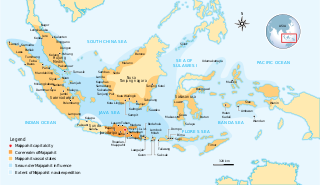
Majapahit, also known as Wilwatikta, was a Javanese Hindu-Buddhist thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was based on the island of Java. It existed from 1292 to c. 1527 and reached its peak during the era of the queen Tribhuvana and her son Hayam Wuruk, whose reigns in the mid-14th century were marked by conquests that extended throughout Southeast Asia. This achievement is also credited to the famous prime minister Gajah Mada. According to the Deśavarṇana written in 1365, Majapahit was an empire of 98 tributaries, stretching from Sumatra to New Guinea; including territories in present-day Indonesia, Singapore, Malaysia, Brunei, southern Thailand, Timor Leste, southwestern Philippines although the scope of Majapahit sphere of influence is still the subject of debate among historians. The nature of Majapahit's relations and influence upon its overseas vassals and also its status as an empire still provokes discussion.

Srivijaya, also spelled Sri Vijaya, was a Buddhist thalassocratic empire based on the island of Sumatra that influenced much of Southeast Asia. Srivijaya was an important centre for the expansion of Buddhism from the 7th to 11th century AD. Srivijaya was the first polity to dominate much of western Maritime Southeast Asia. Due to its location, Srivijaya developed complex technology utilizing maritime resources. In addition, its economy became progressively reliant on the booming trade in the region, thus transforming it into a prestige goods-based economy.
Hayam Vuruk (1334–1389), also called Rajasanagara, Pa-ta-na-pa-na-wu, or Bhatara Prabhu after 1350, was a Javanese Hindu emperor from the Rajasa dynasty and the 4th emperor of the Majapahit Empire. Together with his prime minister Gajah Mada, he reigned the empire at the time of its greatest power. During his reign, the Hindu epics, the Ramayana and the Mahabharata, became ingrained in the culture and worldview of the Javanese through the wayang kulit. He was preceded by Tribhuwana Wijayatunggadewi, and succeeded by his son-in-law Wikramawardhana.

The Shailendra dynasty was the name of a notable Indianised dynasty that emerged in 8th-century Java, whose reign signified a cultural renaissance in the region. The Shailendras were active promoters of Mahayana Buddhism and covered the Kedu Plain of Central Java with Buddhist monuments, one of which is the colossal stupa of Borobudur, now a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

The Mataram Kingdom ; also known as Medang Kingdom was a Javanese Hindu-Buddhist kingdom that flourished between the 8th and 11th centuries. It was based in Central Java, and later in East Java. Established by King Sanjaya, the kingdom was ruled by the Shailendra dynasty and Ishana dynasty.

Pekalongan is a city of Central Java, Indonesia. It was formerly the seat of Pekalongan Regency on the northern coast of the province, but is now an independent municipality within the province. It covers a land area of 45.25 km2 and had a population of 281,434 at the 2010 Census and 307,150 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 317,524. The city is Central Java's most important port, and is known for its batik. Since December 2014, Pekalongan has been a member of UNESCO's World's Creative Cities Network, the first Southeast Asian city to be added to the list.
Keling or Kling is an exonym to denote a Tamilian or someone deemed to have originated from South India. Originally a neutral term, since the mid-20th century it has been considered derogatory and an ethnic slur, and it is sometimes euphemistically referred to as the K-word. The term is used in parts of Southeast Asia, particularly the Malay Archipelago where there are a significant Tamil diaspora – specifically Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore and Brunei – but cognates exist in neighbouring countries as well.

Jepara is a town in the province of Central Java, Indonesia. Jepara is on the north coast of Java, northeast of Semarang, not far from Mount Muria, with a population of 81,920 in mid-2022. It is also the main town of Jepara Regency. Jepara is known for the Javanese teak wood carving art as well as the birthplace of Kartini, a pioneer in the area of women's rights for Indonesians.

The Nagarakretagama or Nagarakṛtāgama, also known as Desawarnana or Deśavarṇana, is an Old Javanese eulogy to Hayam Wuruk, a Javanese king of the Majapahit Empire. It was written on lontar as a kakawin by Mpu Prapanca in 1365. The Nagarakretagama contains detailed descriptions of the Majapahit Empire during its greatest extent. The poem affirms the importance of Hindu–Buddhism in the Majapahit empire by describing temples and palaces and several ceremonial observances.

The Sanjaya dynasty was a Javanese dynasty which ruled the Mataram Kingdom in Java during the first millennium CE. The dynasty promoted Hinduism on the island.

Nyi Roro Kidul is a supernatural being in Indonesian folklore. She is the Queen of the Southern Sea in Sundanese and Javanese mythology.

Airlangga, regnal name Rakai Halu Sri Lokeswara Dharmawangsa Airlangga Anantawikramottunggadewa, was the only king of the Kingdom of Kahuripan.

The Galuh Kingdom was a medieval Sundanese kingdom located in the eastern part of Tatar Sunda, present-day Indonesia. It was established as a breakaway kingdom of the Tarumanagara around the 7th century. Traditionally the kingdom was associated with the Central & Eastern Parahyangan cultural regions, with territory spanning from Citarum River in the west, to Cipamali and Cisarayu River in the east. Its capital was first located in Karangkamulyan, Ciamis Regency, then Saunggalah, Kuningan and Kawali, north of present-day Ciamis. The etymology of "galuh" is Old Sundanese and Kawi word for "gemstone".

Pramodhawardhani was the queen consort of King Rakai Pikatan of Mataram Kingdom in 9th century Central Java. She was the daughter of Sailendran king Samaratungga.

Kalingga or She-po or She-bo in Chinese sources, or Ho-ling in Arabic scriptures of Umayyad Caliphate era; was a 6th-century Indianized kingdom on the north coast of Central Java, Indonesia.
Dara Petak or Dara Pethak, also known in her formal name as Indreswari, was the consort of King Kertarajasa Jayawardhana, the founder of Majapahit kingdom. She was a Dharmasraya princess from Sumatra and the only non-Javanese wife of Kertarajasa, and also the mother of Jayanegara, the second monarch of Majapahit. Tradition mentioned her as a woman of exceptional beauty.
Isyana stylized as Sri Isyana Tunggawijaya was a queen regnant of Mataram Kingdom, in East Java, that ruled since 947 CE. She co-reigned with her spouse, Sri Lokapala. The Isyana dynasty, established by her father, Mpu Sindok that ruled Java circa the 10th century CE, was named after her.
Sannaha was the mother of King Sanjaya, who established the Mataram Kingdom in the early 8th century CE.

The history of Sunda Kingdom spanned almost a millennium, between 7th to 16th century. It is not sure however, whether the Sunda Kingdom was actually a continuous polity or not, nor whether its rulers belongs to a single continuous lineage of dynasty or not. This is because the scarcity of evidences, historical records and archaeological findings that plausibly connected to this kingdom.













