This article needs additional citations for verification .(September 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Coordinates: 28°39′31″N77°14′38″E / 28.658566°N 77.243834°E

A geographic coordinate system is a coordinate system that enables every location on Earth to be specified by a set of numbers, letters or symbols. The coordinates are often chosen such that one of the numbers represents a vertical position and two or three of the numbers represent a horizontal position; alternatively, a geographic position may be expressed in a combined three-dimensional Cartesian vector. A common choice of coordinates is latitude, longitude and elevation. To specify a location on a plane requires a map projection.


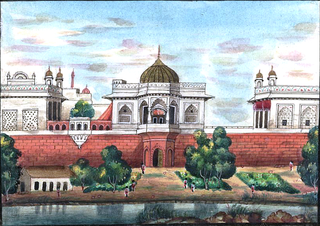
The Shahi Burj (Urdu: Emperor's Tower) is a three-storey octagonal tower of the Red Fort in Delhi.

Red Fort is a historic fort in the city of Delhi in India. It was the main residence of the emperors of the Mughal dynasty for nearly 200 years, until 1856. It is located in the centre of Delhi and houses a number of museums. In addition to accommodating the emperors and their households, it was the ceremonial and political center of the Mughal state and the setting for events critically impacting the region.
The tower is located at the northeastern corner of the imperial enclosure. The water feeding, the Nahr-i-Bihisht, is channeled up from the river with a hydraulic system through the tower and then carried by channels into various other buildings of the fort. Adjacent to the south of the tower is a white marble pavilion that was constructed during Aurangzeb's rule. The pavilion features five arches supported on fluted columns and with low whale back roofs. In the centre of the north wall is a marble cascade sloping into a scalloped basin. [1]

Muhi-ud-Din Muhammad, commonly known by the sobriquet Aurangzeb or by his regnal title Alamgir, was the sixth Mughal emperor, who reigned for a period of 49 years from 1658 until his death in 1707. He is widely considered to be the last effective Mughal emperor.
The tower was damaged during the Indian Rebellion of 1857 and again during a heavy earthquake in 1904. Originally there was a chhatri that is now missing. The tower and pavilion have been undergoing renovation work for many years and are closed to the public. [1]

The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major, but ultimately unsuccessful, uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the form of a mutiny of sepoys of the Company's army in the garrison town of Meerut, 40 miles northeast of Delhi. It then erupted into other mutinies and civilian rebellions chiefly in the upper Gangetic plain and central India, though incidents of revolt also occurred farther north and east. The rebellion posed a considerable threat to British power in that region, and was contained only with the rebels' defeat in Gwalior on 20 June 1858. On 1 November 1858, the British granted amnesty to all rebels not involved in murder, though they did not declare the hostilities formally to have ended until 8 July 1859. The rebellion is known by many names, including the Sepoy Mutiny, the Indian Mutiny, the Great Rebellion, the Revolt of 1857, the Indian Insurrection, and the First War of Independence.

Chhatris, are elevated, dome-shaped pavilions used as an element in Indian architecture. The word Chhatri means "canopy" or "umbrella." In the context of architecture, the word is used to refer to two different things. The usual and more widely understood meaning is of a memorial, usually very ornate, built over the site where the funeral (cremation) of an important personage was performed. Such memorials usually consist of a platform girded by a set of ornate pillars which hold up a stone canopy. The word chhatri is also used to refer to the small pavilions that mark the corners and roof of the entrance of a major building. These pavilions are purely decorative and have no utility, but are a classic folly displaying the status and wealth of the owner.
On the south-eastern corner is the Asad Burj, which is a similar tower. [1]