Related Research Articles

Three-phase electric power is a common type of alternating current (AC) used in electricity generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system employing three wires and is the most common method used by electrical grids worldwide to transfer power.
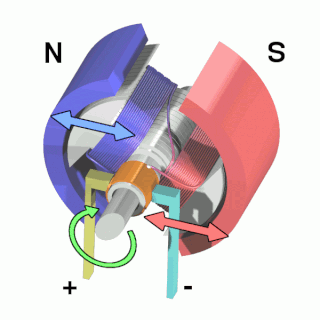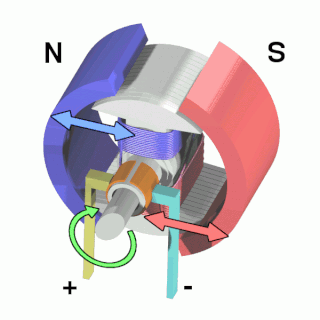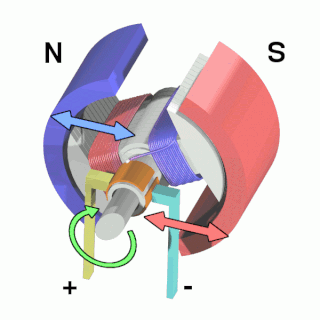
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates with a reversed flow of power, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
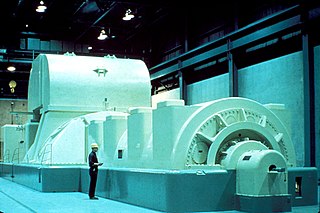
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motive power or fuel-based power into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines, wind turbines and even hand cranks. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. Generators provide nearly all of the power for electric power grids.
Field-emission electric propulsion (FEEP) is an advanced electrostatic space propulsion concept, a form of ion thruster, that uses a liquid metal as a propellant – usually either caesium, indium, or mercury.

A drill is a tool used for making round holes or driving fasteners. It is fitted with a bit, either a drill or driverchuck. Hand-operated types are dramatically decreasing in popularity and cordless battery-powered ones proliferating due to increased efficiency and ease of use.

An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses one or more electric motors for propulsion. It can be powered by a collector system, with electricity from extravehicular sources, or it can be powered autonomously by a battery. EVs include, but are not limited to, road and rail vehicles, surface and underwater vessels, electric aircraft, and electric spacecraft. For road vehicles, together with other emerging automotive technologies such as autonomous driving, connected vehicles, and shared mobility, EVs form a future mobility vision called Connected, Autonomous, Shared, and Electric (CASE) Mobility.

Arc welding is a welding process that is used to join metal to metal by using electricity to create enough heat to melt metal, and the melted metals, when cool, result in a binding of the metals. It is a type of welding that uses a welding power supply to create an electric arc between a metal stick ("electrode") and the base material to melt the metals at the point of contact. Arc welding power supplies can deliver either direct (DC) or alternating (AC) current to the work, while consumable or non-consumable electrodes are used.

Dynamic braking is the use of an electric traction motor as a generator when slowing a vehicle such as an electric or diesel-electric locomotive. It is termed "rheostatic" if the generated electrical power is dissipated as heat in brake grid resistors, and "regenerative" if the power is returned to the supply line. Dynamic braking reduces wear on friction-based braking components, and regeneration lowers net energy consumption. Dynamic braking may also be used on railcars with multiple units, light rail vehicles, electric trams, trolleybuses, and electric and hybrid electric automobiles.

A synchronous electric motor is an AC electric motor in which, at steady state, the rotation of the shaft is synchronized with the frequency of the supply current; the rotation period is exactly equal to an integral number of AC cycles. Synchronous motors use electromagnets as the stator of the motor which create a magnetic field that rotates in time with the oscillations of the current. The rotor with permanent magnets or electromagnets turns in step with the stator field at the same rate and as a result, provides the second synchronized rotating magnet field. A synchronous motor is termed doubly fed if it is supplied with independently excited multiphase AC electromagnets on both the rotor and stator.

A DC motor is any of a class of rotary electrical motors that converts direct current (DC) electrical energy into mechanical energy. The most common types rely on the forces produced by induced magnetic fields due to flowing current in the coil. Nearly all types of DC motors have some internal mechanism, either electromechanical or electronic, to periodically change the direction of current in part of the motor.

FedEx Express is a major American cargo airline based in Memphis, Tennessee, United States. As of 2023, it is the world's largest cargo airline in terms of fleet size and freight tons flown. It is the namesake and leading subsidiary of FedEx Corporation, delivering freight and packages to more than 375 destinations over 220 countries across six continents each day. FedEx Express is also the world's largest express transportation company.
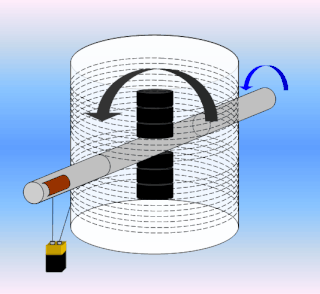
Newman's Energy Machine was a DC motor which the inventor, Joseph Newman, claimed to produce mechanical power exceeding the electrical power being supplied to it. In 1979, Newman attempted to patent the device, but it was rejected by the United States Patent Office as being a perpetual motion machine. When the rejection was later appealed, the United States district court requested that Newman's machine be tested by the National Bureau of Standards (NBS). The NBS concluded in June 1986 that output power was not greater than the input. Thus, the patent was again denied. The scientific community has rejected Newman's ideas about electricity and magnetism as pseudoscientific and his claims as false.

Railway electrification using alternating current (AC) at 15 kilovolts (kV) and 16.7 hertz (Hz) are used on transport railways in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Sweden, and Norway. The high voltage enables high power transmission with the lower frequency reducing the losses of the traction motors that were available at the beginning of the 20th century. Railway electrification in late 20th century tends to use 25 kV, 50 Hz AC systems which has become the preferred standard for new railway electrifications but extensions of the existing 15 kV networks are not completely unlikely. In particular, the Gotthard Base Tunnel still uses 15 kV, 16.7 Hz electrification.

A sander is a power tool used to smooth surfaces by abrasion with sandpaper. Sanders have a means to attach the sandpaper and a mechanism to move it rapidly contained within a housing with means to hand-hold it or fix it to a workbench. Woodworking sanders are usually powered electrically, and those used in auto-body repair work by compressed air. There are many different types of sanders for different purposes. Multi-purpose power tools and electric drills may have sander attachments.
Doubly fed electric machines, also slip-ring generators, are electric motors or electric generators, where both the field magnet windings and armature windings are separately connected to equipment outside the machine.
A brushed DC electric motor is an internally commutated electric motor designed to be run from a direct current power source and utilizing an electric brush for contact.
In electrical engineering, electric machine is a general term for machines using electromagnetic forces, such as electric motors, electric generators, and others. They are electromechanical energy converters: an electric motor converts electricity to mechanical power while an electric generator converts mechanical power to electricity. The moving parts in a machine can be rotating or linear. Besides motors and generators, a third category often included is transformers, which although they do not have any moving parts are also energy converters, changing the voltage level of an alternating current.

The Pacific Electric Sub-Station No. 14 is a former traction substation in Santa Ana, California. It was built by the Pacific Electric Railway to provide electricity to run the railway's streetcars in central Orange County, California. The building was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1983.
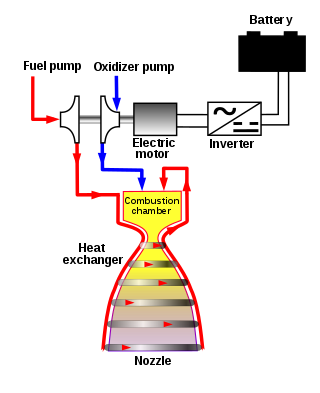
The electric-pump-fed engine is a bipropellant rocket engine in which the fuel pumps are electrically powered, and so all of the input propellant is directly burned in the main combustion chamber, and none is diverted to drive the pumps. This differs from traditional rocket engine designs, in which the pumps are driven by a portion of the input propellants.
References
- ↑ Ceraolo, Massimo & Poli, Davide (Apr 7, 2014). Fundamentals of Electric Power Engineering: From Electromagnetics to Power Systems. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1118679692.