
A simulation is an approximate imitation of the operation of a process or system; that represents its operation over time.

Application software is a program or group of programs designed for end users. Examples of an application include a word processor, a spreadsheet, an accounting application, a web browser, an email client, a media player, a file viewer, simulators, a console game or a photo editor. The collective noun application software refers to all applications collectively. This contrasts with system software, which is mainly involved with running the computer.
A submarine simulator is usually a computer game in which the player commands a submarine. The usual form of the game is to go on a series of missions, each of which features a number of encounters where the goal is to sink surface ships and to survive counterattacks by destroyers. Submarine simulators are notable for the highly-variable pace of the game; it may take hours of simulated time to get into position to attack a well-defended convoy, and sub simulators typically include an option for players to adjust the ratio of real time to simulated time up and down as desired.
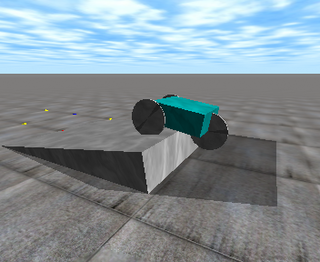
The Open Dynamics Engine (ODE) is a physics engine written in C/C++. Its two main components are a rigid body dynamics simulation engine and a collision detection engine. It is free software licensed both under the BSD license and the LGPL.

OrCAD Systems Corporation was a software company that made OrCAD, a proprietary software tool suite used primarily for electronic design automation (EDA). The software is used mainly by electronic design engineers and electronic technicians to create electronic schematics, perform mixed-signal simulation and electronic prints for manufacturing printed circuit boards. OrCAD was taken over by Cadence Design Systems in 1999 and was integrated with Cadence Allegro since 2005.
Ngspice is a mixed-level/mixed-signal electronic circuit simulator. It is a successor of the latest stable release of Berkeley SPICE, version 3f.5, which was released in 1993. A small group of maintainers and the user community contribute to the ngspice project by providing new features, enhancements and bug fixes.
Large-scale Atomic/Molecular Massively Parallel Simulator (LAMMPS) is a molecular dynamics program from Sandia National Laboratories. LAMMPS makes use of Message Passing Interface (MPI) for parallel communication and is free and open-source software, distributed under the terms of the GNU General Public License.
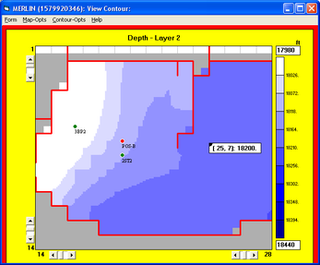
Reservoir simulation is an area of reservoir engineering in which computer models are used to predict the flow of fluids through porous media.
Hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) simulation, or HWIL, is a technique that is used in the development and test of complex real-time embedded systems. HIL simulation provides an effective platform by adding the complexity of the plant under control to the test platform. The complexity of the plant under control is included in test and development by adding a mathematical representation of all related dynamic systems. These mathematical representations are referred to as the “plant simulation”. The embedded system to be tested interacts with this plant simulation.

Microsoft Robotics Developer Studio is a Windows-based environment for robot control and simulation. It is aimed at academic, hobbyist, and commercial developers and handles a wide variety of robot hardware. It requires the Microsoft Windows 7 operating system.
A robotics suite is a visual environment for robot control and simulation. They are typically an end-to-end platform for robotics development and include tools for visual programming and creating and debugging robot applications. Developers can often interact with robots through web-based or visual interfaces.

The Player Project is a project to create free software for research into robotics and sensor systems. Its components include the Player network server and the Stage robot platform simulators. Although accurate statistics are hard to obtain, Player is one of the most popular open-source robot interfaces in research and post-secondary education. Most of the major intelligent robotics journals and conferences regularly publish papers featuring real and simulated robot experiments using Player and Stage.

OpenSimulator is an open-source server platform for hosting virtual worlds and the Metaverse. At one point, it was compatible with the client for Second Life but compatibility has waned for several years.

Webots is a free and open-source 3D robot simulator used in industry, education and research.

A robotics simulator is a simulator used to create application for a physical robot without depending on the actual machine, thus saving cost and time. In some case, these applications can be transferred onto the physical robot without modifications.
Vortex Studio is a complete simulation software platform. It features a high-fidelity, realtime physics engine developed by CM Labs Simulations that simulates rigid body dynamics, collision detection, contact determination, and dynamic reactions. It also contains model import and preparation tools, an image generator, and networking tools for distributed simulation, accessed through a desktop editor via a GUI. Vortex adds accurate physical motion and interactions to objects in visual-simulation applications for operator training, mission planning, product concept validation, heavy machinery and robotics design and testing, haptics devices, immersive and virtual reality (VR) environments.
Amateur flight simulation refers to the simulation of various aspects of flight or the flight environment for purposes other than flight training or aircraft development. A significant community of simulation enthusiasts is supported by several commercial software packages, as well as commercial and homebuilt hardware.
AirSim is an open-source, cross platform simulator for drones, ground vehicles such as cars and various other objects, built on Epic Games’ Unreal Engine 4 as a platform for AI research. It is developed by Microsoft and can be used to experiment with deep learning, computer vision and reinforcement learning algorithms for autonomous vehicles. This allows testing of autonomous solutions without worrying about real-world damage.









