Related Research Articles
Swing music is a style of jazz that developed in the United States during the late 1920s and early '30s. It became nationally popular from the mid-1930s. The name derived from its emphasis on the off-beat, or nominally weaker beat. Swing bands usually featured soloists who would improvise on the melody over the arrangement. The danceable swing style of big bands and bandleaders such as Benny Goodman was the dominant form of American popular music from 1935 to 1946, known as the swing era, when people were dancing the Lindy Hop. The verb "to swing" is also used as a term of praise for playing that has a strong groove or drive. Musicians of the swing era include Duke Ellington, Benny Goodman, Count Basie, Cab Calloway, Jimmy Dorsey, Tommy Dorsey, Woody Herman, Harry James, Lionel Hampton, Glenn Miller, Artie Shaw, Jimmie Lunceford, and Django Reinhardt.

James Fletcher Hamilton Henderson was an American pianist, bandleader, arranger and composer, important in the development of big band jazz and swing music. He was one of the most prolific black musical arrangers and, along with Duke Ellington, is considered one of the most influential arrangers and bandleaders in jazz history. Henderson's influence was vast. He helped bridge the gap between the Dixieland and the swing eras. He was often known as "Smack" Henderson.

Coleman Randolph Hawkins, nicknamed "Hawk" and sometimes "Bean", was an American jazz tenor saxophonist. One of the first prominent jazz musicians on his instrument, as Joachim E. Berendt explained: "there were some tenor players before him, but the instrument was not an acknowledged jazz horn". Hawkins biographer John Chilton described the prevalent styles of tenor saxophone solos prior to Hawkins as "mooing" and "rubbery belches". Hawkins denied being first and noted his contemporaries Happy Caldwell, Stump Evans, and Prince Robinson, although he was the first to tailor his method of improvisation to the saxophone rather than imitate the techniques of the clarinet. Hawkins' virtuosic, arpeggiated approach to improvisation, with his characteristic rich, emotional, and vibrato-laden tonal style, was the main influence on a generation of tenor players that included Chu Berry, Charlie Barnet, Tex Beneke, Ben Webster, Vido Musso, Herschel Evans, Buddy Tate, and Don Byas, and through them the later tenormen, Arnett Cobb, Illinois Jacquet, Flip Phillips, Ike Quebec, Al Sears, Paul Gonsalves, and Lucky Thompson. While Hawkins became known with swing music during the big band era, he had a role in the development of bebop in the 1940s.

The Jazz Age was a period in the 1920s and 1930s in which jazz music and dance styles gained worldwide popularity. The Jazz Age's cultural repercussions were primarily felt in the United States, the birthplace of jazz. Originating in New Orleans as mainly sourced from the culture of African Americans, jazz played a significant part in wider cultural changes in this period, and its influence on popular culture continued long afterwards.

George Gard "Buddy" DeSylva was an American songwriter, film producer and record executive. He wrote or co-wrote many popular songs, and along with Johnny Mercer and Glenn Wallichs, he co-founded Capitol Records.
James Wesley "Bubber" Miley was an American early jazz trumpet and cornet player, specializing in the use of the plunger mute.
"King Porter Stomp" is a jazz standard by pianist Jelly Roll Morton, first recorded in 1923. The composition is considered to be important in the development of jazz. It became a hit during the swing era, when it was recorded by Benny Goodman.
Rosa Henderson was an American jazz and classic female blues singer and vaudeville entertainer of the Harlem Renaissance era.

"Chinatown, My Chinatown" is a popular song written by William Jerome (words) and Jean Schwartz (music) in 1906 and later interpolated into the musical Up and Down Broadway (1910). The song has been recorded by numerous artists and is considered an early jazz standard.
In music and jazz harmony, the Stomp progression is an eight-bar chord progression named for its use in the "stomp" section of the composition "King Porter Stomp" (1923) by Jelly Roll Morton. The composition was later arranged by Fletcher Henderson, adding greater emphasis on the Trio section, containing a highly similar harmonic loop to that found in the Stomp section. It was one of the most popular tunes of the swing era, and the Stomp progression was often used.
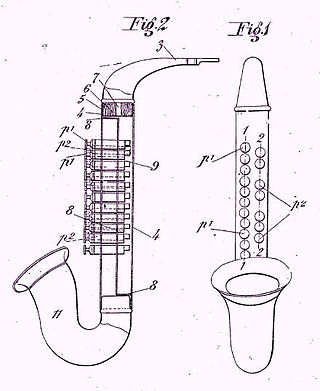
The couesnophone, also known as the goofus or queenophone, is a free-reed musical instrument resembling a saxophone harmonicor. Its reeds vibrate when the desired keys are activated and the player blows through a tube. "Best described as a mouth-blown accordion," "it sounded like a cross between a harmonica and an accordion." French manufacturer Couesnon was awarded patent no. 569294 in 1924 for an instrument that was described as a saxophone jouet. However, the couesnophone is a polyphonic instrument, while the saxophone is monophonic.

"How Come You Do Me Like You Do?" is a song written by vaudeville comedy duo Gene Austin and Roy Bergere in 1924. It has later been covered by many artists, and is considered a jazz standard.

The period from the end of the First World War until the start of the Depression in 1929 is known as the "Jazz Age". Jazz had become popular music in America, although older generations considered the music immoral and threatening to cultural values. Dances such as the Charleston and the Black Bottom were very popular during the period, and jazz bands typically consisted of seven to twelve musicians. Important orchestras in New York were led by Fletcher Henderson, Paul Whiteman and Duke Ellington. Many New Orleans jazzmen had moved to Chicago during the late 1910s in search of employment; among others, the New Orleans Rhythm Kings, King Oliver's Creole Jazz Band and Jelly Roll Morton recorded in the city. However, Chicago's importance as a center of jazz music started to diminish toward the end of the 1920s in favor of New York.
Catherine "Katie" Crippen, also billed as Little Katie Crippen or Ella White, was an American entertainer and singer.

"A Pretty Girl Is Like A Melody" is a popular song written by Irving Berlin in 1919 which became the theme song of the Ziegfeld Follies. The first verse and refrain are considered part of the Great American Songbook and are often covered as a jazz standard.

Copenhagen is a jazz standard composed in 1924 by bandleader Charlie Davis and first recorded in that year by the Wolverine Orchestra featuring Bix Beiderbecke in a foxtrot tempo. The title refers to Copenhagen tobacco, favored by Davis's bass player. Lyrics were added by Walter Melrose to the tune, which is a blues in B-flat.

Clarinet Marmalade, later Clarinet Marmalade Blues, is a 1918 dixieland jazz standard composed by Larry Shields and Henry Ragas of the Original Dixieland Jass Band. It is played in the key of F major. It was recorded by Fletcher Henderson in 1926 and Frankie Trumbauer in 1927.

"Tar Paper Stomp" is a 1930 jazz recording by American bandleader and jazz trumpeter Wingy Manone. The instrumental featured a riff that was used in the subsequent releases "Hot and Anxious", "There's Rhythm in Harlem", "In the Mood", "Hot String Beans", and in 1939 in "Jumpy Nerves".
References
- 1 2 "Shanghai Shuffle / Naughty Man", rateyourmusic.com
- ↑ "Shanghai Shuffle – Fletcher Henderson & His Orchestra", 20sjazz.com
- ↑ Schuller, Gunther (1968). The History of Jazz. Oxford University Press. p. 259.
- ↑ Magee, Jeffrey (13 January 2005). The Uncrowned King of Swing: Fletcher Henderson and Big Band Jazz. Oxford University Press. p. 185. ISBN 978-0-19-509022-2.