly in underground soil burrows or above ground leaf litter. Their consumption behaviours are influenced by environment and seasonal factors. Given their lack of economic value and marginal medical significance, G.flavus remains largely understudied in mainstream research. Some recent studies have detailed the evolutionary development of G.flavus and Geophilidae generally, illustrating developed predatory features like forcipule venom glands.

In biology, being semi-aquatic refers to various macroorganisms that live regularly in both aquatic and terrestrial environments. When referring to animals, the term describes those that actively spend part of their daily time in water, or land animals that have spent at least one life stages in aquatic environments. When referring to plants, the term describes land plants whose roots have adapted well to tolerate regular, prolonged submersion in water, as well as emergent and (occasionally) floating-leaved aquatic plants that are only partially immersed in water.
Dendrothereua is a genus of house centipedes in the family Scutigeridae. There are at least three described species in Dendrothereua, found in the southern United States and the Neotropics.
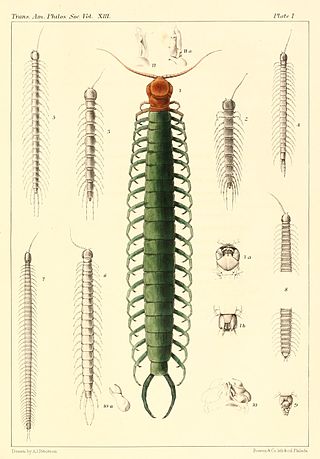
Scolopocryptops is a genus of bark centipedes in the family Scolopocryptopidae. There are over 20 described species in Scolopocryptops.

Scolopendra sumichrasti is a species of arthropod; a scolopendrid centipede found in Latin America.