
Hugh O'Neill, was an Irish Gaelic lord, Earl of Tyrone and was later created The Ó Néill Mór, Chief of the Name. O'Neill's career was played out against the background of the Tudor conquest of Ireland, and he is best known for leading a coalition of Irish clans during the Nine Years' War, the strongest threat to the House of Tudor in Ireland since the uprising of Silken Thomas against King Henry VIII.

The Plantation of Ulster was the organised colonisation (plantation) of Ulster – a province of Ireland – by people from Great Britain during the reign of King James I. Most of the settlers came from southern Scotland and northern England; their culture differed from that of the native Irish. Small privately funded plantations by wealthy landowners began in 1606, while the official plantation began in 1609. Most of the colonised land had been confiscated from the native Gaelic chiefs, several of whom had fled Ireland for mainland Europe in 1607 following the Nine Years' War against English rule. The official plantation comprised an estimated half a million acres (2,000 km2) of arable land in counties Armagh, Cavan, Fermanagh, Tyrone, Donegal, and Londonderry. Land in counties Antrim, Down, and Monaghan was privately colonised with the king's support.

Sir Phelim Roe O'Neill of Kinard was an Irish politician and soldier who started the Irish rebellion in Ulster on 23 October 1641. He joined the Irish Catholic Confederation in 1642 and fought in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms under his cousin, Owen Roe O'Neill, in the Confederate Ulster Army. After the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland O’Neill went into hiding but was captured, tried and executed in 1653.

The Irish Rebellion of 1641 was a Catholic-led uprising in Ireland, whose demands included an end to anti-Catholic discrimination, greater Irish self-governance, and return of confiscated Catholic lands. Its timing was partially driven by the dispute between Charles I and his opponents—the English Parliamentarians and Scottish Covenanters—which the rebels feared would lead to an invasion and further anti-Catholic measures. Beginning as an attempted coup d'état by Catholic gentry and military officers, it developed into a widespread rebellion and ethnic conflict with English and Scottish Protestant settlers. It led to the 1641–1652 Irish Confederate Wars, part of the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, with up to 20% of the Irish population becoming casualties.

Plantations in 16th- and 17th-century Ireland involved the confiscation of Irish-owned land by the English Crown and the colonisation of this land with settlers from Great Britain. The Crown saw the plantations as a means of controlling, anglicising and 'civilising' Gaelic Ireland. The main plantations took place from the 1550s to the 1620s, the biggest of which was the plantation of Ulster. The plantations led to the founding of many towns, massive demographic, cultural and economic changes, changes in land ownership and the landscape, and also to centuries of ethnic and sectarian conflict. They took place before and during the earliest English colonisation of the Americas, and a group known as the West Country Men were involved in both Irish and American colonization.

The O’Doherty family is an Irish clan based in County Donegal in the north of the island of Ireland.
Count Redmond O'Hanlon, was a 17th-century Irish tóraidhe or rapparee; an outlawed member of the Gaelic nobility of Ireland who still held to the code of conduct of the traditional chiefs of the Irish clans.
Sir Cahir O'Doherty was the last Gaelic Chief of the Name of Clan O'Doherty and Lord of Inishowen, in what is now County Donegal. O'Doherty was a noted loyalist during Tyrone's Rebellion and became known as the Queen's O'Doherty for his service on the Crown's side during the fighting.
Events from the year 1608 in Ireland.

The Portadown massacre took place in November 1641 at Portadown, County Armagh, during the Irish Rebellion of 1641. Irish Catholic rebels, likely under the command of Toole McCann, killed about 100 British Protestant settlers by forcing them off the bridge into the River Bann, and shooting those who tried to swim to safety. The settlers were being marched east from a prison camp at Loughgall. This was the biggest massacre of Protestants during the rebellion, and one of the bloodiest during the Irish Confederate Wars. The Portadown massacre, and others like it, terrified Protestants in Ireland and Great Britain, and were used to justify the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland and later to lobby against Catholic rights.
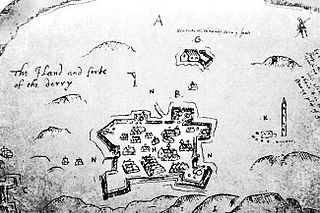
Sir George Paulet (1553–1608), also known as Pawlett, Pawlet, or Powlet, was an English soldier and administrator. He served as governor of Derry in Ireland. His arrogant and insolent behaviour caused O'Doherty's Rebellion in 1608. Paulet was killed by the rebels during the Burning of Derry.

O'Doherty's Rebellion, also called O'Dogherty's Revolt, was an uprising against the Crown authorities in western Ulster, Ireland. Sir Cahir O'Doherty, lord of Inishowen, a Gaelic chieftain, had been a supporter of the Crown during the Nine Years' War (1593–1603), but angered at his treatment by Sir George Paulet, governor of Derry, he attacked and burned Derry in April 1608. O'Dogherty was defeated and killed in the Battle of Kilmacrennan in July. The rebellion ended with the surrender of the last die-hards at the Siege of Tory Island later in the same year.
Richard Nugent, 1st Earl of Westmeath (1583–1642) was an Irish nobleman and politician of the seventeenth century. He was imprisoned for plotting against the English Crown in 1607, but soon obtained a royal pardon, and thereafter was, in general, to be a reliable supporter of the Government, although his loyalty was questioned from time to time. His death resulted from his refusal to take up arms against the English Crown during the Irish Rebellion of 1641.

The Battle of Kilmacrennan was a skirmish fought near Kilmacrennan, County Donegal in 1608 during O'Doherty's Rebellion. Sir Cahir O'Doherty was a traditional supporter of the Crown whose treatment at the hands of local officials had led him to launch a rebellion in which he had seized the garrison town of Derry, killing his enemy George Paulet. O'Doherty raised local forces and possibly hoped to negotiate an agreement with the government as had been common with leaders of previous rebellions.

The Burning of Derry took place on 19 April 1608 during O'Doherty's Rebellion when Sir Cahir O'Doherty led a force of rebels to storm Derry in Ulster. He launched his rebellion with an attack on the garrison town of Derry, which was taken thanks to the element of surprise. The town was then almost entirely destroyed by fire.

Burt Castle is a ruined castle located close to Newtowncunningham and Burt, two villages in the east of County Donegal in Ulster, Ireland. Historically it was sometimes spelt as Birt Castle. It is also known by the name O'Doherty's Castle, and should not be mistaken for O'Doherty's Keep near Buncrana.
Henry Hart (1566-1637) was an Anglo-Irish soldier and landowner of the Elizabethan and early Stuart eras. He served in the Nine Years' War (1584-1603) and was later involved in the opening incident of O'Doherty's Rebellion in 1608. As a servitor he acquired an estate in County Donegal.

Phelim Reagh MacDavitt or Phelim Reagh MacDevitt was a Gaelic Irish warrior and landowner notable for his participation in the Nine Years War and later in O'Doherty's Rebellion in 1608. After playing a leading part in the Burning of Derry, he was captured and executed following the Battle of Kilmacrennan.
Sir Turlough McHenry O'Neill is known for having been killed together with his father, Henry, fighting for the crown in O'Doherty's Rebellion and for being the father of Sir Phelim O'Neill, who started the Irish Rebellion of 1641.
Rosa O'Neill was a member of the O'Doherty family of County Donegal who lived during the late Tudor and Stuart eras.









