
The Maratha Confederacy, also referred to as the Maratha Empire, was an early modern polity in the Indian subcontinent. It comprised the realms of the Peshwa and four major independent Maratha states often subordinate to the former. It was established in 1674 with the coronation of Shivaji as the Maratha Chhatrapati and recognised by Emperor Bahadur Shah I as a tributary state in 1707 following a prolonged rebellion. Following this, the Marathas continued to recognise the Mughal emperor as their nominal suzerain, similar to other contemporary Indian entities, though in practice, imperial politics at Delhi were largely influenced by the Marathas between 1737 and 1803.

Raipur district is a district in the Chhattisgarh state of India. Its administrative headquarters is the city of Raipur. The district is rich in mineral resources and there are many wildlife sanctuaries. With a population of 2 million, it is the most populous district of Chhattisgarh.

Balaji Baji Rao, often referred to as Nana Saheb I, was the 8th Peshwa of the Maratha Confederacy. He was appointed as Peshwa in 1740 upon the death of his father, the Peshwa Bajirao I.

The Kingdom of Nagpur was a kingdom within the Maratha Confederacy in the 18th and 19th centuries. It was ruled by the Maratha Bhonsle dynasty in the mid-18th century. The city of Nagpur was the capital of the state.

The Kingdom of Haihaiyavansi, ruled by the Kalachuris of Raipur was a Garh Under Garha Kingdom which consisted of the central part of the present-day state of Chhattisgarh located in India.

Raghuji I was a Maratha general of the Bhonsle clan who established the Nagpur Kingdom in much of east-central India during the reign of Chhatrapati Shahu I. His successors ruled the kingdom until 1853.

Vyankojirajah Bhonsle or Ekojirajah I Bhonsle was the younger half-brother of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj and founder of Maratha rule in Thanjavur in modern day Tamil Nadu. He was the progenitor of the junior branch of the Bhonsle family which ruled Thanjavur until the formal annexation of the kingdom by the British East India Company in 1855.

Narnala Fort or Narnala Qila Sarkar, also known as Shahnoor Fort, is a hill fortress in the Satpura Range of Vidarbh, Maharashtra, India, named after the Rajput Solanki Chaulukya Ruler, Raja Narnal Singh, also known as Narnal Singh Swami. It was renamed as "Shahnoor" by Islamic rulers but again acquired, rebuilt and got its name "Narnala" by ruler Rao Rana Narnal Singh Solanki, who migrated from Patan in Gujarat.
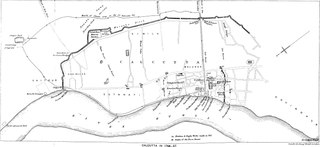
The Maratha invasions of Bengal (1742–1751), also known as the Maratha expeditions in Bengal, were the frequent invasions by the Maratha forces in the Bengal Subah, after their successful campaign in the Carnatic region at the Battle of Trichinopoly. The leader of the expeditions was Raghoji Bhonsle of Nagpur. The Marathas invaded Bengal many times from April 1742 to March 1751, which caused widespread economic losses in the Bengal Subah.
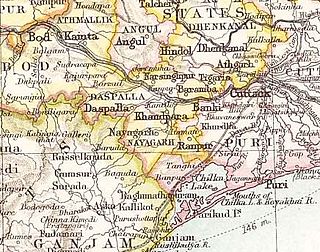
Nayagarh State was one of the princely states of India during the British Raj. It was located in present-day Nayagarh district, Odisha.

Mudhoji I was the ruler of the Nagpur kingdom from 1772 to 1788. During his regency the Maratha kingdom remained peaceful and prospered.

The Kalachuris of Ratnapura, also known as the Haihayas of Ratanpur, were a dynasty that ruled in Central India during the 12th and 13th centuries. They ruled parts of present-day Chhattisgarh from their capital at Ratnapura. They were an offshoot of the Kalachuris of Tripuri, and ruled as vassals of the parent dynasty for many years.

Chand Sultan (1706-1739) was a Gond king of Nagpur. He was the eldest son and successor of Bakht Buland Shah of Deogarh. He ascended the throne of Deogarh in 1706 and shifted his capital from Deogarh to Nagpur. He carried out further reforms in his kingdom and planned layout of the new city of Nagpur and under him, the kingdom prospered. He was a kind ruler who loved his people and extended his territory considerably to the east of the river Wainganga.

The Garha kingdom, also called Garha-Mandla or Garha Katanga, was an early-modern-era kingdom in India. It was the first large kingdom to be founded by the Gond tribe kings and was based in Central India. The kingdom was founded in the 15th century and lasted until conquest by the Maratha Confederacy in 1781.
Marathas under Raghunath Rao and Malhar Rao Holkar laid siege to the fort of Barwara. The fort was successfully defended by the garrison. After which the Marathas agreed to a smaller sum than what was initially demanded.

The Gonds of Deogarh were a Gond royal house that ruled large parts of the Vidarbha region and parts of present-day southern Madhya Pradesh. Their Kingdom consisted of the area which later became the Nagpur Kingdom. They made Nagpur region a prosperous and plentiful kingdom, founding the city of Nagpur and building further infrastructure. However, internal bickering led to their decline and they were practically made state pensioneries by the Maratha general Raghoji I Bhonsle in the 1743.
Bhaskar Ram Kolhatkar, known as Baba Bhaskar Pandit or Bhaskar Pant by the people of Bengal and Maharashtra, was a Maratha general and statesman. He was the dewan of the Maharaja of Nagpur, Raghuji Bhonsle. He played an important role in the kingdom of Nagpur's expansion. The first Maratha invasion of Bengal in 1741, as also the third in 1744, was led by him. He was an able military leader, proven by his success in the Maratha invasions of Bengal and conquest of Chhattisgarh. He was killed by Alivardi Khan on 30 March 1744.
The Kingdom of Chanda was one of the main Gond kingdoms, ruling parts of central India. In 1751, it was conquered by the Maratha ruler of Nagpur, Raghoji I Bhonsle.

Bimbaji Bhonsle was the youngest son of Raghoji I Bhonsle, the Maratha ruler of Nagpur. Bimbaji was the ruler of Chhattisgarh on behalf of the Maharaja of Nagpur. However, he was only nominally subordinate to the Maharaja of Nagpur, as he had a separate army and court with ministers at his capital of Ratanpur.
Mohan Singh was the last ruler of the Haihaiyavanshi Kingdom, the dynasty which ruled Chhattisgarh for over 700 years. He ruled Chhattisgarh under the suzerainty of the Bhonsles of Nagpur Kingdom.















