Related Research Articles

The geography of Mexico describes the geographic features of Mexico, a country in the Americas. Mexico is located at about 23° N and 102° W in the southern portion of North America. From its farthest land points, Mexico is a little over 3,200 km (2,000 mi) in length. Mexico is bounded to the north by the United States, to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean, to the east by the Gulf of Mexico, and to the southeast by Belize, Guatemala, and the Caribbean Sea. The northernmost constituent of Latin America, it is the most populous Spanish-speaking country in the world. Mexico is the world's 13th largest country, three times the size of Texas.

The Continental Divide of the Americas is the principal, and largely mountainous, hydrological divide of the Americas. The Continental Divide extends from the Bering Strait to the Strait of Magellan, and separates the watersheds that drain into the Pacific Ocean from those river systems that drain into the Atlantic and Arctic Ocean, including those that drain into the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean Sea, and Hudson Bay.
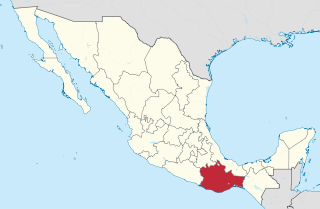
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the Federative Entities of the United Mexican States. It is divided into 570 municipalities, of which 418 are governed by the system of usos y costumbres with recognized local forms of self-governance. Its capital city is Oaxaca de Juárez.

The Isthmus of Tehuantepec is an isthmus in Mexico. It represents the shortest distance between the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean. Before the opening of the Panama Canal, it was a major overland transport route known simply as the Tehuantepec Route. The name is taken from the town of Santo Domingo Tehuantepec in the state of Oaxaca; this was derived from the Nahuatl term Tēcuāntepēc.

Tehuantepec is a city and municipality in the southeast of the Mexican state of Oaxaca. It is part of the Tehuantepec District in the west of the Istmo Region. The area was important in pre-Hispanic period as part of a trade route that connected Central America with what is now the center of Mexico. Later it became a secondary capital of the Zapotec dominion, before it was conquered by the Spanish in the early 16th century.

The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consist of an almost continuous sequence that form the western "sounds" of North America, Central America, South America, and West Antarctica.

The Sierra Madre Oriental is a mountain range in northeastern Mexico. The Sierra Madre Oriental is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of North America, Central America, South America, and Antarctica.

The Sierra Madre del Sur is a mountain range in southern Mexico, extending 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) from southern Michoacán east through Guerrero, to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in eastern Oaxaca.
The geography of Mesoamerica describes the geographic features of Mesoamerica, a culture area in the Americas inhabited by complex indigenous pre-Columbian cultures exhibiting a suite of shared and common cultural characteristics. Several well-known Mesoamerican cultures include the Olmec, Teotihuacan, the Maya, the Aztec and the Purépecha. Mesoamerica is often subdivided in a number of ways. One common method, albeit a broad and general classification, is to distinguish between the highlands and lowlands. Another way is to subdivide the region into sub-areas that generally correlate to either culture areas or specific physiographic regions.

The Sierra Madre is a major mountain range in Central America. It is known as the Sierra Madre de Chiapas in Mexico. It crosses El Salvador, Guatemala, Mexico and Honduras. The Sierra Madre is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of North America, Central America, and South America.

The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca pine–oak forests is a tropical and subtropical coniferous forests ecoregion in Southern Mexico.

The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca is a mountain range in southern Mexico. It is primarily in the state of Oaxaca, and extends north into the states of Puebla and Veracruz.

The Guatemalan Highlands is an upland region in southern Guatemala, lying between the Sierra Madre de Chiapas to the south and the Petén lowlands to the north.

The Coatzacoalcos is a large river that feeds mainly the south part of the state of Veracruz; it originates in the Sierra de Niltepec and crosses the state of Oaxaca in the region of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, flowing for 325 kilometres toward the Gulf of Mexico. Tributaries include El Corte, Sarabia, Jaltepec, Chalchijalpa, El Chiquito, Uxpanapa, and Calzadas. The merging of all these rivers creates one of the largest current flows in the entire region. Two-thirds of the streams are navigable.

The Tehuantepec River is a river in Oaxaca, Mexico. The Tehuantepec flows into the Gulf of Tehuantepec on the Pacific Ocean coast of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec. The mountainous terrain of the region it occupies allows for no navigable rivers; instead, there are a large number of smaller ones, which often change name from area to area. The continental divide passes through the state, meaning there is drainage toward both the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific. Most of the drainage toward the Gulf is represented by the Papaloapan and Coatzacoalcos rivers and their tributaries such as the Grande and Salado Rivers. Three rivers account for most of the water headed for the Pacific: the Atoyac River, Mixteco River, and the Tehuantepec River, with their tributaries.
El Corte River is the primary tributary of the Coatzacoalcos River, flowing through the Mexican states of Oaxaca and Veracruz to the Gulf of Mexico.
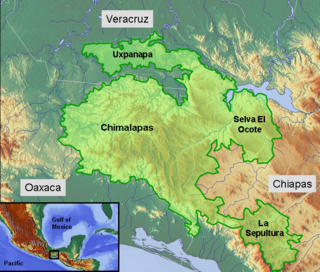
The Selva Zoque, which includes the Chimalapas rain forest, is an area of great ecological importance in Mexico. Most of the forest lies in the state of Oaxaca but parts are in Chiapas and Veracruz. It is the largest tract of tropical rainforest in Mexico, and contains the majority of terrestrial biodiversity in the country. The forest includes the Selva El Ocote, a federally-protected biosphere reserve, but is otherwise not yet protected. Despite the rich ecology of the region, a 2003 study that focused on bird populations stated that "the fauna of the heart of the Chimalapas, including its vast rainforests, have seen little or no study". As it is an impoverished region, efforts to preserve the ecology are often at odds with demands to improve the economy.

The Sierra Juárez is a range of mountains in Oaxaca state, Mexico between latitudes 17°20'-17°50'N and longitudes 96°15'-97°00'W, with an area of about 1,700 km². It is part of the Sierra Madre de Oaxaca. The range is separated from the Sierra de Zongólica to the north by the Santo Domingo River, flowing through the Tecomavaca Canyon. It stretches south-eastward to the Cajones River and the Sierra de Villa Alta. The mountains are in the district of Ixtlán de Juárez in the Sierra Norte de Oaxaca region. The range is named after Mexico's only indigenous president, Benito Juárez, who was born here in 1806 in the small village of San Pablo Guelatao. The heavily wooded area is about 62 km (39 mi) from the city of Oaxaca on Federal highway 175, heading towards Tuxtepec.

Istmo de Tehuantepec is the largest region of the state of Oaxaca, located in southwestern Mexico.

Juchitán District is located in the east of the Istmo de Tehuantepec region of the State of Oaxaca, Mexico, covering the southern part of a low-lying corridor through the mountains that separates the Gulf of Mexico from the Pacific ocean. The district has an area of 13,300 km2 and a population as of 2005 of 339,445.