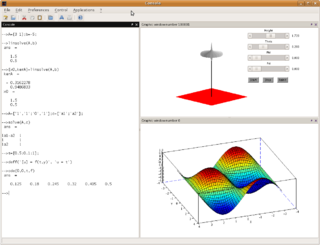
Scilab is a free and open-source, cross-platform numerical computational package and a high-level, numerically oriented programming language. It can be used for signal processing, statistical analysis, image enhancement, fluid dynamics simulations, numerical optimization, and modeling, simulation of explicit and implicit dynamical systems and symbolic manipulations.

Simulink is a MATLAB-based graphical programming environment for modeling, simulating and analyzing multidomain dynamical systems. Its primary interface is a graphical block diagramming tool and a customizable set of block libraries. It offers tight integration with the rest of the MATLAB environment and can either drive MATLAB or be scripted from it. Simulink is widely used in automatic control and digital signal processing for multidomain simulation and model-based design.

MathWorks is an American privately held corporation that specializes in mathematical computing software. Its major products include MATLAB and Simulink, which support data analysis and simulation.
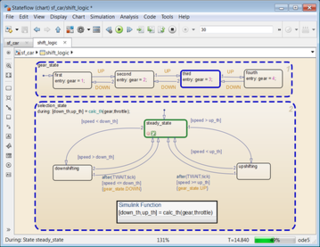
Stateflow is a control logic tool used to model reactive systems via state machines and flow charts within a Simulink model. Stateflow uses a variant of the finite-state machine notation established by David Harel, enabling the representation of hierarchy, parallelism and history within a state chart. Stateflow also provides state transition tables and truth tables.

PLECS is a software tool for system-level simulations of electrical circuits developed by Plexim. It is especially designed for power electronics but can be used for any electrical network.
VisSim is a visual block diagram program for simulation of dynamical systems and model based design of embedded systems, with its own visual language. It is developed by Visual Solutions of Westford, Massachusetts. Visual Solutions was acquired by Altair in August 2014 and its products have been rebranded as Altair Embed as a part of Altair's Model Based Development Suite. With Embed, you can develop virtual prototypes of dynamic systems. Models are built by sliding blocks into the work area and wiring them together with the mouse. Embed automatically converts the control diagrams into C-code ready to be downloaded to the target hardware.

Computational science and engineering (CSE) is a relatively new discipline that deals with the development and application of computational models and simulations, often coupled with high-performance computing, to solve complex physical problems arising in engineering analysis and design as well as natural phenomena. CSE has been described as the "third mode of discovery". In many fields, computer simulation is integral and therefore essential to business and research. Computer simulation provides the capability to enter fields that are either inaccessible to traditional experimentation or where carrying out traditional empirical inquiries is prohibitively expensive. CSE should neither be confused with pure computer science, nor with computer engineering, although a wide domain in the former is used in CSE and some problems in the latter can be modeled and solved with CSE methods.
The George E. Brown, Jr. Network for Earthquake Engineering Simulation (NEES) was created by the National Science Foundation (NSF) to improve infrastructure design and construction practices to prevent or minimize damage during an earthquake or tsunami. Its headquarters were at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Indiana as part of cooperative agreement #CMMI-0927178, and it ran from 2009 till 2014. The mission of NEES is to accelerate improvements in seismic design and performance by serving as a collaboratory for discovery and innovation.
ModelSim is a multi-language HDL simulation environment by Mentor Graphics, for simulation of hardware description languages such as VHDL, Verilog and SystemC, and includes a built-in C debugger. ModelSim can be used independently, or in conjunction with Intel Quartus Prime, Xilinx ISE or Xilinx Vivado. Simulation is performed using the graphical user interface (GUI), or automatically using scripts.

MapleSim is a Modelica-based, multi-domain modeling and simulation tool developed by Maplesoft. MapleSim generates model equations, runs simulations, and performs analyses using the symbolic and numeric mathematical engine of Maple. Models are created by dragging-and-dropping components from a library into a central workspace, resulting in a model that represents the physical system in a graphical form. Maplesoft began development of MapleSim partly in response to a request from Toyota to produce physical modeling tools to aid in their new model-based development process.
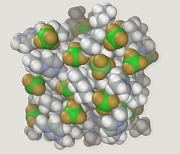
Molecular modeling on GPU is the technique of using a graphics processing unit (GPU) for molecular simulations.
Real-time simulation refers to a computer model of a physical system that can execute at the same rate as actual "wall clock" time. In other words, the computer model runs at the same rate as the actual physical system. For example, if a tank takes 10 minutes to fill in the real-world, the simulation would take 10 minutes as well.

SimulationX is a CAE software application running on Microsoft Windows for the physical simulation of technical systems developed and sold by ESI ITI GmbH in Dresden, Germany.
The Functional Mock-up Interface defines a standardized interface to be used in computer simulations to develop complex cyber-physical systems.

20-sim is commercial modeling and simulation program for multi-domain dynamic systems, which is developed by Controllab. With 20-sim models can be entered as equations, block diagrams, bond graphs and physical components. 20-sim is widely used for modeling complex multi-domain systems and the development of control systems.
Moving horizon estimation (MHE) is an optimization approach that uses a series of measurements observed over time, containing noise and other inaccuracies, and produces estimates of unknown variables or parameters. Unlike deterministic approaches, MHE requires an iterative approach that relies on linear programming or nonlinear programming solvers to find a solution.

Simcenter Amesim is a commercial simulation software for the modeling and analysis of multi-domain systems. It is part of systems engineering domain and falls into the mechatronic engineering field.
FEATool Multiphysics is a physics, finite element analysis (FEA), and PDE simulation toolbox. FEATool Multiphysics features the ability to model fully coupled heat transfer, fluid dynamics, chemical engineering, structural mechanics, fluid-structure interaction (FSI), electromagnetics, as well as user-defined and custom PDE problems in 1D, 2D (axisymmetry), or 3D, all within a simple graphical user interface (GUI) or optionally as convenient script files. Having specifically been designed to have a low learning curve and to be able to be used without requiring reading documentation, FEATool has been employed and used in academic research, teaching, and industrial engineering simulation contexts.













