
In engineering and its various subdisciplines, acceptance testing is a test conducted to determine if the requirements of a specification or contract are met. It may involve chemical tests, physical tests, or performance tests.
Project management is the process of supervising the work of a team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. The primary constraints are scope, time and budget. The secondary challenge is to optimize the allocation of necessary inputs and apply them to meet predefined objectives.

Configuration management (CM) is a management process for establishing and maintaining consistency of a product's performance, functional, and physical attributes with its requirements, design, and operational information throughout its life. The CM process is widely used by military engineering organizations to manage changes throughout the system lifecycle of complex systems, such as weapon systems, military vehicles, and information systems. Outside the military, the CM process is also used with IT service management as defined by ITIL, and with other domain models in the civil engineering and other industrial engineering segments such as roads, bridges, canals, dams, and buildings.

In systems engineering, information systems and software engineering, the systems development life cycle (SDLC), also referred to as the application development life cycle, is a process for planning, creating, testing, and deploying an information system. The SDLC concept applies to a range of hardware and software configurations, as a system can be composed of hardware only, software only, or a combination of both. There are usually six stages in this cycle: requirement analysis, design, development and testing, implementation, documentation, and evaluation.

Forrester is one of the most influential research and advisory firms in the world, empowering leaders in technology, customer experience, digital, marketing, sales, and product functions to be bold at work and accelerate growth through customer obsession. Forrester's unique research and continuous guidance model helps executives and their teams achieve their initiatives and outcomes faster and with confidence.

In industry, product lifecycle management (PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its inception through the engineering, design, and manufacture, as well as the service and disposal of manufactured products. PLM integrates people, data, processes, and business systems and provides a product information backbone for companies and their extended enterprises.
Information technology service management (ITSM) are the activities performed by an organization to design, build, deliver, operate and control IT services offered to customers.
The Information Services Procurement Library (ISPL) is a best practice library for the management of Information Technology related acquisition processes. It helps both the customer and supplier organization to achieve the desired quality using the corresponded amount of time and money by providing methods and best practices for risk management, contract management, and planning. ISPL focuses on the relationship between the customer and supplier organization: It helps constructing the request for proposal, it helps constructing the contract and delivery plan according to the project situation and risks, and it helps monitoring the delivery phase. ISPL is a unique Information Technology method because where most other Information Technology methods and frameworks focus on development, ISPL focuses purely on the procurement of information services. The target audience for ISPL consists of procurement managers, acquisition managers, programme managers, contract managers, facilities managers, service level managers, and project managers in the IT area. Because of ISPL's focus on procurement it is very suitable to be used with ITIL and PRINCE2.
The Application Services Library (ASL) is a public domain framework of best practices used to standardize processes within Application Management, the discipline of producing and maintaining information systems and applications. The term "library" is used because ASL is presented as a set of books describing best practices from the IT industry.
Microsoft Operations Framework (MOF) 4.0 is a series of guides aimed at helping information technology (IT) professionals establish and implement reliable, cost-effective services.
A product manager (PM) is a professional role that is responsible for the development of products for an organization, known as the practice of product management. Product managers own the product strategy behind a product, specify its functional requirements, and manage feature releases. Product managers coordinate work done by many other functions, and are ultimately responsible for product outcomes.
A service delivery platform (SDP) is a set of components that provides a service(s) delivery architecture for a type of service delivered to consumer, whether it be a customer or other system. Although it is commonly used in the context of telecommunications, it can apply to any system that provides a service. Although the TM Forum (TMF) is working on defining specifications in this area, there is no standard definition of SDP in industry and different players define its components, breadth, and depth in slightly different ways.
IT portfolio management is the application of systematic management to the investments, projects and activities of enterprise Information Technology (IT) departments. Examples of IT portfolios would be planned initiatives, projects, and ongoing IT services. The promise of IT portfolio management is the quantification of previously informal IT efforts, enabling measurement and objective evaluation of investment scenarios.
Software Quality Management (SQM) is a management process that aims to develop and manage the quality of software in such a way so as to best ensure that the product meets the quality standards expected by the customer while also meeting any necessary regulatory and developer requirements, if any. Software quality managers require software to be tested before it is released to the market, and they do this using a cyclical process-based quality assessment in order to reveal and fix bugs before release. Their job is not only to ensure their software is in good shape for the consumer but also to encourage a culture of quality throughout the enterprise.
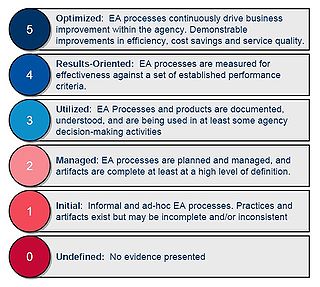
The Enterprise Architecture Assessment Framework (EAAF) was created by the US Federal government Office of Management and Budget (OMB) to allow federal agencies to assess and report their enterprise architecture activity and maturity, and advance the use of enterprise architecture in the federal government.
Team service management (TSM) is an open-source management framework that uses and integrates existing management methods and techniques to help teams deliver ever improving services. TSM is designed to be used by any and all teams within an enterprise including sales, production, administration, IT, finance and management teams.

A definitive media library is a secure information technology repository in which an organisation's definitive, authorised versions of software media are stored and protected. Before an organisation releases any new or changed application software into its operational environment, any such software should be fully tested and quality assured. The definitive media library provides the storage area for software objects ready for deployment and should only contain master copies of controlled software media configuration items (CIs) that have passed appropriate quality assurance checks, typically including both procured and bespoke application and gold build source code and executables. In the context of the ITIL best practice framework, the term definitive media library supersedes the term definitive software library referred to prior to version ITIL v3.

Tudor IT Process Assessment (TIPA) is a methodological framework for process assessment. Its first version was published in 2003 by the Public Research Centre Henri Tudor based in Luxembourg. TIPA is now a registered trademark of the Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology (LIST). TIPA offers a structured approach to determine process capability compared to recognized best practices. TIPA also supports process improvement by providing a gap analysis and proposing improvement recommendations.
The Service Portfolio is described in the ITIL books Service Strategy and Service Design. The Service Portfolio is the core repository for all information for all services in an organization. Each service is listed along with its current status and history. The main descriptor in the Service Portfolio is the Service Design Package (SDP).
ITIL is framework with set of practices for IT activities such as IT service management (ITSM) and IT asset management (ITAM) that focus on aligning IT services with the needs of the business.







