Related Research Articles

Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide, cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are representative members of this class. The field of organometallic chemistry combines aspects of traditional inorganic and organic chemistry.
Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are two important and related classes of reactions in organometallic chemistry. Oxidative addition is a process that increases both the oxidation state and coordination number of a metal centre. Oxidative addition is often a step in catalytic cycles, in conjunction with its reverse reaction, reductive elimination.
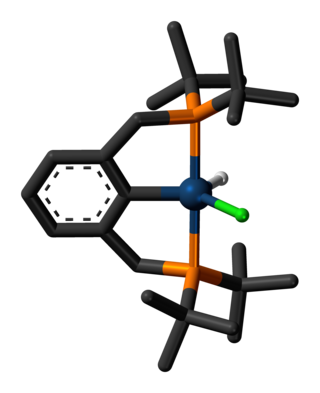
In chemistry, a transition metal pincer complex is a type of coordination complex with a pincer ligand. Pincer ligands are chelating agents that binds tightly to three adjacent coplanar sites in a meridional configuration. The inflexibility of the pincer-metal interaction confers high thermal stability to the resulting complexes. This stability is in part ascribed to the constrained geometry of the pincer, which inhibits cyclometallation of the organic substituents on the donor sites at each end. In the absence of this effect, cyclometallation is often a significant deactivation process for complexes, in particular limiting their ability to effect C-H bond activation. The organic substituents also define a hydrophobic pocket around the reactive coordination site. Stoichiometric and catalytic applications of pincer complexes have been studied at an accelerating pace since the mid-1970s. Most pincer ligands contain phosphines. Reactions of metal-pincer complexes are localized at three sites perpendicular to the plane of the pincer ligand, although in some cases one arm is hemi-labile and an additional coordination site is generated transiently. Early examples of pincer ligands were anionic with a carbanion as the central donor site and flanking phosphine donors; these compounds are referred to as PCP pincers.

In organic chemistry, olefin metathesis is an organic reaction that entails the redistribution of fragments of alkenes (olefins) by the scission and regeneration of carbon-carbon double bonds. Because of the relative simplicity of olefin metathesis, it often creates fewer undesired by-products and hazardous wastes than alternative organic reactions. For their elucidation of the reaction mechanism and their discovery of a variety of highly active catalysts, Yves Chauvin, Robert H. Grubbs, and Richard R. Schrock were collectively awarded the 2005 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
A transition metal carbene complex is an organometallic compound featuring a divalent carbon ligand, itself also called a carbene. Carbene complexes have been synthesized from most transition metals and f-block metals, using many different synthetic routes such as nucleophilic addition and alpha-hydrogen abstraction. The term carbene ligand is a formalism since many are not directly derived from carbenes and most are much less reactive than lone carbenes. Described often as =CR2, carbene ligands are intermediate between alkyls (−CR3) and carbynes (≡CR). Many different carbene-based reagents such as Tebbe's reagent are used in synthesis. They also feature in catalytic reactions, especially alkene metathesis, and are of value in both industrial heterogeneous and in homogeneous catalysis for laboratory- and industrial-scale preparation of fine chemicals.

Alkyne metathesis is an organic reaction that entails the redistribution of alkyne chemical bonds. The reaction requires metal catalysts. Mechanistic studies show that the conversion proceeds via the intermediacy of metal alkylidyne complexes. The reaction is related to olefin metathesis.
In organic chemistry and organometallic chemistry, carbon–hydrogen bond activation is a type of organic reaction in which a carbon–hydrogen bond is cleaved and replaced with a C−X bond. Some authors further restrict the term C–H activation to reactions in which a C–H bond, one that is typically considered to be "unreactive", interacts with a transition metal center M, resulting in its cleavage and the generation of an organometallic species with an M–C bond. The intermediate of this step could then undergo subsequent reactions with other reagents, either in situ or in a separate step, to produce the functionalized product.

Organoactinide chemistry is the science exploring the properties, structure, and reactivity of organoactinide compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to actinide chemical bond.
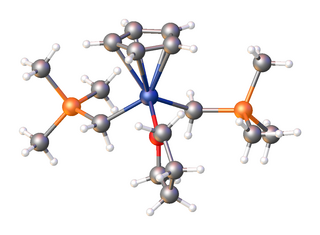
Organoscandium chemistry is an area with organometallic compounds focused on compounds with at least one carbon to scandium chemical bond. The interest in organoscandium compounds is mostly academic but motivated by potential practical applications in catalysis, especially in polymerization. A common precursor is scandium chloride, especially its THF complex.
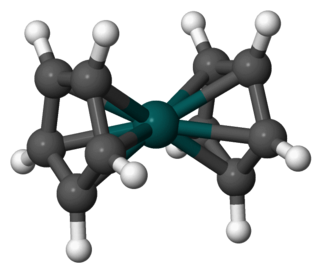
Rhodocene is a chemical compound with the formula [Rh(C5H5)2]. Each molecule contains an atom of rhodium bound between two planar aromatic systems of five carbon atoms known as cyclopentadienyl rings in a sandwich arrangement. It is an organometallic compound as it has (haptic) covalent rhodium–carbon bonds. The [Rh(C5H5)2] radical is found above 150 °C (302 °F) or when trapped by cooling to liquid nitrogen temperatures (−196 °C [−321 °F]). At room temperature, pairs of these radicals join via their cyclopentadienyl rings to form a dimer, a yellow solid.
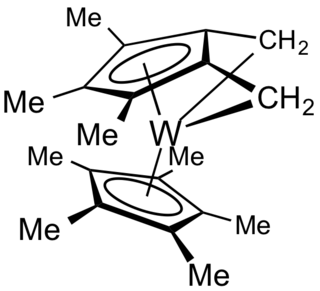
In organometallic chemistry, a tuck-in complex usually refers to derivatives of Cp* ligands wherein a methyl group is deprotonated and the resulting methylene attaches to the metal. The C5–CH2–M angle is acute. The term "tucked in" was coined to describe derivatives of organotungsten complexes. Although most "tucked-in" complexes are derived from Cp* ligands, other pi-bonded rings undergo similar reactions.
Transition metal carbyne complexes are organometallic compounds with a triple bond between carbon and the transition metal. This triple bond consists of a σ-bond and two π-bonds. The HOMO of the carbyne ligand interacts with the LUMO of the metal to create the σ-bond. The two π-bonds are formed when the two HOMO orbitals of the metal back-donate to the LUMO of the carbyne. They are also called metal alkylidynes—the carbon is a carbyne ligand. Such compounds are useful in organic synthesis of alkynes and nitriles. They have been the focus on much fundamental research.
In organometallic chemistry, metal sulfur dioxide complexes are complexes that contain sulfur dioxide, SO2, bonded to a transition metal. Such compounds are common but are mainly of theoretical interest. Historically, the study of these compounds has provided insights into the mechanisms of migratory insertion reactions.
A metal carbido complex is a coordination complex that contains a carbon atom as a ligand. They are analogous to metal nitrido complexes. Carbido complexes are a molecular subclass of carbides, which are prevalent in organometallic and inorganic chemistry. Carbido complexes represent models for intermediates in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis, olefin metathesis, and related catalytic industrial processes. Ruthenium-based carbido complexes are by far the most synthesized and characterized to date. Although, complexes containing chromium, gold, iron, nickel, molybdenum, osmium, rhenium, and tungsten cores are also known. Mixed-metal carbides are also known.

Transition metal benzyne complexes are organometallic complexes that contain benzyne ligands (C6H4). Unlike benzyne itself, these complexes are less reactive although they undergo a number of insertion reactions.
Methane functionalization is the process of converting methane in its gaseous state to another molecule with a functional group, typically methanol or acetic acid, through the use of transition metal catalysts.

Transition metal alkyl complexes are coordination complexes that contain a bond between a transition metal and an alkyl ligand. Such complexes are not only pervasive but are of practical and theoretical interest.
Organoniobium chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing niobium-carbon (Nb-C) bonds. Compared to the other group 5 transition metal organometallics, the chemistry of organoniobium compounds most closely resembles that of organotantalum compounds. Organoniobium compounds of oxidation states +5, +4, +3, +2, +1, 0, -1, and -3 have been prepared, with the +5 oxidation state being the most common.

A lanthanocene is a type of metallocene compound that contains an element from the lanthanide series. The most common lanthanocene complexes contain two cyclopentadienyl anions and an X type ligand, usually hydride or alkyl ligand.
A transition metal phosphido complex is a coordination complex containing a phosphido ligand (R2P, where R = H, organic substituent). With two lone pairs on phosphorus, the phosphido anion (R2P−) is comparable to an amido anion (R2N−), except that the M-P distances are longer and the phosphorus atom is more sterically accessible. For these reasons, phosphido is often a bridging ligand. The -PH2 ion or ligand is also called phosphanide or phosphido ligand.
References
- ↑ Waterman, Rory (2013). "σ-Bond Metathesis: A 30-Year Retrospective". Organometallics. 32: 7249–7263. doi:10.1021/om400760k.
- ↑ Watson, Patricia (1983). "Methane exchange reactions of lanthanide and early-transition-metal methyl complexes". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 32: 6491–6493. doi:10.1021/ja00359a023.