Related Research Articles

Differential geometry is a mathematical discipline that studies the geometry of smooth shapes and smooth spaces, otherwise known as smooth manifolds. It uses the techniques of differential calculus, integral calculus, linear algebra and multilinear algebra. The field has its origins in the study of spherical geometry as far back as antiquity. It also relates to astronomy, the geodesy of the Earth, and later the study of hyperbolic geometry by Lobachevsky. The simplest examples of smooth spaces are the plane and space curves and surfaces in the three-dimensional Euclidean space, and the study of these shapes formed the basis for development of modern differential geometry during the 18th and 19th centuries.
In the mathematical field of geometric topology, the Poincaré conjecture is a theorem about the characterization of the 3-sphere, which is the hypersphere that bounds the unit ball in four-dimensional space.

Riemannian geometry is the branch of differential geometry that studies Riemannian manifolds, defined as smooth manifolds with a Riemannian metric. This gives, in particular, local notions of angle, length of curves, surface area and volume. From those, some other global quantities can be derived by integrating local contributions.
In mathematics, Thurston's geometrization conjecture states that each of certain three-dimensional topological spaces has a unique geometric structure that can be associated with it. It is an analogue of the uniformization theorem for two-dimensional surfaces, which states that every simply connected Riemann surface can be given one of three geometries . In three dimensions, it is not always possible to assign a single geometry to a whole topological space. Instead, the geometrization conjecture states that every closed 3-manifold can be decomposed in a canonical way into pieces that each have one of eight types of geometric structure. The conjecture was proposed by William Thurston (1982), and implies several other conjectures, such as the Poincaré conjecture and Thurston's elliptization conjecture.

Grigori Yakovlevich Perelman is a Russian mathematician who is known for his contributions to the fields of geometric analysis, Riemannian geometry, and geometric topology. In 2005, Perelman abruptly quit his research job at the Steklov Institute of Mathematics, and in 2006 stated that he had quit professional mathematics, due to feeling disappointed over the ethical standards in the field. He lives in seclusion in Saint Petersburg, and has not accepted offers for interviews since 2006.
In Riemannian geometry, the sectional curvature is one of the ways to describe the curvature of Riemannian manifolds. The sectional curvature K(σp) depends on a two-dimensional linear subspace σp of the tangent space at a point p of the manifold. It can be defined geometrically as the Gaussian curvature of the surface which has the plane σp as a tangent plane at p, obtained from geodesics which start at p in the directions of σp. The sectional curvature is a real-valued function on the 2-Grassmannian bundle over the manifold.
In the mathematical field of Riemannian geometry, the scalar curvature is a measure of the curvature of a Riemannian manifold. To each point on a Riemannian manifold, it assigns a single real number determined by the geometry of the metric near that point. It is defined by a complicated explicit formula in terms of partial derivatives of the metric components, although it is also characterized by the volume of infinitesimally small geodesic balls. In the context of the differential geometry of surfaces, the scalar curvature is twice the Gaussian curvature, and completely characterizes the curvature of a surface. In higher dimensions, however, the scalar curvature only represents one particular part of the Riemann curvature tensor.
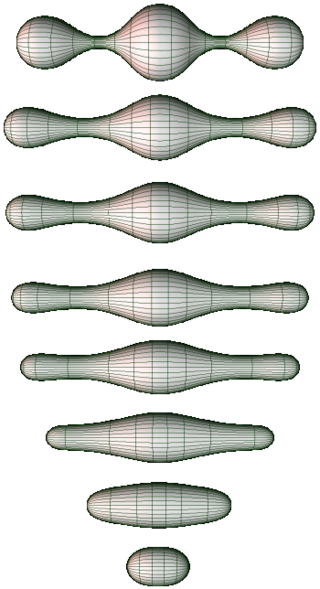
In the mathematical fields of differential geometry and geometric analysis, the Ricci flow, sometimes also referred to as Hamilton's Ricci flow, is a certain partial differential equation for a Riemannian metric. It is often said to be analogous to the diffusion of heat and the heat equation, due to formal similarities in the mathematical structure of the equation. However, it is nonlinear and exhibits many phenomena not present in the study of the heat equation.

Shing-Tung Yau is a Chinese-American mathematician and the William Caspar Graustein Professor of Mathematics at Harvard University. In April 2022, Yau announced retirement from Harvard to become Chair Professor of mathematics at Tsinghua University.

In mathematics, low-dimensional topology is the branch of topology that studies manifolds, or more generally topological spaces, of four or fewer dimensions. Representative topics are the structure theory of 3-manifolds and 4-manifolds, knot theory, and braid groups. This can be regarded as a part of geometric topology. It may also be used to refer to the study of topological spaces of dimension 1, though this is more typically considered part of continuum theory.

Richard Streit Hamilton is an American mathematician who serves as the Davies Professor of Mathematics at Columbia University. He is known for contributions to geometric analysis and partial differential equations. Hamilton is best known for foundational contributions to the theory of the Ricci flow and the development of a corresponding program of techniques and ideas for resolving the Poincaré conjecture and geometrization conjecture in the field of geometric topology. Grigori Perelman built upon Hamilton's results to prove the conjectures, and was awarded a Millennium Prize for his work. However, Perelman declined the award, regarding Hamilton's contribution as being equal to his own.

Mikhael Leonidovich Gromov is a Russian-French mathematician known for his work in geometry, analysis and group theory. He is a permanent member of Institut des Hautes Études Scientifiques in France and a professor of mathematics at New York University.
In mathematics, the soul theorem is a theorem of Riemannian geometry that largely reduces the study of complete manifolds of non-negative sectional curvature to that of the compact case. Jeff Cheeger and Detlef Gromoll proved the theorem in 1972 by generalizing a 1969 result of Gromoll and Wolfgang Meyer. The related soul conjecture, formulated by Cheeger and Gromoll at that time, was proved twenty years later by Grigori Perelman.
In mathematics, Hopf conjecture may refer to one of several conjectural statements from differential geometry and topology attributed to Heinz Hopf.

Tian Gang is a Chinese mathematician. He is a professor of mathematics at Peking University and Higgins Professor Emeritus at Princeton University. He is known for contributions to the mathematical fields of Kähler geometry, Gromov-Witten theory, and geometric analysis.

Thierry Aubin was a French mathematician who worked at the Centre de Mathématiques de Jussieu, and was a leading expert on Riemannian geometry and non-linear partial differential equations. His fundamental contributions to the theory of the Yamabe equation led, in conjunction with results of Trudinger and Schoen, to a proof of the Yamabe Conjecture: every compact Riemannian manifold can be conformally rescaled to produce a manifold of constant scalar curvature. Along with Yau, he also showed that Kähler manifolds with negative first Chern classes always admit Kähler–Einstein metrics, a result closely related to the Calabi conjecture. The latter result, established by Yau, provides the largest class of known examples of compact Einstein manifolds. Aubin was the first mathematician to propose the Cartan–Hadamard conjecture.
In geometry, Alexandrov spaces with curvature ≥ k form a generalization of Riemannian manifolds with sectional curvature ≥ k, where k is some real number. By definition, these spaces are locally compact complete length spaces where the lower curvature bound is defined via comparison of geodesic triangles in the space to geodesic triangles in standard constant-curvature Riemannian surfaces.
The Geometry Festival is an annual mathematics conference held in the United States.

John William Lott is a professor of Mathematics at the University of California, Berkeley. He is known for contributions to differential geometry.
In mathematics, the Cartan–Hadamard conjecture is a fundamental problem in Riemannian geometry and Geometric measure theory which states that the classical isoperimetric inequality may be generalized to spaces of nonpositive sectional curvature, known as Cartan–Hadamard manifolds. The conjecture, which is named after French mathematicians Élie Cartan and Jacques Hadamard, may be traced back to work of André Weil in 1926.
References
- ↑ Sharafutdinov, V. A. (1979), "Convex sets in a manifold of nonnegative curvature", Mathematical Notes, 26 (1): 556–560, doi:10.1007/BF01140282, S2CID 119764156
- ↑ Perelman, Grigori (1994), "Proof of the soul conjecture of Cheeger and Gromoll", Journal of Differential Geometry, 40 (1): 209–212, doi: 10.4310/jdg/1214455292 , MR 1285534