
Pharmacognosy is the study of crude drugs obtained from medicinal plants, animals, fungi, and other natural sources. The American Society of Pharmacognosy defines pharmacognosy as "the study of the physical, chemical, biochemical, and biological properties of drugs, drug substances, or potential drugs or drug substances of natural origin as well as the search for new drugs from natural sources".
A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. Designer drugs include psychoactive substances that have been designated by the European Union, Australia, and New Zealand, as new psychoactive substances (NPS) as well as analogs of performance-enhancing drugs such as designer steroids.

Phytochemistry is the study of phytochemicals, which are chemicals derived from plants. Phytochemists strive to describe the structures of the large number of secondary metabolites found in plants, the functions of these compounds in human and plant biology, and the biosynthesis of these compounds. Plants synthesize phytochemicals for many reasons, including to protect themselves against insect attacks and plant diseases. The compounds found in plants are of many kinds, but most can be grouped into four major biosynthetic classes: alkaloids, phenylpropanoids, polyketides, and terpenoids.
The Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs (ACMD) is a British statutory advisory non-departmental public body, which was established under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971.
The American Society of Pharmacognosy (ASP) is a scientific society that promotes the growth and development of pharmacognosy through presentation of research achievements and publication of meritorious research.

Jeffrey Barry Harborne FRS was a British chemist who specialised in phytochemistry. He was Professor of Botany at the University of Reading, 1976–93, then Professor emeritus. He contributed to more than 40 books and 270 research papers and was a pioneer in ecological biochemistry, particularly in the complex chemical interactions between plants, microbes and insects.

Phytotherapy Research is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing original research papers, short communications, reviews, and letters on medicinal plant research. Key areas of interest are pharmacology, toxicology, and the clinical applications of herbs and natural products in medicine, from case histories to full clinical trials, including studies of herb-drug interactions and other aspects of the safety of herbal medicines. Papers concerned with the effects of common food ingredients and standardised plant extracts, including commercial products, are particularly relevant, as are mechanistic studies on isolated natural products.

Mephedrone, also known as 4-methylmethcathinone, 4-MMC, and 4-methylephedrone, is a synthetic stimulant drug belonging to the amphetamine and cathinone classes. It is commonly referred to by slang names such as drone, M-CAT, White Magic, meow meow,and bubble. Chemically, it is similar to the cathinone compounds found in the Khat plant, native to eastern Africa.

Lysergic acid 2,4-dimethylazetidide (LA-SS-Az, LSZ) is an analog of LSD developed by the team led by David E. Nichols at Purdue University. It was developed as a rigid analog of LSD with the diethylamide group constrained into an azetidine ring in order to map the binding site at the 5-HT2A receptor. There are three possible stereoisomers around the azetidine ring, with the (S,S)-(+) isomer being the most active, slightly more potent than LSD itself in drug discrimination tests using trained rats.
John Wilkinson is an English independent scientist specialising primarily in organic chemistry, phytochemistry, pharmacognosy, and synergism in botanical medicines, botanical foods and ecological biochemistry, and who led the first European degree course for herbal medicine, at Middlesex University in the United Kingdom in 1994.

David John Nutt is an English neuropsychopharmacologist specialising in the research of drugs that affect the brain and conditions such as addiction, anxiety, and sleep. He is the chairman of Drug Science, a non-profit which he founded in 2010 to provide independent, evidence-based information on drugs. In 2019 he co-founded the company GABAlabs and its subsidiary SENTIA Spirits which research and market alternatives to alcohol. Until 2009, he was a professor at the University of Bristol heading their Psychopharmacology Unit. Since then he has been the Edmond J Safra chair in Neuropsychopharmacology at Imperial College London and director of the Neuropsychopharmacology Unit in the Division of Brain Sciences there. Nutt was a member of the Committee on Safety of Medicines, and was President of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
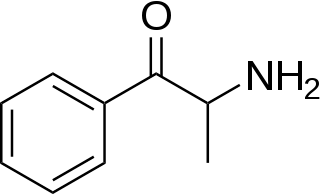
Substituted cathinones, or simply cathinones, which include some stimulants and entactogens, are derivatives of cathinone. They feature a phenethylamine core with an alkyl group attached to the alpha carbon, and a ketone group attached to the beta carbon, along with additional substitutions. Cathinone occurs naturally in the plant khat whose leaves are chewed as a recreational drug.
6-APB is an empathogenic psychoactive drug of the substituted benzofuran and substituted phenethylamine classes. 6-APB and other compounds are sometimes informally called "Benzofury" in newspaper reports. It is similar in structure to MDA, but differs in that the 3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl ring system has been replaced with a benzofuran ring. 6-APB is also the unsaturated benzofuran derivative of 6-APDB. It may appear as a tan grainy powder.

Methoxetamine (MXE) is a dissociative hallucinogen that has been sold as a designer drug. It differs from many dissociatives such as ketamine and phencyclidine (PCP) that were developed as pharmaceutical drugs for use as general anesthetics in that it was designed specifically to increase the antidepressant effects of ketamine.
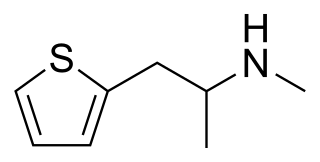
Methiopropamine (MPA), also known as N-methylthiopropamine, is an organic compound structurally related to methamphetamine. Originally reported in 1942, the molecule consists of a thiophene group with an alkyl amine substituent at the 2-position. It appeared for public sale in the United Kingdom in December 2010 as a "research chemical" or "legal high", recently branded as Blow. It has limited popularity as a recreational stimulant.

Psychoactive plants are plants, or preparations thereof, that upon ingestion induce psychotropic effects. As stated in a reference work:
Psychoactive plants are plants that people ingest in the form of simple or complex preparations in order to affect the mind or alter the state of consciousness.
Ivan Addae-Mensah, is a Ghanaian chemist and university administrator who served as the Vice-Chancellor of the University of Ghana, Legon from 1996 to 2002. He is an Emeritus Professor of Chemistry at the same institution. He is a Life Fellow of the Royal Society of Chemistry, Fellow of the Ghana Academy of Arts and Sciences and a Fellow of the Ghana Chemical Society.

The Psychoactive Substances Act 2016 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom intended to restrict the production, sale and supply of a new class of psychoactive substances often referred to as "legal highs". The bill was given Royal Assent on 28 January 2016, and came into force on 26 May 2016 across the entire United Kingdom.
Undurti Narasimha Das shortly Undurti N. Das and U. N. Das is an Indian clinical immunologist, endocrinologist and the founder president and chief executive officer of UND Life Sciences. Additionally, he serves as the Chief Medical Officer and the Chairman of the Scientific Advisory Board of Asha Nutrition Sciences, Inc. An elected fellow of the National Academy of Medical Sciences, Das is known for his researches in the fields of Immunology, Endocrinology and Rheumatology. He holds a number of patents for his work The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for his contributions to Medical Sciences in 1992.
Ahmed Sulaiman Al-Harrasi is an Omani scientist and a professor of organic chemistry at the University of Nizwa, Nizwa, Sultanate of Oman.












