
Amyloids are aggregates of proteins characterised by a fibrillar morphology of typically 7–13 nm in diameter, a β-sheet secondary structure and ability to be stained by particular dyes, such as Congo red. In the human body, amyloids have been linked to the development of various diseases. Pathogenic amyloids form when previously healthy proteins lose their normal structure and physiological functions (misfolding) and form fibrous deposits within and around cells. These protein misfolding and deposition processes disrupt the healthy function of tissues and organs.
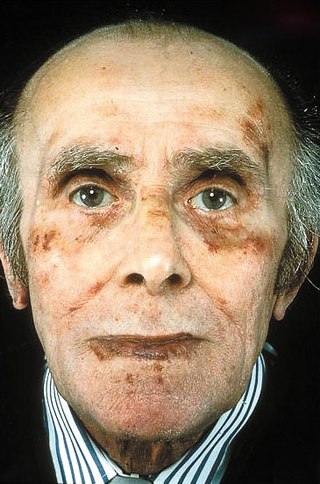
Amyloidosis is a group of diseases in which abnormal proteins, known as amyloid fibrils, build up in tissue. There are several non-specific and vague signs and symptoms associated with amyloidosis. These include fatigue, peripheral edema, weight loss, shortness of breath, palpitations, and feeling faint with standing. In AL amyloidosis, specific indicators can include enlargement of the tongue and periorbital purpura. In wild-type ATTR amyloidosis, non-cardiac symptoms include: bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome, lumbar spinal stenosis, biceps tendon rupture, small fiber neuropathy, and autonomic dysfunction.

Transthyretin (TTR or TBPA) is a transport protein in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid that transports the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) and retinol to the liver. This is how transthyretin gained its name: transports thyroxine and retinol. The liver secretes TTR into the blood, and the choroid plexus secretes TTR into the cerebrospinal fluid.

Bence Jones protein is a monoclonal globulin protein or immunoglobulin light chain found in the urine, with a molecular weight of 22–24 kDa. Detection of Bence Jones protein may be suggestive of multiple myeloma or Waldenström's macroglobulinemia.

The serum amyloid P component (SAP) is the identical serum form of the amyloid P component (AP), a 25 kDa pentameric protein first identified as the pentagonal constituent of in vivo pathological deposits called "amyloid". APCS is its human gene.

Familial amyloid polyneuropathy, also called transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis, transthyretin amyloidosis abbreviated also as ATTR, or Corino de Andrade's disease, is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disease. It is a form of amyloidosis, and was first identified and described by Portuguese neurologist Mário Corino da Costa Andrade, in 1952. FAP is distinct from senile systemic amyloidosis (SSA), which is not inherited, and which was determined to be the primary cause of death for 70% of supercentenarians who have been autopsied. FAP can be ameliorated by liver transplantation.

Cardiac amyloidosis is a subcategory of amyloidosis where there is depositing of the protein amyloid in the cardiac muscle and surrounding tissues. Amyloid, a misfolded and insoluble protein, can become a deposit in the heart's atria, valves, or ventricles. These deposits can cause thickening of different sections of the heart, leading to decreased cardiac function. The overall decrease in cardiac function leads to a plethora of symptoms. This multisystem disease was often misdiagnosed, with diagnosis previously occurring after death during autopsy. However, recent advancements of technologies have increased the diagnosis of the disease. Cardiac amyloidosis has multiple sub-types including light chain, familial, and senile. One of the most studied types is light chain cardiac amyloidosis. Prognosis depends on the extent of the deposits in the body and the type of amyloidosis. New treatment methods are actively being researched in regards to the treatment of heart failure and specific cardiac amyloidosis problems.

In medicine, proteinopathy, or proteopathy, protein conformational disorder, or protein misfolding disease, is a class of diseases in which certain proteins become structurally abnormal, and thereby disrupt the function of cells, tissues and organs of the body. Often the proteins fail to fold into their normal configuration; in this misfolded state, the proteins can become toxic in some way or they can lose their normal function. The proteinopathies include such diseases as Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease and other prion diseases, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, amyloidosis, multiple system atrophy, and a wide range of other disorders. The term proteopathy was first proposed in 2000 by Lary Walker and Harry LeVine.

Surfactant protein C (SP-C), is one of the pulmonary surfactant proteins. In humans this is encoded by the SFTPC gene.

Serum amyloid A1 (SAA1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SAA1 gene. SAA1 is a major acute-phase protein mainly produced by hepatocytes in response to infection, tissue injury and malignancy. When released into blood circulation, SAA1 is present as an apolipoprotein associated with high-density lipoprotein (HDL). SAA1 is a major precursor of amyloid A (AA), the deposit of which leads to inflammatory amyloidosis.

Leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin-2 (LECT2) is a protein first described in 1996 as a chemotactic factor for neutrophils, i.e. it stimulated human neutrophils to move directionally in an in vitro assay system. The protein was detected in and purified from cultures of Phytohaemagglutinin-activated human T-cell leukemia SKW-3 cells. Subsequent studies have defined LECT2 as a hepatokine, i.e. a substance made and released into the circulation by liver hepatocyte cells that regulates the function of other cells: it is a hepatocyte-derived, hormone-like, signaling protein.
Plasma cell dyscrasias are a spectrum of progressively more severe monoclonal gammopathies in which a clone or multiple clones of pre-malignant or malignant plasma cells over-produce and secrete into the blood stream a myeloma protein, i.e. an abnormal monoclonal antibody or portion thereof. The exception to this rule is the disorder termed non-secretory multiple myeloma; this disorder is a form of plasma cell dyscrasia in which no myeloma protein is detected in serum or urine of individuals who have clear evidence of an increase in clonal bone marrow plasma cells and/or evidence of clonal plasma cell-mediated tissue injury. Here, a clone of plasma cells refers to group of plasma cells that are abnormal in that they have an identical genetic identity and therefore are descendants of a single genetically distinct ancestor cell.
Amyloid light-chain (AL) amyloidosis, also known as primary amyloidosis, is the most common form of systemic amyloidosis in the US. The disease is caused when a person's antibody-producing cells do not function properly and produce abnormal protein fibers made of components of antibodies called light chains. These light chains come together to form amyloid deposits which can cause serious damage to different organs. Abnormal light chains in urine are sometimes referred to as "Bence Jones protein".
AA amyloidosis is a form of amyloidosis, a disease characterized by the abnormal deposition of fibers of insoluble protein in the extracellular space of various tissues and organs. In AA amyloidosis, the deposited protein is serum amyloid A protein (SAA), an acute-phase protein which is normally soluble and whose plasma concentration is highest during inflammation.
The familial amyloid neuropathies are a rare group of autosomal dominant diseases wherein the autonomic nervous system and/or other nerves are compromised by protein aggregation and/or amyloid fibril formation.

Tafamidis, sold under the brand names Vyndaqel and Vyndamax, is a medication used to delay disease progression in adults with certain forms of transthyretin amyloidosis. It can be used to treat both hereditary forms, familial amyloid cardiomyopathy and familial amyloid polyneuropathy, as well as wild-type transthyretin amyloidosis, which formerly was called senile systemic amyloidosis. It works by stabilizing the quaternary structure of the protein transthyretin. In people with transthyretin amyloidosis, transthyretin falls apart and forms clumps called (amyloid) that harm tissues including nerves and the heart.
Familial amyloid cardiomyopathy (FAC), or transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM) results from the aggregation and deposition of mutant and wild-type transthyretin (TTR) protein in the heart. TTR is usually circulated as a homo-tetramer—a protein made up of four identical subunits—however, in FAC populations, TTR dissociates from this typical form and misassembles into amyloid fibrils which are insoluble and resistant to degradation. Due to this resistance to degradation, when amyloid fibrils accumulate in the heart's walls, specifically the left ventricle, rigidity prevents the heart from properly relaxing and refilling with blood: this is called diastolic dysfunction which can ultimately lead to heart failure.

LECT2 Amyloidosis (ALECT2) is a form of amyloidosis caused by the LECT2 protein. It was found to be the third most common cause of amyloidosis in a set of more than 4,000 individuals studied at the Mayo Clinic; the first and second most common forms the disorder were AL amyloidosis and AA amyloidosis, respectively. Amyloidosis is a disorder in which the abnormal deposition of a protein in organs and/or tissues gradually leads to organ failure and/or tissue injury.
Wild-type transthyretin amyloid (WTTA), also known as senile systemic amyloidosis (SSA), is a disease that typically affects the heart and tendons of elderly people. It is caused by the accumulation of a wild-type protein called transthyretin. This is in contrast to a related condition called transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis where a genetically mutated transthyretin protein tends to deposit much earlier than in WTTA due to abnormal conformation and bioprocessing. It belongs to a group of diseases called amyloidosis, chronic progressive conditions linked to abnormal deposition of normal or abnormal proteins, because these proteins are misshapen and cannot be properly degraded and eliminated by the cell metabolism.
Monoclonal gammopathy of renal significance (MGRS) are a group of kidney disorders that present with kidney damage due to nephrotoxic monoclonal immunoglobulins secreted by clonal plasma cells or B cells. By definition, people with MGRS do not meet criteria for multiple myeloma or other hematologic malignancies. The term MGRS was introduced in 2012 by the International Kidney and Monoclonal Gammopathy Research Group (IKMG). MGRS is associated with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS). People with MGUS have a monoclonal gammopathy but does not meet the criteria for the clonal burden nor the presence of end organ damage seen in hematologic malignancies. In a population based study based on the NHANES III health survey; 6% of patients with MGUS were subsequently classified as having MGRS. The prevalence and incidence of MGRS in the general population or in specific populations is not known but it is more prevalent in those over the age of 50 as there is a monoclonal protein (M-protein) present in 3% of those 50 and years older and 5% of those 70 years and older, placing those 50 and older at increased risk of MGRS.













