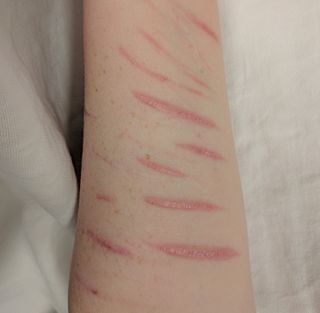
Self-harm is intentional behavior that is considered harmful to oneself. This is most commonly regarded as direct injury of one's own skin tissues usually without a suicidal intention. Other terms such as cutting, self-injury, and self-mutilation have been used for any self-harming behavior regardless of suicidal intent. Common forms of self-harm include damaging the skin with a sharp object or by scratching, hitting, or burning. The exact bounds of self-harm are imprecise, but generally exclude tissue damage that occurs as an unintended side-effect of eating disorders or substance abuse, as well as societally acceptable body modification such as tattoos and piercings.

Suffering, or pain in a broad sense, may be an experience of unpleasantness or aversion, possibly associated with the perception of harm or threat of harm in an individual. Suffering is the basic element that makes up the negative valence of affective phenomena. The opposite of suffering is pleasure or happiness.
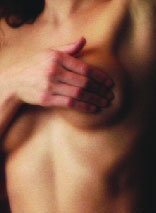
Breast self-examination (BSE) is a screening method used in an attempt to detect early breast cancer. The method involves the woman herself looking at and feeling each breast for possible lumps, distortions or swelling.
Elder abuse is "a single, or repeated act, or lack of appropriate action, occurring within any relationship where there is an expectation of trust, which causes harm or distress to an older person." This definition has been adopted by the World Health Organization (WHO) from a definition put forward by Hourglass in the UK. Laws protecting the elderly from abuse are similar to and related to laws protecting dependent adults from abuse.
Self-hatred is personal self-loathing or low self-esteem which may lead to self-harm.
Suicide is the second leading cause of death for people in the United States from the ages of 9 to 56.
The orange ribbon is a symbol adopted for a very wide variety of uses in different places.

The autism rights movement, also known as the autistic acceptance movement, is a social movement allied with disability rights that emphasizes a neurodiversity paradigm, viewing autism as a disability with variations in the human brain rather than as a disease to be cured. The movement advocates for several goals, including greater acceptance of autistic traits and behaviors; reforms of services - i.e. services that focus on improving quality of life and well-being instead of suppression and masking of autistic traits that are adaptive or not harmful or imitations of social behaviors of neurotypical (non-autistic) peers ; the creation of social networks and events that allow autistic people to socialize on their own terms; and the recognition of the autistic community as a minority group.

World Health Day is a global health awareness day celebrated every year on 7 April, under the sponsorship of the World Health Organization (WHO), as well as other related organizations.

Suicide prevention is a collection of efforts to reduce the risk of suicide. Suicide is often preventable, and the efforts to prevent it may occur at the individual, relationship, community, and society level. Suicide is a serious public health problem that can have long-lasting effects on individuals, families, and communities. Preventing suicide requires strategies at all levels of society. This includes prevention and protective strategies for individuals, families, and communities. Suicide can be prevented by learning the warning signs, promoting prevention and resilience, and committing to social change.

Invisible disabilities, also known as hidden disabilities or non-visible disabilities (NVDs), are disabilities that are not immediately apparent. They are typically chronic illnesses and conditions that significantly impair normal activities of daily living.

To Write Love on Her Arms (TWLOHA) is an American nonprofit organization that aims to present hope for people struggling with addiction, depression, self-injury and thoughts of suicide, while also investing in treatment and recovery. Based in Melbourne, Florida, TWLOHA seeks to connect people to treatment centers, websites, books, support groups, helplines, and other resources. TWLOHA also encourages people to have honest conversations about mental health, and to live in community.

A caregiver, carer or support worker is a paid or unpaid person who helps an individual with activities of daily living. Caregivers who are members of a care recipient's family or social network, and who may have no specific professional training, are often described as informal caregivers. Caregivers most commonly assist with impairments related to old age, disability, a disease, or a mental disorder.

Compulsive behavior is defined as performing an action persistently and repetitively. Compulsive behaviors could be an attempt to make obsessions go away. Compulsive behaviors are a need to reduce apprehension caused by internal feelings a person wants to abstain from or control. A major cause of compulsive behavior is said to be obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD). "The main idea of compulsive behavior is that the likely excessive activity is not connected to the purpose to which it appears directed." There are many different types of compulsive behaviors including shopping, hoarding, eating, gambling, trichotillomania and picking skin, itching, checking, counting, washing, sex, and more. Also, there are cultural examples of compulsive behavior.

The Senang Hati Foundation, also known as Yayasan Senang Hati, is a non-profit organization in Bali that assists people living with disabilities. The name Senang Hati loosely translates as "Happy Hearts" in Indonesian. The foundation creates programmes to develop self-confidence, physical and economic independence, and increase awareness in the general community of the rights of people with disabilities. Senang Hati accomplishes this through the assistance of volunteers, who provide skills training and social interaction. The society also provides wheelchairs and housing, and runs Senang Hati Places, a home for disabled children.
World Suicide Prevention Day (WSPD) is an awareness day always observed on 10 September every year, in order to provide worldwide commitment and action to prevent suicides, with various activities around the world since 2003. The International Association for Suicide Prevention (IASP) collaborates with the World Health Organization (WHO) and the World Federation for Mental Health (WFMH) to host World Suicide Prevention Day. In 2011 an estimated 40 countries held awareness events to mark the occasion. According to WHO's Mental Health Atlas released in 2014, no low-income country reported having a national suicide prevention strategy, while less than 10% of lower-middle income countries, and almost a third of upper-middle and high-income countries had.

The Sam Schmidt Paralysis Foundation (SSPF) is a charitable organization founded in 2000 and headquartered in Pennington, New Jersey. It has since been renamed Conquer Paralysis Now.
Historically, suicide terminology has been rife with issues of nomenclature, connotation, and outcomes, and terminology describing suicide has often been defined differently depending on the purpose of the definition. A lack of agreed-upon nomenclature and operational definitions has complicated understanding. In 2007, attempts were made to reach some consensus. There is also opposition to the phrase "to commit suicide" as implying negative moral judgment and association with criminal or sinful activity.
Project Semicolon – stylized as Project ; – is an American nonprofit organization known for its advocacy of mental health wellness and its focus as an anti-suicide initiative. Founded in 2013, the movement's aim is "presenting hope and love to those who are struggling with depression, suicide, addiction and self-injury". They are known for encouraging people to tattoo the punctuation mark semicolon (;) as a form of solidarity between people dealing with mental illness or the death of someone from suicide.
Suicide in Ireland has the 17th highest rate in Europe and the 4th highest for the males aged 15–25 years old which was a main contributing factor to the improvement of suicides in Ireland.











