
Shērōē, better known by his dynastic name of Kavad II, was king (shah) of the Sasanian Empire briefly in 628. He was the son of Khosrow II, whom he succeeded after having him overthrown in a coup d'état. Kavad's reign is seen as a turning point in Sasanian history, and has been argued by some scholars as playing a key role in the fall of the Sasanian Empire.

Hormizd II was king (shah) of the Sasanian Empire. He ruled for seven years and five months, from 303 to 309. He was a son and successor of Narseh.

Abū Jaʿfar Muḥammad ibn Jarīr ibn Yazīd al-Ṭabarī, more commonly known as al-Ṭabarī (الطبري), was a Muslim historian and scholar from Amol, Tabaristan. Among the most prominent figures of the Islamic Golden Age, al-Tabari is known for his historical works and his expertise in Qur'anic exegesis, but he has also been described as "an impressively prolific polymath". He wrote works on a diverse range of subjects, including world history, poetry, lexicography, grammar, ethics, mathematics, and medicine.

Muḥammad ibn Isḥāq ibn Yasār ibn Khiyār was an 8th-century Muslim historian and hagiographer. Ibn Ishaq collected oral traditions that formed the basis of an important biography of the Islamic prophet Muhammad.

Yusuf ibn Yaqub ibn Ishaaq ibn Ibrahim is a prophet mentioned in the Quran, and corresponds to Joseph, a person from the Tanakh, the Jewish religious scripture, and the Christian Bible, who was estimated to have lived in Egypt before the New Kingdom. Of all of Jacob's children, Joseph was the one given the gift of prophecy. Although the narratives of other prophets are mentioned in various Surahs, the complete narrative of Joseph is given only in one Surah, Yusuf, making it unique. It is said to be the most detailed narrative in the Qur'an and contains more details than the Biblical counterpart.

Al-Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib was a paternal uncle and Sahabi (companion) of Muhammad, just three years older than his nephew. A wealthy merchant, during the early years of Islam he protected Muhammad while he was in Mecca, but only became a convert after the Battle of Badr in 624 CE (2 AH). His descendants founded the Abbasid dynasty in 750.
Abu al-Hasan Ali ibn Sahl Rabban al-Tabari, was a Persian Muslim scholar, physician and psychologist, who produced one of the first encyclopedia of medicine titled Firdous al-Hikmah. Ali ibn Sahl spoke Syriac and Greek, the two sources of the medical tradition of Antiquity which had been lost by medieval Europe, and transcribed in meticulous calligraphy. His famous student Muhammad ibn Zakariya al-Razi has darkened his fame. He wrote the first encyclopedic work on medicine. He lived for over 70 years and interacted with important figures of the time, such as Muslim caliphs, governors, and eminent scholars. Because of his family's religious history, as well as his religious work, al-Tabarī was one of the most controversial scholars. He first discovered that the pulmonary tuberculosis was contagious.
Māriyya bint Shamʿūn, better known as Māriyya al-Qibṭiyya or al-Qubṭiyya, or Mary the Copt, died 637, was an Egyptian woman who, along with her sister Sirin, was sent to the Islamic prophet Muhammad in 628 as a gift by Muqawqis, a Christian governor of Alexandria, during the territory's Persian occupation. She and her sister were slaves. She spent the rest of her life in Medina where she converted to Islam and lived with Muhammad where she bore a son, Ibrahim. The son would die as an infant and then she died almost five years later.

Artabanus IV, also known as Ardavan IV, incorrectly known in older scholarship as Artabanus V, was the last ruler of the Parthian Empire from c. 213 to 224. He was the younger son of Vologases V, who died in 208.

Ya'qūb ibn al-Layth al-Saffār, was a coppersmith and the founder of the Saffarid dynasty of Sistan, with its capital at Zaranj. Under his military leadership, he conquered much of the eastern portions of Greater Iran consisting of modern-day Iran, Afghanistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan as well as portions of western Pakistan and a small part of Iraq. He was succeeded by his brother, Amr ibn al-Layth.

Jāmiʿ al-bayān ʿan taʾwīl āy al-Qurʾān, popularly Tafsīr al-Ṭabarī, is a Sunni tafsir by the Persian scholar Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari (838–923). It immediately won high regard and retained its importance for scholars to the present day. It is the earliest major running commentary of the Quran to have survived in its original form. Like his history, al-Tabari's tafsir is notable for its comprehensiveness and citation of multiple, often conflicting sources. The book was translated into Persian by a group of scholars from Transoxania on commission of the Samanid king, Mansur I (961–976).

The History of the Prophets and Kings, more commonly known as Tarikh al-Tabari or Tarikh-i Tabari or The History of al-Tabari is an Arabic-language historical chronicle completed by the Muslim historian Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari in 915 AD. It begins with creation, and charts Muslim and Middle Eastern history from the myths and legends associated with the Old Testament through to the history of the Abbasid era, down to the year 915. An appendix or continuation, was written by Abu Abdullah b. Ahmad b. Ja'far al-Farghani, a student of al-Tabari.

Azarmidokht was Sasanian queen regnant (banbishn) of Iran from 630 to 631. She was the daughter of king (shah) Khosrow II. She was the second Sasanian queen; her sister Boran ruled before and after her. Azarmidokht came to power in Iran after her cousin Shapur-i Shahrvaraz was deposed by the Parsig faction, led by Piruz Khosrow, who helped Azarmidokht ascend the throne. Her rule was marked by an attempt of a nobleman and commander Farrukh Hormizd to marry her and come to power. After the queen's refusal, he declared himself an anti-king. Azarmidokht had him killed as a result of a successful plot. She was, however, killed herself shortly afterwards by Rostam Farrokhzad in retaliation for his father's death. She was succeeded by Boran.
Yaḥyā ibn ʿUmar ibn Yaḥyā ibn al-Ḥusayn ibn Zayd ibn ʿAlī Zayn al-ʿĀbidīn ibn al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib was an Alid Imam. His mother was Umm al-Ḥusayn Fāṭima bint al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Ismāʿīl ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Jaʿfar ibn Abī Ṭālib. In the days of the Abbasid caliph Al-Musta'in, he marched out from Kufa and lead an abortive uprising from Kufa in 250 A.H., but was killed by the Abbasid forces led by Husayn ibn Isma'il, who had been sent to deal with him.

The Pishdadian dynasty is a mythical line of primordial kings featured in Zoroastrian belief and Persian mythology, who are presented in legend as originally rulers of the world but whose realm was eventually limited to Ērānshahr or Greater Iran. Although there are scattered references to them in the Zoroastrian scriptures – the Avesta – and later Pahlavi literature, it is through the 11th century Iranian national epic, the Shahnameh, that the canonical form of their legends is known. From the 9th century, Muslim writers, notably Tabari, re-told many of the Pishdadian legends in prose histories and other works. The Pishdadian kings and the stories relating to them have no basis in historical fact, however.
Ibrāhīm ibn al-Mahdī was an Abbasid prince, singer, composer and poet. He was the son of the third Abbasid caliph, al-Mahdi, and the half-brother of the poet and musician Ulayya. Ibrahim was contemporary of Abbasid caliph al-Hadi, al-Rashid and his three nephews caliph al-Amin, al-Ma'mun, al-Mu'tasim.

Sind was an administrative division of the Umayyad Caliphate and later of the Abbasid Caliphate in post-classical India, from around 711 CE with the conquest of Sind by the Arab military commander Muhammad ibn Qasim, to around 854 CE with the emergence of the independent dynasties of the Habbarid Emirate and the Multan Emirate. The "Governor of Sind" was an official who administered the caliphates' province over what is now Sindh, Pakistan.

The Principality of Ushrusana was a local dynasty ruling the Ushrusana region, in the northern area of modern Tajikistan, from an unknown date to 892 CE. Ushrusana, just like Ferghana, did not belong to Sogdia proper, but its inhabitants wrote in Sogdian, and may have spoken the Sogdian language as well. The rulers of the principality were known by their title of Afshin.
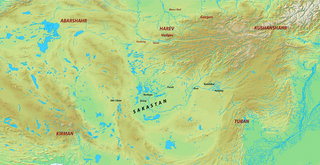
The Persian Empire's province of Sistan in the 7th century extended from the modern Iranian province of Sistan to central Afghanistan and Baluchistan province of Pakistan.

The medieval story of al-Nadirah is about the fall of Hatra and its princess, who fell in love with the young king Shapur I while he was besieging the city.















