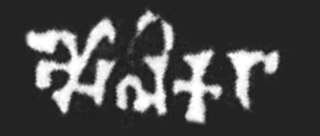Chandragupta II, also known by his title Vikramaditya, as well as Chandragupta Vikramaditya, was the third ruler of the Gupta Empire in India. Modern scholars generally identify him with King Chandra of the Delhi iron pillar inscription.

The Pratihara dynasty, also called the Gurjara-Pratiharas, the Pratiharas of Kannauj or the Imperial Pratiharas, was a prominent medieval Indian dynasty which ruled over the Kingdom of Kannauj. It initially ruled the Gurjaradesa until its victory in the Tripartite Struggle in 816 which secured its right to the throne of Kannauj. Cadet branches of the dynasty ruled other minor states in the subcontinent.

Mandu or Mandavgad is an ancient city in the present-day Mandav area of the Dhar district. It is located in the Malwa and Nimar region of western Madhya Pradesh, India, at 35 km from Dhar city. In the 11th century, Mandu was the sub division of the Tarangagadh or Taranga kingdom. This fortress town on a rocky outcrop about 100 km (62 mi) from Indore is celebrated for its architecture.
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central parts of India, between 35 and 415 CE. The Western Satraps were contemporaneous with the Kushans who ruled the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, and were possibly vassals of the Kushans. They were also contemporaneous with the Satavahana who ruled in Central India. They are called "Western Satraps" in modern historiography in order to differentiate them from the "Northern Satraps", who ruled in Punjab and Mathura until the 2nd century CE.

The Vakataka dynasty was an ancient Indian dynasty that originated from the Deccan in the mid-3rd century CE. Their state is believed to have extended from the southern edges of Malwa and Gujarat in the north to the Tungabhadra River in the south as well as from the Arabian Sea in the west to the edges of Chhattisgarh in the east. They were the most important successors of the Satavahanas in the Deccan and contemporaneous with the Guptas in northern India.
Parantaka II was a Chola emperor. He is also known as Sundara Chola as he was considered an epitome of male beauty. He was the son of Arinjaya Chola and queen Kalyani, a princess of Vaidumba family. Parantaka II ascended the Chola throne despite the fact that his cousin Madurantaka Uttama Chola, the son of Gandaraditya Chola was alive and he had equal if not more claim to the Chola throne. During his reign, Parantaka Sundara Chola defeated the Pandyas and Ceylon and then recaptured the Tondaimandalam from Rashtrakutas.

The Telugu Chodas or Telugu Cholas were rulers who ruled parts of present-day Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and southern Odissa between the 5th to 15th centuries as samantas (vassals) of the Pallavas, and later as vassals of the Imperial Cholas. There are many branches like Renati Chodas, Pottapi Chodas, Konidena Chodas, Nannuru Chodas, Nellore Chodas and Kunduru Chodas. They claimed descent from the early Chola Tamil king Karikala Chola.

Chittorgarh, also known as Chittod Fort, is one of the largest forts in India. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The fort was the capital of Mewar and is located in the present-day city of Chittorgarh. It sprawls over a hill 180 m (590.6 ft) in height spread over an area of 280 ha above the plains of the valley drained by the Berach River. The fort covers 65 historic structures, which include four palaces, 19 large temples, 20 large water bodies, 4 memorials and a few victory towers.

The history of human settlement in the western Indian state of Rajasthan dates back to about 100,000 years ago. Around 5000 to 2000 BCE many regions of Rajasthan belonged as the site of the Indus Valley Civilization. Kalibangan is the main Indus site of Rajasthan, here fire altars have been discovered, similar to those found at Lothal.

Bastar state was a princely state in India during the British Raj. It was founded in the early 13th century by Annamaraja, a brother of the last ruler of the Kakatiya dynasty, Prataparudra II.

The House of Paramara was a prominent Indian Rajput dynasty that ruled over the Kingdom of Malwa, the Garhwal Kingdom, and many other kingdoms, princely states and feudal estates in North India. They belonged to the Parmara clan of the Rajputs.
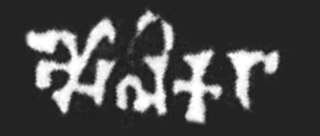
The Aulikaras, were an ancient clan that ruled the Kingdom of Malwa between the 4th-century CE and 6th-century CE.

Ravivarman, styled Maharaja Ravivarman, Kulasekhara was the ruler of Venatu, with capital at port Kolambam (Quilon), southern India between 1299 – 1316/7. He – in all likelihood – was a descendant of the ancient Cheras. and was the son-in-law of the Pandya ruler of Maravarman Kulasekhara. Ravivarman raided large parts of southern India in a short period by skillfully taking advantage of the weakening of the Pandya kingdom and the confusion prevailed after the Khalji raids (1311).
The history of human settlement in the west Indian state of Rajasthan dates back to about 5,000 years ago.

The Kalachuris of Tripuri, also known the Kalachuris of Chedi, ruled parts of central India during 7th to 13th centuries. They are also known as the Later Kalachuris to distinguish them from their earlier namesakes, especially the Kalachuris of Mahishmati. Their core territory included the historical Chedi region, and their capital was located at Tripuri.

The Kalachuris of Mahismati, or the Early Kalachuris, were an early medieval Indian dynasty that ruled present-day Maharashtra, as well as parts of mainland Gujarat and southern Madhya Pradesh. Their capital was located at Mahishmati. Epigraphic and numismatic evidence suggests that the earliest of the Ellora and Elephanta cave monuments were built during the Kalachuri rule.
The Shailodbhava dynasty ruled parts of eastern India during the 6th-8th centuries. Their core territory was known as Kongoda-mandala, and included parts of the present-day Ganjam, Khordha and Puri districts in the Odisha state. Their capital was located at Kongoda, which is identified with modern Banapur.

Kongu Chera dynasty, or Cheras of Kongu or Karur, or simply as the Chera dynasty, were a medieval royal lineage in south India, initially ruling over western Tamil Nadu and central Kerala. The headquarters of the Kongu Cheras was located at Karur in central Tamil Nadu. The Chera rulers of Kongu were subordinate to or conquered by Pallava, Pandya and Chola rulers are also said to have overrun the Kongu Chera country.
The Second Aulikara dynasty was a royal dynasty that ruled over the Kingdom of Malwa, and at its peak under Yashodharman Vishnuvardhana controlled a vast area, consisting of almost all of Northern India and parts of Deccan plateau. It was the second royal house of the Aulikara clan.