Related Research Articles

Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the surgical treatment of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nervous system.

A simulation is an imitative representation of a process or system that could exist in the real world. In this broad sense, simulation can often be used interchangeably with model. Sometimes a clear distinction between the two terms is made, in which simulations require the use of models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or process, whereas the simulation represents the evolution of the model over time. Another way to distinguish between the terms is to define simulation as experimentation with the help of a model. This definition includes time-independent simulations. Often, computers are used to execute the simulation.
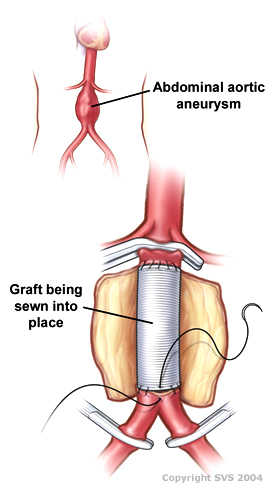
Vascular surgery is a surgical subspecialty in which vascular diseases involving the arteries, veins, or lymphatic vessels, are managed by medical therapy, minimally-invasive catheter procedures and surgical reconstruction. The specialty evolved from general and cardiovascular surgery where it refined the management of just the vessels, no longer treating the heart or other organs. Modern vascular surgery includes open surgery techniques, endovascular techniques and medical management of vascular diseases - unlike the parent specialities. The vascular surgeon is trained in the diagnosis and management of diseases affecting all parts of the vascular system excluding the coronaries and intracranial vasculature. Vascular surgeons also are called to assist other physicians to carry out surgery near vessels, or to salvage vascular injuries that include hemorrhage control, dissection, occlusion or simply for safe exposure of vascular structures.

Minimally invasive procedures encompass surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed, thereby reducing wound healing time, associated pain, and risk of infection. Surgery by definition is invasive and many operations requiring incisions of some size are referred to as open surgery. Incisions made during open surgery can sometimes leave large wounds that may be painful and take a long time to heal. Advancements in medical technologies have enabled the development and regular use of minimally invasive procedures. For example, endovascular aneurysm repair, a minimally invasive surgery, has become the most common method of repairing abdominal aortic aneurysms in the US as of 2003. The procedure involves much smaller incisions than the corresponding open surgery procedure of open aortic surgery.
Image-guided surgery (IGS) is any surgical procedure where the surgeon uses tracked surgical instruments in conjunction with preoperative or intraoperative images in order to directly or indirectly guide the procedure. Image guided surgery systems use cameras, ultrasonic, electromagnetic or a combination of fields to capture and relay the patient's anatomy and the surgeon's precise movements in relation to the patient, to computer monitors in the operating room or to augmented reality headsets. This is generally performed in real-time though there may be delays of seconds or minutes depending on the modality and application.
Computer-assisted surgery (CAS) represents a surgical concept and set of methods, that use computer technology for surgical planning, and for guiding or performing surgical interventions. CAS is also known as computer-aided surgery, computer-assisted intervention, image-guided surgery, digital surgery and surgical navigation, but these are terms that are more or less synonymous with CAS. CAS has been a leading factor in the development of robotic surgery.
An instructional simulation, also called an educational simulation, is a simulation of some type of reality but which also includes instructional elements that help a learner explore, navigate or obtain more information about that system or environment that cannot generally be acquired from mere experimentation. Instructional simulations are typically goal oriented and focus learners on specific facts, concepts, or applications of the system or environment. Today, most universities make lifelong learning possible by offering a virtual learning environment (VLE). Not only can users access learning at different times in their lives, but they can also immerse themselves in learning without physically moving to a learning facility, or interact face to face with an instructor in real time. Such VLEs vary widely in interactivity and scope. For example, there are virtual classes, virtual labs, virtual programs, virtual library, virtual training, etc. Researchers have classified VLE in 4 types:

GIMIAS is a workflow-oriented environment focused on biomedical image computing and simulation. The open-source framework is extensible through plug-ins and is focused on building research and clinical software prototypes. Gimias has been used to develop clinical prototypes in the fields of cardiac imaging and simulation, angiography imaging and simulation, and neurology
A medical animation is a short educational film, usually based around a physiological or surgical topic, that is rendered using 3D computer graphics. While it may be intended for an array of audiences, the medical animation is most commonly utilized as an instructional tool for medical professionals or their patients.
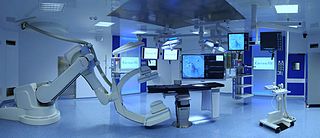
A hybrid operating room is a very advanced surgical theatre that is equipped with advanced medical imaging devices such as fixed C-Arms, X-ray tomography (CT) scanners or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners. These imaging devices enable minimally-invasive surgery. Minimally-invasive surgery is intended to be less traumatic for the patient and minimize incisions on the patient and perform surgery procedure through one or several small cuts.
Valdecilla virtual Hospital (VvH) is a healthcare simulation center located in the city of Santander, Cantabria, Spain. It was created by a consortium between the Cantabrian Government, the Marqués de Valdecilla University Hospital, and the University of Cantabria.
A surgery simulator is computer technology developed to simulate surgical procedures for the purpose of training medical professionals, without the need of a patient, cadaver or animal. The concept goes back to the 1980s with video games, but only in the 1990s with three-dimensional graphics and the 2000s with the use of motion sensors for realistic movements has the technology been able to simulate the real situation. The most common type of surgery taught through this method is laparoscopic surgery, although it has also been used to do a trial run before other kinds of procedures. Cataract surgery and other ophthalmic procedures are also widely taught using surgical simulators.

Mazor Robotics was an Israeli medical device company and manufacturer of a robotic guidance system for spine surgery that was acquired by Medtronic in December 2018. Surgeons that utilized Mazor Robotics Renaissance generally specialize in orthopedic surgery or neurosurgery.

BioDigital is a New York-based biomedical visualization company that is often referred to as being "Google Earth for the Human Body". BioDigital offers an interactive, 3D software platform that enables individuals and businesses to explore and visualize health information. Their flagship product, the BioDigital Human, is a "searchable, customizable map of the human body".
The Dextroscope is a medical equipment system that creates a virtual reality (VR) environment in which surgeons can plan neurosurgical and other surgical procedures.
Augmented reality-assisted surgery (ARAS) is a surgical tool utilizing technology that superimposes a computer-generated image on a surgeon's view of the operative field, thus providing a composite view for the surgeon of the patient with a computer generated overlay enhancing the operative experience. It can be used for training, preparation for an operation, or performance of an operation. ARAS can be performed using a wide array of technology, including an optical head-mounted display (OHMD)—such as the Google Glass XE 22.1 or Vuzix STAR 1200 XL—and a digital overlay from robotic and laparoscopic surgery feeds. The technique has been primarily been tested in the urological and cardiovascular domains.
Touch Surgery is a London, New York City, Sydney and Auckland-based health technology app and trading name for the company Digital Surgery LTD. Digital Surgery is a health tech company shaping the future of surgery through the convergence of surgical expertise and technology. The app was first discussed in 2010. The Touch Surgery mobile app is a mobile surgical training platform designed to simulate surgical procedures. As of October 2019, The Touch Surgery mobile app included surgical instructions for about 200 surgical procedures in 17 different specialties.
MSR – The Israel Center for Medical Simulation is Israel's national institute for simulation-based medical education (SBME) and patient safety training. It is located at the Chaim Sheba Medical Center in the Tel HaShomer neighborhood of Ramat Gan, in the Tel Aviv District. MSR is internationally recognized as leader in patient safety simulation-based training.
VirtaMed is a Swiss company that develops virtual reality simulators for post-graduate medical education. The company was founded in 2007 as a spin-off of ETH Zurich by Gabor Székely, Co-Head of the Computer Vision Laboratory at ETH Zurich and Director of the Swiss National Centre of Competence in Research (NCCR) for Computer-Aided and Image-Guided Medical Interventions (CO-ME). Co-founders were Stefan Tuchschmid, Daniel Bachofen, Matthias Harders, Michael Bajka and Raimundo Sierra.
Gianluca De Novi is an Italian-born scientist known for his contributions to computer haptics, robotics, medical simulation, and surgical robotics.
References
- ↑ Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedures—Advances in Research and Application: 2012 Edition: ScholarlyBrief. ScholarlyEditions. 26 December 2012. ISBN 9781464995156 – via Google Books.
- 1 2 Sagi Cohen (March 14, 2019). "Virtual Blood Vessels, 3D Printed Organs: No Animals Were Harmed in Training These Surgeons". Haaretz.
- ↑ EYTAN HALON (February 17, 2019). "VIRTUAL SCALPEL, PLEASE: ISRAELI TECH REVOLUTIONIZES THE OPERATING THEATER". Jerusalem Post.
- ↑ "Simbionix Ltd - Company Profile and News". www.bloomberg.com.
- ↑ Issues in Genitourinary Medicine: 2011 Edition. ScholarlyEditions. 9 January 2012. ISBN 9781464964503 – via Google Books.
- ↑ Bar-Meir, Simon (1 July 2006). "Simbionix simulator". Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Clinics of North America. 16 (3): 471–478, vii. doi:10.1016/j.giec.2006.03.013. PMID 16876719.
- ↑ "Endovascular Today - Simbionix Introduces Angio Mentor Suite for Endovascular Team Training". Endovascular Today.
- ↑ Keshavan, Meghana (31 July 2014). "Simbionix acquired by 3D Systems for $120 million".
- ↑ Griffiths, Laura (18 September 2014). "3D Systems Introduces New Simbionix Robotics Medical Training Simulator". TCT Magazine.
- ↑ "3D Systems launches virtual reality simulator featuring a 3D printed spine". 3D Printing Industry. 12 June 2017.
- ↑ "Simbionix enters into an agreement to be acquired by 3D printing company". Crain's Cleveland Business. 30 July 2014.
- ↑ Orpaz, Inbal (1 August 2014). "3D Systems Snaps Up Israel's Simbionix for $120 Million". Haaretz.
- ↑ Kaplan, Joel A. (20 October 2016). Kaplan's Cardiac Anesthesia E-Book: In Cardiac and Noncardiac Surgery. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 9780323463010 – via Google Books.
- ↑ Seymour, Neal; Scott, Daniel (21 June 2010). Simulation and Surgical Competency, An Issue of Surgical Clinics - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 978-1455700684 – via Google Books.
- ↑ Hawes, Robert H.; Fockens, Paul (1 November 2010). Endosonography E-Book: Expert Consult. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 9781437735697 – via Google Books.