
The Snake River is a major river of the greater Pacific Northwest region in the United States. At 1,078 miles (1,735 km) long, it is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, in turn the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean. The Snake River rises in western Wyoming, then flows through the Snake River Plain of southern Idaho, the rugged Hells Canyon on the Oregon–Idaho border and the rolling Palouse Hills of Washington, emptying into the Columbia River at the Tri-Cities, Washington.

The Yakima River is a tributary of the Columbia River in south central and eastern Washington state, named for the indigenous Yakama people. The length of the river from headwaters to mouth is 214 miles (344 km), with an average drop of 9.85 feet per mile (1.866 m/km). It is the longest river entirely in Washington state.

The Bruneau River is a 153-mile-long (246 km) tributary of the Snake River, in the U.S. states of Idaho and Nevada. It runs through a narrow canyon cut into ancient lava flows in southwestern Idaho. The Bruneau Canyon, which is up to 1,200 feet (370 m) deep and 40 miles (64 km) long, features rapids and hot springs, making it a popular whitewater trip.

The Tongue River is a tributary of the Yellowstone River, approximately 265 mi (426 km) long, in the U.S. states of Wyoming and Montana. The Tongue rises in Wyoming in the Big Horn Mountains, flows through northern Wyoming and southeastern Montana and empties into the Yellowstone River at Miles City, Montana. Most of the course of the river is through the beautiful and varied landscapes of eastern Montana, including the Tongue River Canyon, the Tongue River breaks, the pine hills of southern Montana, and the buttes and grasslands that were formerly the home of vast migratory herds of American bison. The Tongue River watershed encompasses parts of the Cheyenne and Crow Reservations. The Headwaters lie on the Big Horn National Forest, and the watershed encompasses the Ashland Ranger District of the Custer National Forest.

The Merced River, in the central part of the U.S. state of California, is a 145-mile (233 km)-long tributary of the San Joaquin River flowing from the Sierra Nevada into the San Joaquin Valley. It is most well known for its swift and steep course through the southern part of Yosemite National Park, where it is the primary watercourse flowing through Yosemite Valley. The river's character changes dramatically once it reaches the plains of the agricultural San Joaquin Valley, where it becomes a slow-moving meandering stream.

The Little Bighorn River is a 138-mile-long (222 km) tributary of the Bighorn River in the United States in the states of Montana and Wyoming. The Battle of the Little Bighorn, also known as the Battle of the Greasy Grass, was fought on its banks on June 25, in 1876, as well as the Battle of Crow Agency in 1887.

The Bighorn Mountains are a mountain range in northern Wyoming and southern Montana in the United States, forming a northwest-trending spur from the Rocky Mountains extending approximately 200 miles (320 km) northward on the Great Plains. They are separated from the Absaroka Range, which lie on the main branch of the Rockies in western Wyoming, by the Bighorn Basin. Much of the land is contained within the Bighorn National Forest.
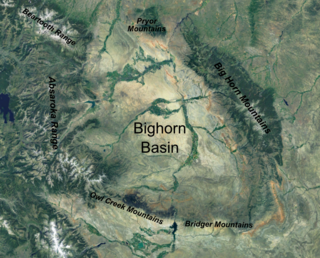
The Bighorn Basin is a plateau region and intermontane basin, approximately 100 miles (160 km) wide, in north-central Wyoming in the United States. It is bounded by the Absaroka Range on the west, the Bighorn Mountains on the east, and the Owl Creek Mountains and Bridger Mountains on the south. It is drained to the north by tributaries of the Bighorn River, which enters the basin from the south, through a gap between the Owl Creek and Bridger Mountains, as the Wind River, and becomes the Bighorn as it enters the basin. The region is semi-arid, receiving only 6–10 in (15–25 cm) of rain annually.

The Bighorn National Forest is a U.S. National Forest located in northern Wyoming, United States and consists of over 1.1 million acres (4,500 km²). Created as a US Forest Reserve in 1897, it is one of the oldest government-protected forest lands in the U.S. The forest is well east of the continental divide and extends from the Montana border for a distance of 80 miles (130 km) along the spine of the Bighorn Mountains, an outlying mountain range separated from the rest of the Rocky Mountains by Bighorn Basin. Elevations range from 5,000 feet along the sagebrush and grass-covered lowlands at the foot of the mountains, to 13,189 feet on top of Cloud Peak, the highest point in the Bighorn Mountains. Around 99% of the land is above 1,500 metres (4,900 ft). The forest is named after the Bighorn River, which is partially fed by streams found in the forest. Streams in the range are fed primarily by snowmelt and snowmelt mixed with driving rainfall.

Eagle Creek is a creek located in Hood River County, Oregon, in the Columbia River Gorge. A tributary of the Columbia River, the creek flows for approximately 15 miles (24 km) from the Thrush Pond between Eagle Butte and Tanner Butte to its mouth near Bonneville Dam. The East Fork Eagle Creek is a major tributary that begins at Wahtum Lake and joins the main stem approximately 2/3 the way between the Thrush Pond and the Columbia River, separated by Indian Mountain.

Bowman Creek is a tributary of the Susquehanna River in Luzerne County and Wyoming County, in Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is approximately 26 miles (42 km) long and flows through Ross Township and Lake Township in Luzerne County and Noxen Township, Monroe Township, and Eaton Township in Wyoming County. The watershed of the creek has an area of 120 square miles (310 km2). The creek is not designated as an impaired waterbody and its pH is close to neutral, although it has experienced some problems with acid rain. It has low concentrations of dissolved solids like calcium. The creek is relatively small in its upper reaches, but by Noxen, its width is 40 to 60 feet. It is also relatively shallow in many reaches. Rock formations in the watershed include the Catskill Formation, the Huntley Mountain Formation, Burgoon Sandstone, the Mauch Chunk Formation, the Pottsville Group, and the Pocono Formation. Soil associations in the creek's watershed include the Wellsboro-Morris-Oquaga association, the Oquaga-Lackawanna-Arnot association, the Mardin-Bath-Volusia association, and the Wyoming-Pope association.

Wind River Canyon is a scenic Wyoming canyon on the Wind River. It is located between the towns of Shoshoni and Thermopolis and is a popular stop for visitors to Yellowstone National Park. It is accessible by U.S. Highway 20 and Wyoming Highway 789. It was designated as a Wyoming Scenic Byway in 2005.

Yellowtail Dam is a dam across the Bighorn River in south central Montana in the United States. The mid-1960s era concrete arch dam serves to regulate the flow of the Bighorn for irrigation purposes and to generate hydroelectric power. The dam and its reservoir, Bighorn Lake, are owned by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation.

San Juan Creek, also called the San Juan River, is a 29-mile (47 km) long stream in Orange County, California draining a watershed of 133.9 square miles (347 km2). Its mainstem begins in the southern Santa Ana Mountains in the Cleveland National Forest. It winds west and south through San Juan Canyon, and is joined by Arroyo Trabuco as it passes through San Juan Capistrano. It flows into the Pacific Ocean at Doheny State Beach. San Juan Canyon provides a major part of the route for California State Route 74.

The Wenaha–Tucannon Wilderness is a federally designated wilderness area in the Blue Mountains of northeastern Oregon, and southeastern Washington, United States. It was created by the Endangered American Wilderness Act of 1978 and encompasses 177,423 acres (71,801 ha) in the Umatilla National Forest — 66,375 acres (26,861 ha) in Oregon and 111,048 acres (44,940 ha) in Washington.
In the U.S. state of Wyoming, U.S. Highway 14 runs east to west across the northern part of the state. The road connects South Dakota on the east with Yellowstone National Park on the west. It is mostly a two lane surface road except for several sections that it shares with Interstate 90.

Salmon Falls Creek is a tributary of the Snake River, flowing from northern Nevada into Idaho in the United States. Formed in high mountains at the northern edge of the Great Basin, Salmon Falls Creek flows northwards 121 miles (195 km), draining an arid and mountainous basin of 2,103 square miles (5,450 km2). The Salmon Falls Creek valley served as a trade route between the Native American groups of the Snake River Plain and Great Basin. Today, most of its water is used for irrigation.

The San Juan-Chama Project is a U.S. Bureau of Reclamation interbasin water transfer project located in the states of New Mexico and Colorado in the United States. The project consists of a series of tunnels and diversions that take water from the drainage basin of the San Juan River – a tributary of the Colorado River – to supplement water resources in the Rio Grande watershed. The project furnishes water for irrigation and municipal water supply to cities along the Rio Grande including Albuquerque and Santa Fe.

The Colorado River is a major river of the western United States and northwest Mexico in North America. Its headwaters are in the Rocky Mountains where La Poudre Pass Lake is its source. Located in north central Colorado it flows southwest through the Colorado Plateau country of western Colorado, southeastern Utah and northwestern Arizona where it flows through the Grand Canyon. It turns south near Las Vegas, Nevada, forming the Arizona–Nevada border in Lake Mead and the Arizona–California border a few miles below Davis Dam between Laughlin, Nevada and Needles, California California before entering Mexico in the Colorado Desert. Most of its waters are diverted into the Imperial Valley of Southern California. In Mexico its course forms the boundary between Sonora and Baja California before entering the Gulf of California. This article describes most of the major features along the river.

























