Related Research Articles

Ophthalmology is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders.

Floaters or eye floaters are sometimes visible deposits within the eye's vitreous humour, which is normally transparent, or between the vitreous and retina. They can become particularly noticeable when looking at a blank surface or an open monochromatic space, such as blue sky. Each floater can be measured by its size, shape, consistency, refractive index, and motility. They are also called muscae volitantes, or mouches volantes. The vitreous usually starts out transparent, but imperfections may gradually develop as one ages. The common type of floater, present in most people's eyes, is due to these degenerative changes of the vitreous. The perception of floaters, which may be annoying or problematic to some people, is known as myodesopsia, or, less commonly, as myodaeopsia, myiodeopsia, or myiodesopsia. It is not often treated, except in severe cases, where vitrectomy (surgery), laser vitreolysis, and medication may be effective.

The Bates method is an ineffective and potentially dangerous alternative therapy aimed at improving eyesight. Eye-care physician William Horatio Bates (1860–1931) held the erroneous belief that the extraocular muscles effected changes in focus and that "mental strain" caused abnormal action of these muscles; hence he believed that relieving such "strain" would cure defective vision. In 1952, optometry professor Elwin Marg wrote of Bates, "Most of his claims and almost all of his theories have been considered false by practically all visual scientists."
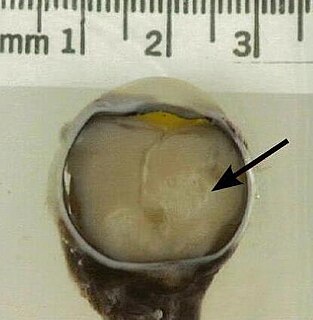
Retinoblastoma (Rb) is a rare form of cancer that rapidly develops from the immature cells of a retina, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. It is the most common primary malignant intraocular cancer in children, and it is almost exclusively found in young children.

Eye surgery, also known as ophthalmic or ocular surgery, is surgery performed on the eye or its adnexa, by an ophthalmologist. Eye surgery is synonymous with ophthalmology. The eye is a very fragile organ, and requires extreme care before, during, and after a surgical procedure to minimize or prevent further damage. An expert eye surgeon is responsible for selecting the appropriate surgical procedure for the patient, and for taking the necessary safety precautions. Mentions of eye surgery can be found in several ancient texts dating back as early as 1800 BC, with cataract treatment starting in the fifth century BC. Today it continues to be a widely practiced type of surgery, with various techniques having been developed for treating eye problems.
Visual impairment, also known as vision impairment, is a medical definition primarily measured based on an individual's better eye visual acuity; in the absence of treatment such as correctable eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment– visual impairment may cause the individual difficulties with normal daily tasks including reading and walking. Low vision is a functional definition of visual impairment that is chronic, uncorrectable with treatment or correctable lenses, and impacts daily living. As such low vision can be used as a disability metric and varies based on an individual's experience, environmental demands, accommodations, and access to services. The American Academy of Ophthalmology defines visual impairment as the best-corrected visual acuity of less than 20/40 in the better eye, and the World Health Organization defines it as a presenting acuity of less than 6/12 in the better eye. The term blindness is used for complete or nearly complete vision loss. In addition to the various permanent conditions, fleeting temporary vision impairment, amaurosis fugax, may occur, and may indicate serious medical problems.

Enucleation is the removal of the eye that leaves the eye muscles and remaining orbital contents intact. This type of ocular surgery is indicated for a number of ocular tumors, in eyes that have sustained severe trauma, and in eyes that are otherwise blind and painful.

Eye-gouging is the act of pressing or tearing the eye using the fingers or instruments. Eye-gouging involves a very high risk of eye injury, such as eye loss or blindness.
Sympathetic ophthalmia (SO), also called spared eye injury, is a diffuse granulomatous inflammation of the uveal layer of both eyes following trauma to one eye. It can leave the affected person completely blind. Symptoms may develop from days to several years after a penetrating eye injury. It typically results from a delayed hypersensitivity reaction.

Patricia Era Bath was an American ophthalmologist, inventor, humanitarian, and academic. She invented an improved device for laser cataract surgery. Her invention was called Laserphaco Probe, which she patented in 1986. She also became the first woman member of the Jules Stein Eye Institute, first woman to lead a post-graduate training program in ophthalmology, and first woman elected to the honorary staff of the UCLA Medical Center. Bath was the first African-American person to serve as a resident in ophthalmology at New York University. She was also the first African-American woman to serve on staff as a surgeon at the UCLA Medical Center. Bath was the first African-American woman doctor to receive a patent for a medical purpose. A holder of five patents, she also founded the non-profit American Institute for the Prevention of Blindness in Washington, D.C.
Oculoplastics, or oculoplastic surgery, includes a wide variety of surgical procedures that deal with the orbit, eyelids, tear ducts, and the face. It also deals with the reconstruction of the eye and associated structures.

Govindappa Venkataswamy popularly known as 'Dr V.' was an Indian ophthalmologist who dedicated his life to eliminate needless blindness. He was the founder and former chairman of Aravind Eye Hospitals. He is best known for developing a high quality, high volume, low-cost service delivery model that has restored sight to millions of people. Since inception, Aravind Eye Care System has seen over 55 million patients, and performed over 6.8 million surgeries. Over 50% of the organisation's patients pay either nothing or highly subsidised rates. Its scale and self-sustainability prompted a 1993 Harvard Business Case Study on the Aravind model.
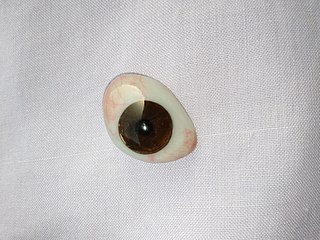
An ocular prosthesis, artificial eye or glass eye is a type of craniofacial prosthesis that replaces an absent natural eye following an enucleation, evisceration, or orbital exenteration. The prosthesis fits over an orbital implant and under the eyelids. Though often referred to as a glass eye, the ocular prosthesis roughly takes the shape of a convex shell and is made of medical grade plastic acrylic. A few ocular prostheses today are made of cryolite glass. A variant of the ocular prosthesis is a very thin hard shell known as a scleral shell which can be worn over a damaged or eviscerated eye. Makers of ocular prosthetics are known as ocularists. An ocular prosthesis does not provide vision; this would be a visual prosthesis. Someone with an ocular prosthesis is altogether blind on the affected side and has monocular vision.
Metabolife International, Inc. was a multi-level marketing company based in San Diego, California which manufactured dietary supplements. Metabolife's best-selling product, an ephedra supplement called Metabolife 356, once generated hundreds of millions of dollars in annual sales. However, Metabolife 356 and other ephedra-containing supplements were linked to thousands of serious adverse events, including deaths, which caused the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to ban the sale of ephedra-containing dietary supplements in 2004.
Marie Diener-West is the Helen Abbey and Margaret Merrell Professor of Biostatistics and the chair of the Master of Public Health Program at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Diener-West is an editor for the Cochrane Eyes and Vision Group and a member of the American Public Health Association, American Statistical Association, Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology, and the Society for Clinical Studies.

Blinding is a type of physical punishment which results in complete or nearly complete loss of vision. It was used as an act of revenge and torture. The punishment has been used since Antiquity; Greek mythology makes several references to blinding as divine punishment, which reflects human practice.
Herbert Edward Kaufman is an American ophthalmologist who discovered idoxuridine, the first clinically useful antiviral agent; co-developed with William Bourne the clinical specular microscope to view the live corneal endothelium, co-developed timolol with Thomas Zimmerman, a new class of medications to treat glaucoma; corneal storage media for eye banks; natamycin, the first commercially available medication to treat fungal infections of the eye; co-developed with Tony Gasset the use of bandage contact lenses; and was involved in the first laser vision photorefractive keratectomy of the eye with Marguarite McDonald.

Hamida Saiduzzafar was an Indian ophthalmologist.
Visual impairment in art is a limited topic covered by research, with its focus being on how visually impaired people are represented in artwork throughout history. This is commonly portrayed through the inclusion of objects such as canes and dogs to symbolize blindness, which is the most frequently depicted visual impairment in art. Many notable figures in art history, such as Leonardo da Vinci, Claude Monet, and Georgia O'Keeffe, were visually impaired, or theorized to be so.

The theme of blindness has been explored by many different cultures throughout history, with blind characters appearing in stories from ancient Greek mythology and Judeo-Christian religious texts. In the modern era, blindness has featured in numerous works of literature and poetry by authors such as William Shakespeare, William Blake, and H. G. Wells, and has also been a recurring trope in film and other visual media.
References
- ↑ NP Jones (1990-09-01). "Self-enucleation and psychosis". The British Journal of Ophthalmology. 74 (9): 571–573. doi:10.1136/bjo.74.9.571. PMC 1042215 . PMID 2393650.
- 1 2 Kee, Caroline (2018-03-14). "A 20-Year-Old Gouged Out Her Own Eyes While In A Drug-Induced Psychosis". BuzzFeed. Archived from the original on 2018-03-14. Retrieved 2018-03-15.
- ↑ Matthew Michael Large, Olav B Nielssen (24 July 2012). "Self-enucleation: forget Freud and Oedipus, it's all about untreated psychosis". British Journal of Ophthalmology. 96 (8): 1056–1057. doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2012-301531. PMID 22373824. S2CID 20826549. Archived from the original on 2018-03-16. Retrieved 2018-03-15.
- ↑ K.N. Rao and Shamshad Begum (1996). "Self-enucleation in depression: A case report". Indian Journal of Psychiatry. 38 (4): 269–270. PMC 2970886 . PMID 21584146.
- ↑ BB Patil (2004-04-07). "Bilateral self-enucleation of eyes". Nature. 18 (4): 431–432. doi: 10.1038/sj.eye.6700667 . PMID 15069443.
- ↑ Taylor, Sharon (7 September 2020). "Dodging the Draft in the Old Country". The Librarians. National Library of Israel. Archived from the original on 9 November 2021. Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ↑ Narins, Elizabeth (2018-03-09). "Kaylee Muthart Talks About Gouging Out Her Own Eyes On Crystal Meth". Cosmopolitan. Archived from the original on 2018-03-15. Retrieved 2018-03-16.
- ↑ Feit, Noah (2018-02-22). "Mom of woman who gouged eyes out tells 'People' she was going to have her committed". thestate. Archived from the original on 2018-03-16. Retrieved 2018-03-15.
- ↑ Feit, Noah (2018-03-18). "'The world just got darker,' SC woman who gouged out her eyes talks about ordeal". thestate. Archived from the original on 2018-03-14. Retrieved 2018-03-15.
- ↑ Davis, Kelly (12 September 2021). "Lawsuit: Jail video shows deputy watched as inmate blinded herself". San Diego Union Tribune. Archived from the original on 7 November 2021. Retrieved 7 November 2021.
- ↑ Davis, Kelly (19 October 2022). "San Diego County will pay $4.35 million to woman who blinded herself in jail" . Retrieved 1 November 2022.