
Kandy is a major city in Sri Lanka located in the Central Province. It was the last capital of the ancient kings' era of Sri Lanka. The city lies in the midst of hills in the Kandy plateau, which crosses an area of tropical plantations, mainly tea. Kandy is both an administrative and religious city and is also the capital of the Central Province. Kandy is the home of The Temple of the Tooth Relic, one of the most sacred places of worship in the Buddhist world. It was declared a world heritage site by UNESCO in 1988.

The Jaffna Kingdom, also known as Kingdom of Aryachakravarti, of modern northern Sri Lanka was a historic monarchy that came into existence around the town of Jaffna on the Jaffna peninsula traditionally thought to be established after the invasion of Magha, who is credited with the founding of the Jaffna kingdom and is said to have been from Kalinga, in India. Established as a powerful force in the north, north east and west of the island, it eventually became a tribute paying feudatory of the Pandyan Empire in modern South India in 1258, gaining independence in 1323, when the last Pandyan ruler of Madurai was defeated and expelled in 1323 by Malik Kafur, the army general of the Muslim Delhi Sultanate. For a brief period, in the early to mid-14th century, it was an ascendant power in the island of Sri Lanka when all regional kingdoms accepted subordination. However, the kingdom was eventually overpowered by the rival Kotte Kingdom, around 1450 when it was invaded by Prince Sapumal under the Kotte Kingdom's directive.
Alagakkonara, also known as Alakeshwara, were a prominent feudal family that provided powerful ministers and military rulers during the medieval period in Sri Lanka. Although some historian say that the family was of Malayali origin, others say they originated from Kanchipuram in Tamil Nadu, India. They arrived in Sri Lanka around the 13th century and naturalized themselves in Sri Lanka. One member of the family is noted for founding the current capital of Sri Lanka, Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte as a fort from which he waged a war against encroaching tax collectors from the Jaffna kingdom in the north. The family lost most of its influence after its leader was taken captive by the Ming Dynasty (Chinese) Admiral Zheng He in 1411.

The Nayaks of Kandy were the rulers of the Kingdom of Kandy between 1739 to 1815, and the last dynasty to rule on the island. Their rise to power came about as a result of the death of Vira Narendrasinha, who left no legitimate heir- the throne passed to his brother-in-law, who was crowned as Sri Vijaya Rajasinha in 1739.

Ceylon was a British Crown colony between 1815 and 1948. Initially the area it covered did not include the Kingdom of Kandy, which was a protectorate from 1815, but from 1817 to 1948 the British possessions included the whole island of Ceylon, now the nation of Sri Lanka.
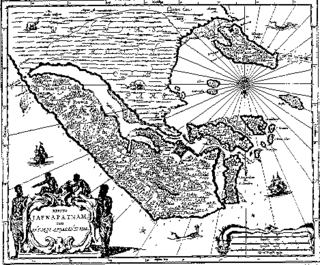
The Portuguese conquest of the Jaffna kingdom occurred after Portuguese traders arrived at the rival Kotte Kingdom in the southwest of modern Sri Lanka in 1505. Many kings of Jaffna, such as Cankili I, initially confronted the Portuguese in their attempts at converting the locals to Roman Catholicism, but eventually made peace with them.

Vimaladharmasūriya I was a king of Kandy from 1590 to 1604. His reputation was built when he successfully repulsed two major Portuguese offensives on Kandy, the Campaign of Danture in 1594 and the Battle of Balana in 1602, in both of which the Portuguese were humiliatingly defeated.

The Kingdom of Sitawaka was a kingdom located in south-central Sri Lanka. It emerged from the division of the Kingdom of Kotte following the Spoiling of Vijayabahu in 1521, and over the course of the next seventy years came to dominate much of the island. Sitawaka also offered fierce resistance to the Portuguese, who had arrived on the island in 1505. Despite its military successes, Sitawaka remained unstable, having to contend with repeated uprisings in its restive Kandyan territories, as well as a wide-ranging and often devastating conflict with the Portuguese. Sitawaka disintegrated soon after the death of its last king Rajasimha I in 1593.

Sri Dalada Maligawa or the Temple of the Sacred Tooth Relic is a Buddhist temple in the city of Kandy, Sri Lanka. It is located in the royal palace complex of the former Kingdom of Kandy, which houses the relic of the tooth of the Buddha. Since ancient times, the relic has played an important role in local politics because it is believed that whoever holds the relic holds the governance of the country. Kandy was the last capital of the Sri Lankan kings and is a World Heritage Site mainly due to the temple.

Portuguese Ceylon was the control of the Kingdom of Kotte by the Portuguese Empire, in present-day Sri Lanka, after the country's Crisis of the Sixteenth Century and into the Kandyan period.
Jayavīra Banḍāra was King of Kandy from 1511 to 1552. He succeeded his father Senasammata Vikramabahu as king and was succeeded by his son Karalliyadde Bandara. During the reign of Banḍāra Catholic friars appeared at court and some conversions took place in the kingdom.
Karalliyadde Banḍāra was King of Kandy, who ruled from 1552 to 1582. During his reign Banḍāra publicly embraced Catholicism, brought to the island by the Portuguese. He and his infant daughter princess Kusumāsana Devi fled the kingdom with his retinue. The princess was later baptized by the Portuguese and called Dona Catarina. He succeeded his father Jayavira Bandara as king and was succeeded by his daughter Kusumasana Devi.

Kusumāsana Devi, also known as Dona Catherina, was ruling Queen of Kandy in 1581.

The Sinhalese–Portuguese War was a series of conflicts waged from 1527 to 1658 between the indigenous Sinhalese kingdoms of Ceylon and their allies against the Portuguese Empire. The Portuguese were seeking to expand from their trading post at Colombo to incorporate Ceylon into their growing empire.

Kandyan Art Association is an association formed in 1882 to revitalise traditional Kandyan arts and crafts and support the traditional craftsmen by providing them a sales outlet.
Vimaladharmasūriya is a Sinhalese regnal name, where Vimaladharma means ‘of the pure doctrine’, while sūriya refers to the ‘dynasty of the Sun’.

The History of the Kandyan Kingdom in Sri Lanka starts with its foundation in 1476.














