Related Research Articles

The Vietnam War was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was a major conflict of the Cold War. While the war was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam, the north was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist states, while the south was supported by the United States and other anti-communist allies, making the war a proxy war between the United States and the Soviet Union. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. military involvement ending in 1973. The conflict also spilled over into neighboring states, exacerbating the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War, which ended with all three countries officially becoming communist states by 1976.

William Childs Westmoreland was a United States Army general, most notably commander of United States forces during the Vietnam War from 1964 to 1968. He served as Chief of Staff of the United States Army from 1968 to 1972.
During the Second Indochina War, better known as the Vietnam War, a distinctive land warfare strategy and organization was used by the National Liberation Front of South Vietnam (NLF) or better known as the Viet Cong (VC) in the West, and the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) or North Vietnamese Army (NVA) to defeat their American and South Vietnamese Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) opponents. These methods involved closely integrated political and military strategy – what was called dau tranh - literally "to struggle". The National Liberation Front, (NLF) was an umbrella of front groups, sympathizers and allies set up by the rulers of North Vietnam to conduct the insurgency in South Vietnam. The NLF also included fully armed formations- regional and local guerrillas, and the People's Liberation Armed Forces (PLAF). The PLAF was the "Main Force" – the Chu Luc or full-time soldiers of the NLF's military wing. Many histories lump both the NLF and the armed formations under the term "Viet Cong" or "VC" in common usage. Both were tightly interwoven and were in turn controlled by the North. Others consider the Viet Cong, or "VC" to primarily refer to the armed elements. The term PAVN, identifies regular troops of the North Vietnamese Army or NVA as they were commonly known by their Western opponents. Collectively, both forces- the southern armed wing and the regulars from the north were part of PAVN.

The Battle of Gang Toi was fought during the Vietnam War between Australian troops and the Viet Cong. The battle was one of the first engagements between the two forces during the war and occurred when A Company, 1st Battalion, Royal Australian Regiment struck a Viet Cong bunker system defended by Company 238 in the Gang Toi Hills, in northern Bien Hoa Province. It occurred during a major joint US-Australian operation codenamed Operation Hump, involving the US 173rd Airborne Brigade, to which 1 RAR was attached. During the latter part of the operation an Australian rifle company clashed with an entrenched company-sized Viet Cong force in well-prepared defensive positions. Meanwhile, an American paratroop battalion was also heavily engaged in fighting on the other side of the Song Dong Nai.

The Brinks Hotel in Saigon, also known as the Brink Bachelor Officers Quarters (BOQ), was bombed by the Viet Cong on the evening of December 24, 1964, during the Vietnam War. Two Viet Cong operatives detonated a car bomb underneath the hotel, which housed United States Army officers. The explosion killed two Americans, an officer and an NCO, and injured approximately 60, including military personnel and Vietnamese civilians.
CIA activities in Vietnam were operations conducted by the Central Intelligence Agency in Vietnam from the 1950s to the late 1960s, before and during the Vietnam War. After the 1954 Geneva Conference, North Vietnam was controlled by communist forces under Ho Chi Minh's leadership. South Vietnam, with the assistance of the U.S., was anti-communist under Ngo Dinh Diem's leadership. The economic and military aid supplied by the U.S. to South Vietnam continued until the 1974. The CIA participated in both the political and military aspect of the wars in Indochina. The CIA provided suggestions for political platforms, supported candidates, used agency resources to refute electoral fraud charges, manipulated the certification of election results by the South Vietnamese National Assembly, and instituted the Phoenix Program. It worked particularly closely with the ethnic minority Montagnards, Hmong, and Khmer. There are 174 National Intelligence Estimates dealing with Vietnam, issued by the CIA after coordination with the U.S. intelligence community.

The 1959 to 1963 phase of the Vietnam War started after the North Vietnamese had made a firm decision to commit to a military intervention in the guerrilla war in the South Vietnam, a buildup phase began, between the 1959 North Vietnamese decision and the Gulf of Tonkin Incident, which led to a major US escalation of its involvement. Vietnamese communists saw this as a second phase of their revolution, the US now substituting for the French.
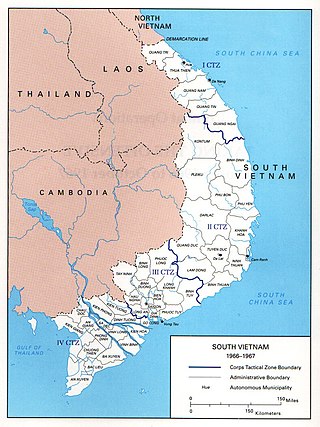
During the Cold War in the 1960s, the United States and South Vietnam began a period of gradual escalation and direct intervention referred to as the "Americanization" of joint warfare in South Vietnam during the Vietnam War. At the start of the decade, United States aid to South Vietnam consisted largely of supplies with approximately 900 military observers and trainers. After the assassination of both Ngo Dinh Diem and John F. Kennedy close to the end of 1963 and Gulf of Tonkin incident in 1964 and amid continuing political instability in the South, the Lyndon Johnson Administration made a policy commitment to safeguard the South Vietnamese regime directly. The American military forces and other anti-communist SEATO countries increased their support, sending large scale combat forces into South Vietnam; at its height in 1969, slightly more than 400,000 American troops were deployed. The People's Army of Vietnam and the allied Viet Cong fought back, keeping to countryside strongholds while the anti-communist allied forces tended to control the cities. The most notable conflict of this era was the 1968 Tet Offensive, a widespread campaign by the communist forces to attack across all of South Vietnam; while the offensive was largely repelled, it was a strategic success in seeding doubt as to the long-term viability of the South Vietnamese state. This phase of the war lasted until the election of Richard Nixon and the change of U.S. policy to Vietnamization, or ending the direct involvement and phased withdrawal of U.S. combat troops and giving the main combat role back to the South Vietnamese military.

The Battle of Suối Châu Pha was fought during the Vietnam War between Australian troops and the Việt Cộng. The battle took place during Operation Ballarat, an Australian search and destroy operation in the eastern Hát Dịch area, north-west of Núi Đất in Phước Tuy province. Following a covert insertion the day before which had caught a number of Việt Cộng sentries by surprise, A Company, 7th Battalion, Royal Australian Regiment had patrolled forward unaware of the presence of a large Việt Cộng main force unit nearby. Clashing with a reinforced company from the Việt Cộng 3rd Battalion, 274th Regiment, a classic encounter battle ensued between two forces of roughly equal size. Fought at close quarters in dense jungle amid a heavy monsoon rain, both sides suffered heavy casualties as neither was able to gain an advantage. Finally, after a battle lasting several hours, the Australian artillery proved decisive and the Việt Cộng were forced to withdraw, dragging many of their dead from the battlefield after having suffered crippling losses.

The Gulf of Tonkin Resolution or the Southeast Asia Resolution, Pub. L.Tooltip Public Law 88–408, 78 Stat. 384, enacted August 10, 1964, was a joint resolution that the United States Congress passed on August 7, 1964, in response to the Gulf of Tonkin incident.
The Sigma war games were a series of classified high level war games played in the Pentagon during the 1960s to strategize the conduct of the burgeoning Vietnam War. The games were designed to replicate then-current conditions in Indochina, with an aim toward predicting future events in the region. In almost all runs, the outcome was either a communist win, or a stalemate that led to protests in the US.
Sigma I-63 was one of the series of Sigma war games. These were a series of classified high level war games played in the Pentagon during the 1960s to strategize the conduct of the burgeoning Vietnam War. These simulations were designed to replicate then-current conditions in Indochina, with an aim toward predicting future foreign affairs events. They were staffed with high-ranking officials standing in to represent both domestic and foreign characters; stand-ins were chosen for their expertise concerning those they were called upon to represent. The games were supervised by a Control appointed to oversee both sides. The opposing Blue and Red Teams customary in war games were designated the friendly and enemy forces as was usual; however, several smaller teams were sometimes subsumed under Red and Blue Teams. Over the course of the games, the Red Team at times contained the Yellow Team for the People's Republic of China, the Brown Team for the Democratic Republic of Vietnam, the Black Team for the Viet Cong, and Green for the USSR.
The Sigma I-65 war game was one of a series of classified high level war games played in The Pentagon during the 1960s to strategize the conduct of the burgeoning Vietnam War. These simulations were designed to replicate then-current conditions in Indochina, with an aim toward predicting future foreign affairs events. They were staffed with high-ranking officials standing in to represent both domestic and foreign characters; stand-ins were chosen for their expertise concerning those they were called upon to represent. The games were supervised by a Control appointed to oversee both sides. The opposing Blue and Red Teams customary in war games were designated the friendly and enemy forces as was usual; however, several smaller teams were sometimes subsumed under Red and Blue Teams. Over the course of the games, the Red Team at times contained the Yellow Team for the People's Republic of China, the Brown Team for the Democratic Republic of Vietnam, the Black Team for the Viet Cong, and Green for the USSR.
The Sigma I-66 war game was one of a series of classified high level war games played in The Pentagon during the 1960s to strategize the conduct of the burgeoning Vietnam War. Sigma I-66 was based on the unrealistic scenario of a famine-stricken and militarily diminished North Vietnam agreeing to de-escalate its war efforts. It ended with a hypothetical force of 100,000 Viet Cong still in South Vietnam.
The Sigma II-66 war game was one of a series of classified high level war games played in the Pentagon during the 1960s to strategize the conduct of the burgeoning Vietnam War. The games were designed to replicate then-current conditions in Indochina, with an aim toward predicting future foreign affairs events. They were staffed with high ranking officials standing in to represent both domestic and foreign characters; stand-ins were chosen for their expertise concerning those they were called upon to represent. The games were supervised by a Control appointed to oversee both sides. The opposing Blue and Red Teams customary in war games were designated the friendly and enemy forces as was usual; however, several smaller teams were sometimes subsumed under Red and Blue Teams. Over the course of the games, the Red Team at times contained the Yellow Team for the People's Republic of China, the Brown Team for the Democratic Republic of Vietnam, the Black Team for the Viet Cong, and Green for the USSR.
The Sigma I-62 war game, played in February 1962, was the first of a series of classified high level war games played in the Pentagon during the 1960s to strategize the conduct of the burgeoning Vietnam War. These simulations were designed to replicate then-current conditions in Indochina, with an aim toward predicting future foreign affairs events. The conclusion drawn from Sigma I-62 was that American intervention in Vietnam would be unsuccessful.
The Sigma I-64 war game, one of the Sigma war games, was played from 6 to 9 April 1964. Its purpose was to test scenarios of escalation of warfare in Vietnam. After rigorous research into information needed to form a scenario, a simulation took place, with knowledgeable officials playing out the roles of actual government decision makers. Participants were drawn from the State Department, Department of Defense, the Central Intelligence Agency, and the Joint Chiefs of Staff. In Sigma I-64, the scenarios to be examined were the burgeoning Viet Cong insurgency in Vietnam, and the possible use of U.S. air power against it.
The Sigma II-64 war game was one of a series of classified high level war games played in The Pentagon during the 1960s to strategize the conduct of the burgeoning Vietnam War. The games were designed to replicate then-current conditions in Indochina, with an aim toward predicting future foreign affairs events. They were staffed with high-ranking officials standing in to represent both domestic and foreign characters; stand-ins were chosen for their expertise concerning those they were called upon to represent. The games were supervised by a Control appointed to oversee both sides. The opposing Blue and Red Teams customary in war games were designated the friendly and enemy forces as was usual; however, several smaller teams were sometimes subsumed under Red and Blue Teams. Over the course of the games, the Red Team at times contained the Yellow Team for the People's Republic of China, the Brown Team for the Democratic Republic of Vietnam, the Black Team for the Viet Cong, and Green for the USSR.
The Sigma I-67 and II-67 War Games were two of a series of classified high level war games played in the Pentagon during the 1960s to strategize the conduct of the burgeoning Vietnam War. The games were designed to replicate then-current conditions in Indochina, with an aim toward predicting future foreign affairs events. They were staffed with high-ranking officials standing in to represent both domestic and foreign characters; stand-ins were chosen for their expertise concerning those they were called upon to represent. The games were supervised by a Control appointed to oversee both sides. The opposing Blue and Red Teams customary in war games were designated the friendly and enemy forces as was usual; however, several smaller teams were sometimes subsumed under Red and Blue Teams. Over the course of the games, the Red Team at times contained the Yellow Team for the People's Republic of China, the Brown Team for the Democratic Republic of Vietnam, the Black Team for the Viet Cong, and Green for the USSR.
The Vietnam War body count controversy centers on the counting of enemy dead by the United States Armed Forces during the Vietnam War (1955–1975). There are issues around killing and counting unarmed civilians (non-combatants) as enemy combatants, as well as inflating the number of actual enemy who were killed in action (KIA). For search and destroy operations, as the objective was not to hold territory or secure populations, victory was assessed by having a higher enemy body count.
References
- Addington, Larry H. (2000) America's War in Vietnam: A Short Narrative History. Indiana University Press, ISBNs 0253213606, 978-0253213600.
- Allen, Thomas B. (1987) War Games: The Secret World of the Creators, Players, and Policy Makers Rehearsing World War III Today. McGraw-Hill. ISBNs 0070011958, 9780070011953.
- Gibbons, William Conrad (1995) The U.S. Government and the Vietnam War. Princeton University Press. ISBNs 0691006350, 978-0691006352.
- McNamara, Robert S. and Brian VanDeMark (1995) In Retrospect: The Tragedies and Lessons of Vietnam. Times Books. ISBNs 0-8129-2523-8, 9780812925234.
- Sorley, Lewis (1998) Honorable Warrior: General Harold K. Johnson and the Ethics of Command (Modern War Studies). University Press of Kansas. ISBNs 0700609520, 978-0700609529.