
Tbilisi, in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis, is the capital and the largest city of Georgia, lying on the banks of the Kura River with a population of around 1.2 million people. Tbilisi was founded in the fifth century AD by Vakhtang I of Iberia, and since then has served as the capital of various Georgian kingdoms and republics. Between 1801 and 1917, then part of the Russian Empire, Tiflis was the seat of the Caucasus Viceroyalty, governing both the northern and the southern parts of the Caucasus.
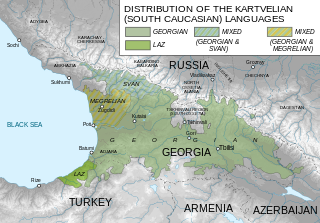
Georgian is the most widely spoken Kartvelian language; it also serves as the literary language or lingua franca for speakers of related languages. It is the official language of Georgia and the native or primary language of 87.6% of its population. Its speakers today amount to approximately four million. Georgian is written in its own unique alphabet.
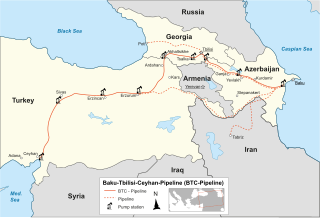
The Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan (BTC) pipeline is a 1,768 kilometres (1,099 mi) long crude oil pipeline from the Azeri–Chirag–Gunashli oil field in the Caspian Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. It connects Baku, the capital of Azerbaijan and Ceyhan, a port on the south-eastern Mediterranean coast of Turkey, via Tbilisi, the capital of Georgia. It is the second-longest oil pipeline in the former Soviet Union, after the Druzhba pipeline. The first oil that was pumped from the Baku end of the pipeline reached Ceyhan on 28 May 2006.

Ivane Javakhishvili Tbilisi State University is a public research university established on 8 February 1918 in Tbilisi, Georgia. Excluding academies and theological seminaries, which have intermittently functioned in Georgia for centuries, TSU is the oldest university in Georgia and the Caucasus region. The total enrollment is over 23,500 students, and there are 5,000 faculty and staff members (collaborators) overall.

The subdivisions of Georgia are autonomous republics, regions, and municipalities.
Abkhazia is a region in the Caucasus that is under the effective control of the partially recognised self-declared Republic of Abkhazia. The de jure majority internationally recognized Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia claims to be its legitimate government.

Shota Rustaveli Tbilisi International Airport, formerly Novo Alexeyevka International Airport, is the busiest international airport in Georgia, located 17 km (11 mi) southeast of capital Tbilisi. The airport handled 3.7 million passengers in 2019. Due to the global coronavirus pandemic, the airspace of Georgia was closed for most of 2020 causing the number of travelers through Tbilisi airport to drop by 84% to less than 600,000.

David Kipiani was a Georgian and Soviet football midfielder and manager, who played for the USSR national team. Kipiani principally played as a playmaker and is considered one of Georgia's greatest players. He was known for his elegant style of play, dribbling ability and passing range.

FC Dinamo Batumi is a Georgian professional football club based in Batumi, Adjara that competes in the Erovnuli Liga, the top division of the national football system.
Armenians in Georgia or Georgian Armenians are Armenian people living within the country of Georgia. The Armenian community is mostly concentrated in the capital Tbilisi, Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia and Samtskhe-Javakheti region. 2014 Census of Georgia puts the Armenians in Samtskhe-Javakheti at 50.5% of the population. In Abkhazia, Armenians are the third largest ethnic group in the region after the Georgians and the Abkhazian majority.

Law enforcement in Georgia is conducted by the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Georgia. Currently, there are more than 42,000 registered police officers.

The flag of Tbilisi, capital of Georgia, is a rectangular white banner with a blue Nordic-type cross outlined in amber that extends to edges of the flag. The point of crossing is crowned by the central detail from the Seal of Tbilisi surrounded by seven-point gold stars lined up in a crescent manner.

The Baku–Tbilisi–Kars (BTK), or Baku–Tbilisi–Akhalkalaki–Kars railway (BTAK), is a railway connecting Azerbaijan, Georgia and Turkey, which became operational on 30 October 2017 following several years of delays. The project was originally due to be completed by 2010, but was delayed to 2013, 2015, 2016, and, following a fifth trilateral meeting in February 2016, foreign ministers of the three countries announced that the railway would finally be completed in 2017.
George Shkinin also known as Gosha, Goga, Georgi, and Giorgi, surname alternately spelled Shkinini, is a Georgian rugby union player. He was first capped for Georgia in 2004, and has played for his country 21 times since then. Playing at wing, He started his career in Georgian club "Hooligana" from Tbilisi. Shkinin has played for the Blois club in France and returned to his old club "Hooligana" in Tbilisi, Georgia. He is player and coach of kids in "Hooligana" till now. He has scored five tries playing for Georgia. Also Shkinin is captain of national Georgian rugby sevens team.

European Route E 117 is part of the International E-road network, which is a series of main roads in Europe.

Chugureti St. Astvatsatsin Church is an Armenian church in Chugureti district of Old Tbilisi, Georgia.

Georgia Time (GET) is a time zone used in Georgia and it is uniform throughout the country. It moved from zone UTC+04:00 to UTC+03:00 on 27 June 2004, then back to UTC+04:00 on 27 March 2005. Georgia does not observe daylight saving time since 2004.

Georgia's road network plays an important role in both domestic and international traffic with the four neighboring countries. This is expressed in the road numbering system. The country has a network of 13 internationally oriented trunk highways that connect the capital Tbilisi, home to about a third of the national population, with its four neighboring countries. This is also the backbone of a network of domestic oriented national roads connecting vital regions with each other.

Georgia–Netherlands relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between Georgia and the Netherlands. Georgia has an embassy in The Hague, which opened in 2007. The Netherlands has an embassy in Tbilisi since 2001. The countries established diplomatic relations on 22 April 1992. Both countries are full members of the Council of Europe. the Netherlands is a member of the European Union, which Georgia applied for in 2022.


















