
Hypoxia is a condition in which the body or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply at the tissue level. Hypoxia may be classified as either generalized, affecting the whole body, or local, affecting a region of the body. Although hypoxia is often a pathological condition, variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during hypoventilation training or strenuous physical exercise.

Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area may feel heavy, and affected joints may be hard to move. Other symptoms depend on the underlying cause.

A pulmonary alveolus also known as an air sac or air space is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide. Alveoli make up the functional tissue of the lungs known as the lung parenchyma, which takes up 90 percent of the total lung volume.

Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a rise in arterial carbon dioxide levels is called hypercapnia. Respiratory failure is classified as either Type 1 or Type 2, based on whether there is a high carbon dioxide level, and can be acute or chronic. In clinical trials, the definition of respiratory failure usually includes increased respiratory rate, abnormal blood gases, and evidence of increased work of breathing. Respiratory failure causes an altered mental status due to ischemia in the brain.
Diffusing capacity of the lung (DL) measures the transfer of gas from air in the lung, to the red blood cells in lung blood vessels. It is part of a comprehensive series of pulmonary function tests to determine the overall ability of the lung to transport gas into and out of the blood. DL, especially DLCO, is reduced in certain diseases of the lung and heart. DLCO measurement has been standardized according to a position paper by a task force of the European Respiratory and American Thoracic Societies.

Pulmonary edema (PE), also known as pulmonary congestion, is liquid accumulation in the tissue and air spaces of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause respiratory failure. It is due to either failure of the left ventricle of the heart to remove blood adequately from the pulmonary circulation, or an injury to the lung tissue or blood vessels of the lung.
Orthopnea or orthopnoea is shortness of breath (dyspnea) that occurs when lying flat, causing the person to have to sleep propped up in bed or sitting in a chair. It is commonly seen as a late manifestation of heart failure, resulting from fluid redistribution into the central circulation, causing an increase in pulmonary capillary pressure. It is also seen in cases of abdominal obesity or pulmonary disease. Orthopnea is the opposite of platypnea, shortness of breath that worsens when sitting or standing up.

Hemolytic anemia is a form of anemia due to hemolysis, the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs), either in the blood vessels or elsewhere in the human body (extravascular). This most commonly occurs within the spleen, but also can occur in the reticuloendothelial system or mechanically. Hemolytic anemia accounts for 5% of all existing anemias. It has numerous possible consequences, ranging from general symptoms to life-threatening systemic effects. The general classification of hemolytic anemia is either intrinsic or extrinsic. Treatment depends on the type and cause of the hemolytic anemia.
Hypoxemia is an abnormally low level of oxygen in the blood. More specifically, it is oxygen deficiency in arterial blood. Hypoxemia has many causes, and often causes hypoxia as the blood is not supplying enough oxygen to the tissues of the body.
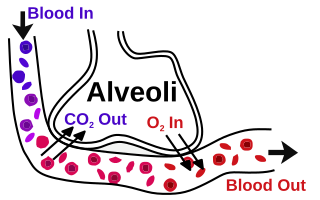
The blood–air barrier or air–blood barrier, exists in the gas exchanging region of the lungs. It exists to prevent air bubbles from forming in the blood, and from blood entering the alveoli. It is formed by the type I pneumocytes of the alveolar wall, the endothelial cells of the capillaries and the basement membrane between the two cells. The barrier is permeable to molecular oxygen, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and many other gases.
Exercise-induced pulmonary hemorrhage (EIPH), also known as "bleeding" or a "bleeding attack", refers to the presence of blood in the airways of the lung in association with exercise. EIPH is common in horses undertaking intense exercise, but it has also been reported in human athletes, racing camels and racing greyhounds. Horses that experience EIPH may also be referred to as "bleeders" or as having "broken a blood vessel". In the majority of cases, EIPH is not apparent unless an endoscopic examination of the airways is performed following exercise. This is distinguished from other forms of bleeding from the nostrils, called epistaxis.
DLCO or TLCO is the extent to which oxygen passes from the air sacs of the lungs into the blood. Commonly, it refers to the test used to determine this parameter. It was introduced in 1909.
In respiratory physiology, the ventilation/perfusion ratio is a ratio used to assess the efficiency and adequacy of the matching of two variables:
A pulmonary shunt refers to the passage of deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the left without participation in gas exchange in the pulmonary capillaries. It is a pathological condition that results when the alveoli of the lungs are perfused with blood as normal, but ventilation fails to supply the perfused region. In other words, the ventilation/perfusion ratio is zero.
The zones of the lung divide the lung into four vertical regions, based upon the relationship between the pressure in the alveoli (PA), in the arteries (Pa), in the veins (Pv) and the pulmonary interstitial pressure (Pi):

Hemosiderosis is a form of iron overload disorder resulting in the accumulation of hemosiderin.
Brown induration is fibrosis and hemosiderin pigmentation of the lungs due to long standing pulmonary congestion. Occurs with mitral stenosis and left sided heart failure. Pathology: The lung vessels are congested with blood and this leads to pulmonary edema when plasma escapes in alveolar spaces. Rupture of congested capillaries leads to release of hemosiderin from damaged red blood cells. When alveolar macrophages engulf hemosiderin they are called heart failure cells. Death of heart failure cells in their journey back to lung tissue with subsequent hemosiderin release leads to lung fibrosis.
Swimming induced pulmonary edema (SIPE), also known as immersion pulmonary edema, occurs when fluids from the blood leak abnormally from the small vessels of the lung into the airspaces (alveoli).
The main pathophysiology of heart failure is a reduction in the efficiency of the heart muscle, through damage or overloading. As such, it can be caused by a wide number of conditions, including myocardial infarction, hypertension and amyloidosis. Over time these increases in workload will produce changes to the heart itself:

The pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome involves fluid accumulation in the lungs not explained by heart failure. It is typically provoked by an acute injury to the lungs that results in flooding of the lungs' microscopic air sacs responsible for the exchange of gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide with capillaries in the lungs. Additional common findings in ARDS include partial collapse of the lungs (atelectasis) and low levels of oxygen in the blood (hypoxemia). The clinical syndrome is associated with pathological findings including pneumonia, eosinophilic pneumonia, cryptogenic organizing pneumonia, acute fibrinous organizing pneumonia, and diffuse alveolar damage (DAD). Of these, the pathology most commonly associated with ARDS is DAD, which is characterized by a diffuse inflammation of lung tissue. The triggering insult to the tissue usually results in an initial release of chemical signals and other inflammatory mediators secreted by local epithelial and endothelial cells.












