
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a union territory of India consisting of 571 islands, of which 37 are inhabited, at the junction of the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. The territory is about 150 km (93 mi) north of Aceh in Indonesia and separated from Thailand and Myanmar by the Andaman Sea. It comprises two island groups, the Andaman Islands (partly) and the Nicobar Islands, separated by the 150 km wide Ten Degree Channel, with the Andaman islands to the north of this latitude, and the Nicobar islands to the south. The Andaman Sea lies to the east and the Bay of Bengal to the west. The island chains are thought to be a submerged extension of the Arakan Mountains.

Mistletoe is the common name for obligate hemiparasitic plants in the order Santalales. They are attached to their host tree or shrub by a structure called the haustorium, through which they extract water and nutrients from the host plant.

Loranthaceae, commonly known as the showy mistletoes, is a family of flowering plants. It consists of about 75 genera and 1,000 species of woody plants, many of them hemiparasites. The three terrestrial species are Nuytsia floribunda, Atkinsonia ligustrina, and Gaiadendron punctatum Loranthaceae are primarily xylem parasites, but their haustoria may sometimes tap the phloem, while Tristerix aphyllus is almost holoparasitic. For a more complete description of the Australian Loranthaceae, see Flora of Australia online., for the Malesian Loranthaceae see Flora of Malesia.

The Nicobar Islands rain forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in the Nicobar Islands. The Nicobar Islands are in the Indian Ocean, lying north of Sumatra and south of the Andaman Islands. The islands are politically part of India, although physically closer to Southeast Asia. Millions of years of isolation from the mainland has given rise to a distinct flora and fauna, including many endemic species.

Mount Harriet National Park, officially renamed as Mount Manipur National Park, is a national park located in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands union territory of India. The park, established in 1969, covers about 4.62 km2 (18.00 mi2). Mount Manipur, which is a part of the park, is the third-highest peak in the Andaman and Nicobar archipelago next to Saddle Peak in North Andaman and Mount Thullier in Great Nicobar.

The Nicobar treeshrew is a treeshrew species within the Tupaiidae. It is endemic to the Nicobar Islands where it inhabits the islands' rain forests. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Monoplex nicobaricus, known as the Nicobar hairy triton or goldmouth triton, is a species of medium-sized predatory sea snail, a tropical marine gastropod mollusc in the family Cymatiidae.

Dendrobium formosum is a species of orchid.

Amyema quandang is a species of hemi-parasitic shrub which is widespread throughout the mainland of Australia, especially arid inland regions, sometimes referred to as the grey mistletoe.

Marmorofusus nicobaricus, common name : the Nicobar spindle, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Fasciolariidae, the spindle snails, the tulip snails and their allies.

The Nicobar jungle flycatcher is a species of bird in the Old World flycatcher family Muscicapidae. It is endemic to the Nicobar Islands, where its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests and subtropical or tropical mangrove forests. It was at one time considered a subspecies of the brown-chested jungle flycatcher.

Amyema melaleucae, also known as the tea-tree mistletoe, is a species of flowering plant within the genus Amyema, an epiphytic hemiparasitic plant of the family Loranthaceae native to Australia and found in Western Australia and South Australia on the coast, from north of Perth almost to the Victorian border.

Cecarria is a monotypic genus in the family Loranthaceae. The sole species is Cecarria obtusifolia, a hemiparasitic aerial shrub.
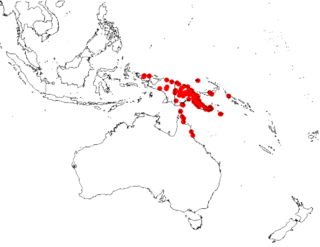
Decaisnina hollrungii is a species of flowering plant, an epiphytic hemiparasitic plant of the family Loranthaceae native to the New Guinea, Queensland, Australia, and in the Bismarck Archipelago and the Solomon Islands.

Amylotheca is a genus of hemi-parasitic aerial shrubs in the family Loranthaceae, found in Borneo, Malaysia, New Caledonia, New Guinea, Australia, Sumatra, Thailand, Vanuatu, and Philippines
Cnemaspis nicobaricus is a species of diurnal, rock-dwelling, insectivorous gecko endemic to India. It is distributed in Great Nicobar Island.

Trilepidea is an extinct monotypic genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Loranthaceae. Its native range was New Zealand. The only species was Trilepidea adamsii, or Adams mistletoe. It was first described in 1880 as Loranthus adamsii and has ever only been collected from a few locations in the North Island. It has been argued that the extinction of this species, vulnerable due to restricted distribution, was caused by interaction of a number of factors, including introduction of an exotic species, in this case the brushtail possum from Australia.

Cyne is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Loranthaceae.
Loranthella deflersii is a species of flowering plant in family Loranthaceae. It is a hemiparasitic epiphyte native to deserts and dry shrublands of the Arabian Peninsula and the Horn of Africa. It is the sole species in genus Loranthella.
















