Computer software, or simply software, is a collection of data or computer instructions that tell the computer how to work. This is in contrast to physical hardware, from which the system is built and actually performs the work. In computer science and software engineering, computer software is all information processed by computer systems, programs and data. Computer software includes computer programs, libraries and related non-executable data, such as online documentation or digital media. Computer hardware and software require each other and neither can be realistically used on its own.

JavaScript, often abbreviated as JS, is a high-level, interpreted programming language that conforms to the ECMAScript specification. It is a language that is also characterized as dynamic, weakly typed, prototype-based and multi-paradigm.

Adobe Photoshop is a raster graphics editor developed and published by Adobe Inc. for macOS and Windows. It was originally created in 1988 by Thomas and John Knoll. Since then, it has become the de facto industry standard in raster graphics editing, to the point that it has also become a generic trademark leading to its use as a verb such as "to photoshop an image", "photoshopping", and "photoshop contest", although Adobe discourages such use. Photoshop can edit and compose raster images in multiple layers and supports masks, alpha compositing, and several color models including RGB, CMYK, CIELAB, spot color, and duotone. Photoshop uses its own PSD and PSB file formats to support these features. In addition to raster graphics, Photoshop has limited abilities to edit or render text, vector graphics, 3D graphics, and video. Its feature set can be expanded by Photoshop plug-ins, programs developed and distributed independently of Photoshop that can run inside it and offer new or enhanced features.

In computer networks, a proxy server is a server that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from other servers. A client connects to the proxy server, requesting some service, such as a file, connection, web page, or other resource available from a different server and the proxy server evaluates the request as a way to simplify and control its complexity. Proxies were invented to add structure and encapsulation to distributed systems.
Avant Browser is a freeware web browser from a Chinese programmer named Anderson Che, which unites the Trident layout engine built into Windows with an interface intended to be more feature-rich, flexible and ergonomic than Microsoft's Internet Explorer (IE). It runs on Windows 2000 and above, including Windows 8, Windows 8.1 and Windows 10. Internet Explorer versions 6 through 11 are supported.
In software engineering, the terms front end and back end refer to the separation of concerns between the presentation layer, and the data access layer of a piece of software, or the physical infrastructure or hardware. In the client–server model, the client is usually considered the front end and the server is usually considered the back end, even when some presentation work is actually done on the server itself.

Dashboard is an application for Apple Inc.'s macOS operating systems, used as a secondary desktop for hosting mini-applications known as widgets. These are intended to be simple applications that do not take time to launch. Dashboard applications supplied with macOS include a stock ticker, weather report, calculator and notepad; users can create or download their own.
Here are some of the features that distinguish Mozilla Firefox from other web browsers, such as Internet Explorer.
In computing, Java Web Start is a framework developed by Sun Microsystems that allows users to start application software for the Java Platform directly from the Internet using a web browser. Some key benefits of this technology include seamless version updating for globally distributed applications and greater control of memory allocation to the Java virtual machine.

Google Web Toolkit, or GWT Web Toolkit, is an open-source set of tools that allows web developers to create and maintain complex JavaScript front-end applications in Java. Other than a few native libraries, everything is Java source that can be built on any supported platform with the included GWT Ant build files. It is licensed under the Apache License version 2.0.

Web mapping is the process of using the maps delivered by geographic information systems (GIS) in World Wide Web. A web map on the World Wide Web is both served and consumed, thus web mapping is more than just web cartography, it is a service by which consumers may choose what the map will show. Web GIS emphasizes geodata processing aspects more involved with design aspects such as data acquisition and server software architecture such as data storage and algorithms, than it does the end-user reports themselves.
Unobtrusive JavaScript is a general approach to the use of JavaScript in web pages. Though the term is not formally defined, its basic principles are generally understood to include:
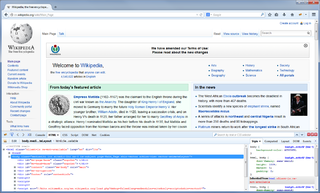
Firebug is a discontinued free and open-source web browser extension for Mozilla Firefox that facilitated the live debugging, editing, and monitoring of any website's CSS, HTML, DOM, XHR, and JavaScript.
Open Wonderland is a Java open-source toolkit for creating collaborative 3D virtual worlds. Within those worlds, users can communicate with high-fidelity, immersive audio, share live desktop applications and documents and conduct real business. Open Wonderland is completely extensible; developers and graphic artists can extend its functionality to create entirely new worlds and add new features to existing worlds.

Epesi is an open source, PHP/Ajax framework for rapid development of web based, database driven applications. The framework includes the Epesi CRM multiuser application. It requires PHP 5.x and MySQL or PostgreSQL database server on the server side and can be accessed using any modern browser. Epesi framework and Epesi CRM application are released under MIT license.
The Facebook Platform is the set of services, tools, and products provided by the social networking service Facebook for third-party developers to create their own applications and services that access data in Facebook.

WorldWide Telescope (WWT) is an open-source set of applications, data and cloud services, originally created by Microsoft Research but now an open source project hosted on GitHub. The .NET Foundation holds the copyright and the project is managed by the American Astronomical Society and has been supported by grants from the Moore Foundation and National Science Foundation. WWT displays astronomical, earth and planetary data allowing visual navigation through the 3-dimensional (3D) Universe. Users are able to navigate the sky by panning and zooming, or explore the 3D universe from the surface of Earth to past the Cosmic microwave background (CMB), viewing both visual imagery and scientific data about that area and the objects in it. Data is curated from hundreds of different data sources, but its open data nature allows users to explore any third party data that conforms to a WWT supported format. With the rich source of multi-spectral all-sky images it is possible to view the sky in many wavelengths of light. The software utilizes Microsoft's Visual Experience Engine technologies to function. WWT can also be used to visualize arbitrary or abstract data sets and time series data.
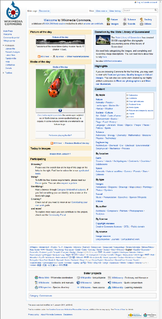
A web page is a document that is suitable to act as a web resource on the World Wide Web. When accessed by a web browser it may be displayed as a web page on a monitor or mobile device.

Google Docs is a word processor included as part of a free, web-based software office suite offered by Google within its Google Drive service. This service also includes Google Sheets and Google Slides, a spreadsheet and presentation program respectively. Google Docs is available as a web application, mobile app for Android, iOS, Windows, BlackBerry, and as a desktop application on Google's ChromeOS. The app is compatible with Microsoft Office file formats. The application allows users to create and edit files online while collaborating with other users in real-time. Edits are tracked by user with a revision history presenting changes. An editor's position is highlighted with an editor-specific color and cursor. A permissions system regulates what users can do. Updates have introduced features using machine learning, including "Explore", offering search results based on the contents of a document, and "Action items", allowing users to assign tasks to other users.