Audio signal processing is a subfield of signal processing that is concerned with the electronic manipulation of audio signals. As audio signals may be represented in either digital or analog format, processing may occur in either domain. Analog processors operate directly on the electrical signal, while digital processors operate mathematically on the digital representation of that signal.
A codec is a device or computer program for encoding or decoding a digital data stream or signal. Codec is a portmanteau of coder-decoder.
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The signals processed in this manner are a sequence of numbers that represent samples of a continuous variable in a domain such as time, space, or frequency.

In information technology, lossy compression or irreversible compression is the class of data encoding methods that uses inexact approximations and partial data discarding to represent the content. These techniques are used to reduce data size for storing, handling, and transmitting content. The different versions of the photo of the cat to the right show how higher degrees of approximation create coarser images as more details are removed. This is opposed to lossless data compression which does not degrade the data. The amount of data reduction possible using lossy compression is much higher than through lossless techniques.
Speech coding is an application of data compression of digital audio signals containing speech. Speech coding uses speech-specific parameter estimation using audio signal processing techniques to model the speech signal, combined with generic data compression algorithms to represent the resulting modeled parameters in a compact bitstream.

Signal processing is a subfield of mathematics, information and electrical engineering that concerns the analysis, synthesis, and modification of signals, which are broadly defined as functions conveying "information about the behavior or attributes of some phenomenon", such as sound, images, and biological measurements. For example, signal processing techniques are used to improve signal transmission fidelity, storage efficiency, and subjective quality, and to emphasize or detect components of interest in a measured signal.
Compression may refer to:

An A-law algorithm is a standard companding algorithm, used in European 8-bit PCM digital communications systems to optimize, i.e. modify, the dynamic range of an analog signal for digitizing. It is one of two versions of the G.711 standard from ITU-T, the other version being the similar µ-law, used in North America and Japan.

Image compression is a type of data compression applied to digital images, to reduce their cost for storage or transmission. Algorithms may take advantage of visual perception and the statistical properties of image data to provide superior results compared with generic data compression methods which are used for other digital data.
A video codec is an electronic circuit or software that compresses or decompresses digital video. It converts uncompressed video to a compressed format or vice versa. In the context of video compression, "codec" is a concatenation of "encoder" and "decoder"—a device that only compresses is typically called an encoder, and one that only decompresses is a decoder.
Rate–distortion theory is a major branch of information theory which provides the theoretical foundations for lossy data compression; it addresses the problem of determining the minimal number of bits per symbol, as measured by the rate R, that should be communicated over a channel, so that the source can be approximately reconstructed at the receiver without exceeding a given distortion D.

Sound quality is typically an assessment of the accuracy, enjoyability, or intelligibility of audio output from an electronic device. Quality can be measured objectively, such as when tools are used to gauge the accuracy with which the device reproduces an original sound; or it can be measured subjectively, such as when human listeners respond to the sound or gauge its perceived similarity to another sound.
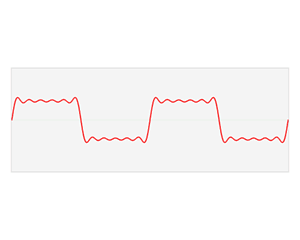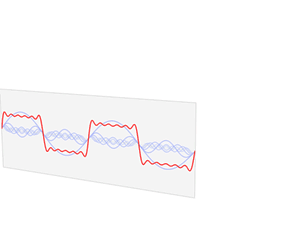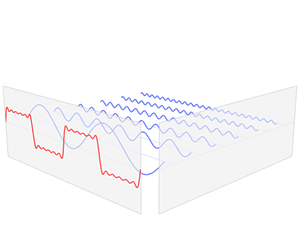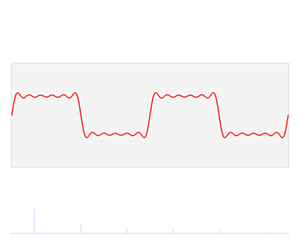
In electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time. Put simply, a time-domain graph shows how a signal changes over time, whereas a frequency-domain graph shows how much of the signal lies within each given frequency band over a range of frequencies. A frequency-domain representation can also include information on the phase shift that must be applied to each sinusoid in order to be able to recombine the frequency components to recover the original time signal.

In telecommunications, transmission is the process of sending and propagating an analogue or digital information signal over a physical point-to-point or point-to-multipoint transmission medium, either wired, optical fiber or wireless.

In mathematics, a wavelet series is a representation of a square-integrable function by a certain orthonormal series generated by a wavelet. This article provides a formal, mathematical definition of an orthonormal wavelet and of the integral wavelet transform.
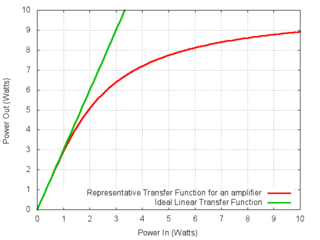
Gain compression is a reduction in "differential" or "slope" gain caused by nonlinearity of the transfer function of the amplifying device. This nonlinearity may be caused by heat due to power dissipation or by overdriving the active device beyond its linear region. It is a large-signal phenomenon of circuits.
Psychoacoustics is the scientific study of sound perception and audiology – how humans perceive various sounds. More specifically, it is the branch of science studying the psychological and physiological responses associated with sound. It can be further categorized as a branch of psychophysics. Psychoacoustics received its name from a field within psychology—i.e., recognition science—which deals with all kinds of human perceptions. It is an interdisciplinary field of many areas, including psychology, acoustics, electronic engineering, physics, biology, physiology, and computer science.

A mixing engineer is a person responsible for combining ("mixing") the different sonic elements of a piece of recorded music into a final version of a song. He or she mixes the elements of a recorded piece together to achieve a good balance of volume, while at the same time deciding other properties such as pan positioning, effects, and so on.










